Adjust css examples formatting (#26127)
This commit is contained in:
@@ -48,16 +48,15 @@ You have to add the following CSS property to achieve the transparency levels.
|
|||||||
opacity:0.0;
|
opacity:0.0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Alternatively you can use a transparent rgba value like this:
|
Alternatively you can use a transparent rgba value like this:
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.class-name{
|
.class-name{
|
||||||
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.5);
|
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.5);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
The example above sets the background to be black with 50% opacity. The last value of an rgba value is the alpha value. An alpha value of 1 equals 100%, and 0.5 (.5 for short) equals 50%. We use this method to add transparency to an element without affecting the content inside.
|
The example above sets the background to be black with 50% opacity. The last value of an rgba value is the alpha value. An alpha value of 1 equals 100%, and 0.5 (.5 for short) equals 50%. We use this method to add transparency to an element without affecting the content inside.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Transparent Hover Effect
|
#### Transparent Hover Effect
|
||||||
The opacity property is often used together with the **:hover** selector to change the opacity on mouse-over:
|
The opacity property is often used together with the **:hover** selector to change the opacity on mouse-over:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -88,10 +87,8 @@ Using the rgba value is most preferable when the background has content like tex
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
The example above sets the background with a 50% opacity using hex alpha code. The alpha digit is the last two numbers `80`. The formats are sometimes referred to as #RRGGBBAA and #RGBA and the the AA part is a hex representation of 0-100. For example the hex alpha code of 0% is `00` and the hex alpha code of 100% is `FF`.
|
The example above sets the background with a 50% opacity using hex alpha code. The alpha digit is the last two numbers `80`. The formats are sometimes referred to as #RRGGBBAA and #RGBA and the the AA part is a hex representation of 0-100. For example the hex alpha code of 0% is `00` and the hex alpha code of 100% is `FF`.
|
||||||
[A codepen example to show hex alpha values](https://codepen.io/chriscoyier/pen/XjbzAW)
|
[A codepen example to show hex alpha values](https://codepen.io/chriscoyier/pen/XjbzAW)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[A codepen example to show background opacity ranges](https://codepen.io/lvcoulter/full/dVrwmK/)
|
[A codepen example to show background opacity ranges](https://codepen.io/lvcoulter/full/dVrwmK/)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
+ [MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/opacity)
|
+ [MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/opacity)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -23,9 +23,9 @@ the second one will be set to auto by default.
|
|||||||
To set this property on multiple background images, separate the values by a comma:
|
To set this property on multiple background images, separate the values by a comma:
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.multiple {
|
.multiple {
|
||||||
background-image: url(1.png), url(2.png);
|
background-image: url(1.png), url(2.png);
|
||||||
background-size: 3px 3px, cover;
|
background-size: 3px 3px, cover;
|
||||||
/* first image is 3x3 px, second image covers the whole area */
|
/* first image is 3x3 px, second image covers the whole area */
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -9,22 +9,22 @@ The `background-color` property allows you to choose the color of your element (
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
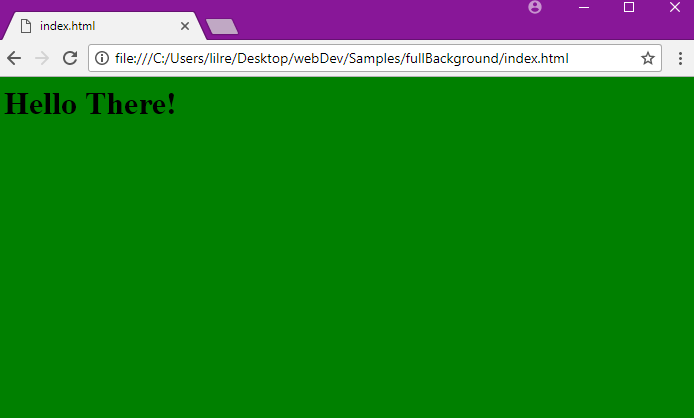
Here is an example of setting the background color for a web page to green.
|
Here is an example of setting the background color for a web page to green.
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
body {
|
body {
|
||||||
background-color: green;
|
background-color: green;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
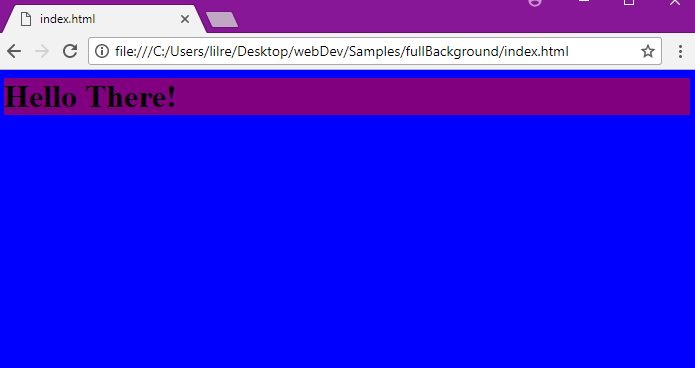
Here is an example of setting the background colors for two elements. This will set the background of the header
|
Here is an example of setting the background colors for two elements. This will set the background of the header to purple and the rest of the page to blue.
|
||||||
to purple and the rest of the page to blue.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
body {
|
body {
|
||||||
background-color: blue;
|
background-color: blue;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
h1 {
|
|
||||||
background–color: purple;
|
h1 {
|
||||||
}
|
background–color: purple;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -11,8 +11,8 @@ Let's look at some examples:
|
|||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
p::before {
|
p::before {
|
||||||
content: "";
|
content: "";
|
||||||
border: solid 5px #ccc
|
border: solid 5px #ccc;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
span.comment::before{
|
span.comment::before{
|
||||||
@@ -42,9 +42,9 @@ In the example above we are prepending a grey border before every paragraph elem
|
|||||||
`::before` is one of the CSS pseudo-elements selectors, which are used to style specified parts of an element. In this case, we can insert content before some HTML element from CSS. Although we will see the content in the page, it is not part of the DOM, what means that we can't manipulate it from Javascript. One trick to solve this handicap: passing the content with a data attribute and use jQuery to manipulate it. Here is an example of use:
|
`::before` is one of the CSS pseudo-elements selectors, which are used to style specified parts of an element. In this case, we can insert content before some HTML element from CSS. Although we will see the content in the page, it is not part of the DOM, what means that we can't manipulate it from Javascript. One trick to solve this handicap: passing the content with a data attribute and use jQuery to manipulate it. Here is an example of use:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
p::before {
|
p::before {
|
||||||
content: "Hello ";
|
content: "Hello ";
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```html
|
```html
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -41,7 +41,6 @@ The `border-style` property can be set to a wide range of different border types
|
|||||||
- `hidden` - Sets a hidden border.
|
- `hidden` - Sets a hidden border.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Each side of the border doesn't need to match.
|
Each side of the border doesn't need to match.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Each side can be styled separately:
|
Each side can be styled separately:
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
border-top-style: solid;
|
border-top-style: solid;
|
||||||
@@ -82,7 +81,6 @@ p {
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### Border Color
|
### Border Color
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now for the creative aspect of CSS Borders! With the use of the `border-color` property, you will be able to create customized borders to fit the flow and layout
|
Now for the creative aspect of CSS Borders! With the use of the `border-color` property, you will be able to create customized borders to fit the flow and layout
|
||||||
of your website. Border colors can be any color defined by RGB, hexadecimal, or key terms. Below is an example of each of these types.
|
of your website. Border colors can be any color defined by RGB, hexadecimal, or key terms. Below is an example of each of these types.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -107,7 +105,6 @@ p {
|
|||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Border-Radius
|
### Border-Radius
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The `border-radius` property allows the corners of a border to be rounded. `border-radius` takes a length as its value which determines the degree of curvature for each corner of the element. The length can be in px or %.
|
The `border-radius` property allows the corners of a border to be rounded. `border-radius` takes a length as its value which determines the degree of curvature for each corner of the element. The length can be in px or %.
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
border-radius: 25px;
|
border-radius: 25px;
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -14,10 +14,10 @@ A box shadow can be described with several properties including:
|
|||||||
### Syntax:
|
### Syntax:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
div {
|
div {
|
||||||
box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
* #### inset (default: none)
|
* #### inset (default: none)
|
||||||
If not specified, the shadow is assumed to be a drop shadow (as if the box were raised above the content).
|
If not specified, the shadow is assumed to be a drop shadow (as if the box were raised above the content).
|
||||||
The presence of the `inset` keyword changes the shadow to one inside the frame.
|
The presence of the `inset` keyword changes the shadow to one inside the frame.
|
||||||
@@ -39,11 +39,11 @@ This value is used to set the color of the shadow, usually defined with hex `#00
|
|||||||
To maximize compatibility, it is recommended that you declare box shadow properties for `moz-appearance` and `webkit`, this extends the normal syntax to:
|
To maximize compatibility, it is recommended that you declare box shadow properties for `moz-appearance` and `webkit`, this extends the normal syntax to:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
div{
|
div{
|
||||||
box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
||||||
-moz-box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
-moz-box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
||||||
-webkit-box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
-webkit-box-shadow: none | [inset? && [ <offset-x> <offset-y> <blur-radius>? <spread-radius>? <color>? ] ]#
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
However, this step can be ignored if it is creating confusion, as moz property and webkit property will only work in specific applications such as Firefox, and are not on a standards track.
|
However, this step can be ignored if it is creating confusion, as moz property and webkit property will only work in specific applications such as Firefox, and are not on a standards track.
|
||||||
@@ -89,10 +89,10 @@ It uses very similar code, but with inset value, which displays shadow inside th
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
div {
|
div {
|
||||||
width: 200px;
|
width: 200px;
|
||||||
height: 50px;
|
height: 50px;
|
||||||
background-color: #333;
|
background-color: #333;
|
||||||
box-shadow: inset 10px 10px 5px #ccc, 10px 10px 5px #ccc;
|
box-shadow: inset 10px 10px 5px #ccc, 10px 10px 5px #ccc;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -123,12 +123,12 @@ Let's turn it into CSS code:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.text1 {
|
.text1 {
|
||||||
font-size: 16px;
|
font-size: 16px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
@media (min-width: 1200px) {
|
@media (min-width: 1200px) {
|
||||||
.text1 {
|
.text1 {
|
||||||
font-size: 20px;
|
font-size: 20px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -141,10 +141,10 @@ It is perfectly fine to use `@media (max-width) {}` . Here is an example:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.text1 {
|
.text1 {
|
||||||
font-size: 20px;
|
font-size: 20px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
@media (max-width: 1199px) {
|
@media (max-width: 1199px) {
|
||||||
font-size: 16px;
|
font-size: 16px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -7,10 +7,12 @@ A Class Selector is used in a CSS file to apply style to the HTML elements with
|
|||||||
To select elements with a specific class, we use a full stop `.` or "period" character, with the name of the class.
|
To select elements with a specific class, we use a full stop `.` or "period" character, with the name of the class.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For example
|
For example
|
||||||
|
```css
|
||||||
.center {
|
.center {
|
||||||
text-align: center;
|
text-align: center;
|
||||||
color: red;
|
color: red;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Here, all HTML elements with `class="center"` will be red and center-aligned.
|
Here, all HTML elements with `class="center"` will be red and center-aligned.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -52,5 +54,3 @@ h1.test, h2.test {
|
|||||||
**Tips: No space between multiple classes.**
|
**Tips: No space between multiple classes.**
|
||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
CSS Syntax and Selectors: <a href='https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_syntax.asp' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>w3schools</a>
|
CSS Syntax and Selectors: <a href='https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_syntax.asp' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>w3schools</a>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -9,17 +9,12 @@ The comment syntax in CSS works for both single and multi-line comments. You can
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
/*
|
/*
|
||||||
This is
|
This is
|
||||||
a multi-line
|
a multi-line
|
||||||
comment
|
comment
|
||||||
*/
|
*/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/* This is a single line comment*/
|
/* This is a single line comment*/
|
||||||
.group:after {
|
|
||||||
content: "";
|
|
||||||
display: table;
|
|
||||||
clear: both;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
By using CSS comments to make your stylesheets more readable, the CSS will be easier to maintain in the future for you or another developer.
|
By using CSS comments to make your stylesheets more readable, the CSS will be easier to maintain in the future for you or another developer.
|
||||||
@@ -47,7 +42,7 @@ You can add as many comments to your stylesheet as you like. It’s good practic
|
|||||||
Comments should be used everyday in your CSS to keep in maintainable and readable by any dev who dives into said CSS.
|
Comments should be used everyday in your CSS to keep in maintainable and readable by any dev who dives into said CSS.
|
||||||
Here are a few exmples to get you started of CSS comments you can use in your daily work to make your life that bit easier.
|
Here are a few exmples to get you started of CSS comments you can use in your daily work to make your life that bit easier.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
``` css
|
```css
|
||||||
/* ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
|
/* ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
|
||||||
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
|
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
|
||||||
CSS TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
CSS TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
||||||
@@ -83,11 +78,11 @@ Here are a few exmples to get you started of CSS comments you can use in your da
|
|||||||
/****************************************************************************
|
/****************************************************************************
|
||||||
6.0 - Body */
|
6.0 - Body */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/************************************************************************
|
/************************************************************************
|
||||||
5.1 - Sliders */
|
6.1 - Sliders */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/************************************************************************
|
/************************************************************************
|
||||||
5.2 - Imagery */
|
6.2 - Imagery */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/****************************************************************************
|
/****************************************************************************
|
||||||
7.0 - Footer */
|
7.0 - Footer */
|
||||||
@@ -103,7 +98,7 @@ Here's how region works:
|
|||||||
/*#region Header */
|
/*#region Header */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.header {
|
.header {
|
||||||
font-size: 12px;
|
font-size: 12px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/*#endregion */
|
/*#endregion */
|
||||||
@@ -112,10 +107,10 @@ Here's how region works:
|
|||||||
------------------------------------------- */
|
------------------------------------------- */
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.footer {
|
.footer {
|
||||||
height: 20px;
|
height: 20px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
/*#endregion */
|
/*#endregion */
|
||||||
````
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### More Information:
|
### More Information:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ button {
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
To animate a button on click use 'button:active':
|
To animate a button on click use 'button:active':
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```css
|
||||||
.button {
|
.button {
|
||||||
display: inline-block;
|
display: inline-block;
|
||||||
padding: 15px 25px;
|
padding: 15px 25px;
|
||||||
@@ -167,4 +167,3 @@ In many cases buttons will have to link to an url. As we can't add an href attri
|
|||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
* https://www.w3schools.com/css/css3_buttons.asp
|
* https://www.w3schools.com/css/css3_buttons.asp
|
||||||
* https://www.w3schools.com/howto/howto_css_animate_buttons.asp
|
* https://www.w3schools.com/howto/howto_css_animate_buttons.asp
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -6,16 +6,16 @@ title: CSS Display
|
|||||||
The display property specifies the type of box used for an HTML element. It has 20 possible keyword values. The commonly used ones are:
|
The display property specifies the type of box used for an HTML element. It has 20 possible keyword values. The commonly used ones are:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.none {display: none}
|
.none {display: none}
|
||||||
.block {display: block}
|
.block {display: block}
|
||||||
.inline-block {display: inline-block}
|
.inline-block {display: inline-block}
|
||||||
.inline {display: inline}
|
.inline {display: inline}
|
||||||
.flex {display: flex}
|
.flex {display: flex}
|
||||||
.inline-flex {display: inline-flex}
|
.inline-flex {display: inline-flex}
|
||||||
.inline-table {display: inline-table}
|
.inline-table {display: inline-table}
|
||||||
.table {display: table}
|
.table {display: table}
|
||||||
.inherit {display: inherit}
|
.inherit {display: inherit}
|
||||||
.initial {display: initial}
|
.initial {display: initial}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The `display:none` property can often be helpful when making a website responsive. For example, you may want to hide an element on a page as the screen size shrinks in order to compensate for the lack of space. `display: none` will not only hide the element, but all other elements on the page will behave as if that element does not exist. This is the biggest difference between this property and the `visibility: hidden` property, which hides the element but keeps all other page elements in the same place as they would appear if the hidden element was visible.
|
The `display:none` property can often be helpful when making a website responsive. For example, you may want to hide an element on a page as the screen size shrinks in order to compensate for the lack of space. `display: none` will not only hide the element, but all other elements on the page will behave as if that element does not exist. This is the biggest difference between this property and the `visibility: hidden` property, which hides the element but keeps all other page elements in the same place as they would appear if the hidden element was visible.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ The `img` element will be rendered by default in most browsers to be displayed a
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
display: inline-block;
|
display: inline-block;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -29,8 +29,8 @@ Another common item in languages are loops, something else CSS lacks. Loops can
|
|||||||
@for $vfoo 35px to 85px {
|
@for $vfoo 35px to 85px {
|
||||||
.margin-#{vfoo} {
|
.margin-#{vfoo} {
|
||||||
margin: $vfoo 10px;
|
margin: $vfoo 10px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
This loop saves us from having the to write the same code multiple times to change the margin size.
|
This loop saves us from having the to write the same code multiple times to change the margin size.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -47,8 +47,8 @@ Here, the background color will change color depending on the width of the page'
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### Mixins
|
### Mixins
|
||||||
There are probably portions of your styling you would like to reuse. Mixins allow you to group any number of properties under one common name. You declare mixin with the @mixin <name> and use it with the @include <name>.
|
There are probably portions of your styling you would like to reuse. Mixins allow you to group any number of properties under one common name. You declare mixin with the @mixin <name> and use it with the @include <name>.
|
||||||
|
These are but a few of the major functions of CSS Preprocessors. As you can see, CSS Preprocessors are incredibly useful and versitile tools. Many web developers use them, and it is highly recommended to learn at least one of them.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
These are but a few of the major functions of CSS Preprocessors. As you can see, CSS Preprocessors are incredibly useful and versatile tools. Many web developers use them, and it is highly recommended to learn at least one of them.
|
|
||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
||||||
SASS: http://sass-lang.com/
|
SASS: http://sass-lang.com/
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ The CSS `background` shorthand property is used to define multiple properties li
|
|||||||
The `background-color` property specifies the background color of an element.
|
The `background-color` property specifies the background color of an element.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background-color : #F00;
|
background-color : #F00;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Background Image
|
### Background Image
|
||||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The `background-image` property specifies an image to use as background of an el
|
|||||||
By default, the image repeats itself to cover the entire surface of the element.
|
By default, the image repeats itself to cover the entire surface of the element.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Background Image - Repetition
|
### Background Image - Repetition
|
||||||
@@ -31,15 +31,15 @@ By default, the `background-image` property repeats on the X and Y axis, to cove
|
|||||||
If you want to set an axis, like X axis, use `background-repeat` property type:
|
If you want to set an axis, like X axis, use `background-repeat` property type:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
||||||
background-repeat: repeat-x;
|
background-repeat: repeat-x;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
But sometimes you don't want to have your background image cover the whole surface, so you've to specify it by typing:
|
But sometimes you don't want to have your background image cover the whole surface, so you've to specify it by typing:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
||||||
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Background Image - Position
|
### Background Image - Position
|
||||||
@@ -47,9 +47,9 @@ But sometimes you don't want to have your background image cover the whole surfa
|
|||||||
You can specify the position of the background by typing :
|
You can specify the position of the background by typing :
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
||||||
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
||||||
background-position : left bottom;
|
background-position : left bottom;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
It will set your background image at the bottom left of the element.
|
It will set your background image at the bottom left of the element.
|
||||||
@@ -59,10 +59,10 @@ It will set your background image at the bottom left of the element.
|
|||||||
If you do not want the background image to scroll with the rest of the page, use the `background-attachement` property:
|
If you do not want the background image to scroll with the rest of the page, use the `background-attachement` property:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
background-image: url("GitHub-Mark.png");
|
||||||
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
||||||
background-position: left bottom;
|
background-position: left bottom;
|
||||||
background-attachment: fixed;
|
background-attachment: fixed;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Shorthand property
|
### Shorthand property
|
||||||
@@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ If you do not want the background image to scroll with the rest of the page, use
|
|||||||
You can pass all the properties in one super-property:
|
You can pass all the properties in one super-property:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background: #F00 url("GitHub-Mark.png") no-repeat fixed left bottom;
|
background: #F00 url("GitHub-Mark.png") no-repeat fixed left bottom;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
When you use this shorthand property, it must be in this order:
|
When you use this shorthand property, it must be in this order:
|
||||||
@@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ When you use this shorthand property, it must be in this order:
|
|||||||
It doesn't matter if one property is missing, so long as the order is maintained:
|
It doesn't matter if one property is missing, so long as the order is maintained:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
background: url("GitHub-Mark.png") no-repeat left bottom;
|
background: url("GitHub-Mark.png") no-repeat left bottom;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This will work even if the color and the attachment are missing.
|
This will work even if the color and the attachment are missing.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -30,12 +30,12 @@ The following example shows a linear gradient that starts at the top. It starts
|
|||||||
<head>
|
<head>
|
||||||
<style>
|
<style>
|
||||||
#grad1 {
|
#grad1 {
|
||||||
height: 200px;
|
height: 200px;
|
||||||
background: red; /* For browsers that do not support gradients */
|
background: red; /* For browsers that do not support gradients */
|
||||||
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(red, green); /* For Safari 5.1 to 6.0 */
|
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(red, green); /* For Safari 5.1 to 6.0 */
|
||||||
background: -o-linear-gradient(red, green); /* For Opera 11.1 to 12.0 */
|
background: -o-linear-gradient(red, green); /* For Opera 11.1 to 12.0 */
|
||||||
background: -moz-linear-gradient(red, green); /* For Firefox 3.6 to 15 */
|
background: -moz-linear-gradient(red, green); /* For Firefox 3.6 to 15 */
|
||||||
background: linear-gradient(red, green); /* Standard syntax (must be last) */
|
background: linear-gradient(red, green); /* Standard syntax (must be last) */
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
</style>
|
</style>
|
||||||
</head>
|
</head>
|
||||||
@@ -66,12 +66,12 @@ The following example shows a linear gradient that starts from the left. It star
|
|||||||
<head>
|
<head>
|
||||||
<style>
|
<style>
|
||||||
#grad1 {
|
#grad1 {
|
||||||
height: 200px;
|
height: 200px;
|
||||||
background: red; /* For browsers that do not support gradients */
|
background: red; /* For browsers that do not support gradients */
|
||||||
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, red , green); /* For Safari 5.1 to 6.0 */
|
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, red , green); /* For Safari 5.1 to 6.0 */
|
||||||
background: -o-linear-gradient(right, red, green); /* For Opera 11.1 to 12.0 */
|
background: -o-linear-gradient(right, red, green); /* For Opera 11.1 to 12.0 */
|
||||||
background: -moz-linear-gradient(right, red, green); /* For Firefox 3.6 to 15 */
|
background: -moz-linear-gradient(right, red, green); /* For Firefox 3.6 to 15 */
|
||||||
background: linear-gradient(to right, red , green); /* Standard syntax (must be last) */
|
background: linear-gradient(to right, red , green); /* Standard syntax (must be last) */
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
</style>
|
</style>
|
||||||
</head>
|
</head>
|
||||||
@@ -106,12 +106,12 @@ The following example shows a linear gradient that starts at top left (and goes
|
|||||||
<head>
|
<head>
|
||||||
<style>
|
<style>
|
||||||
#grad1 {
|
#grad1 {
|
||||||
height: 200px;
|
height: 200px;
|
||||||
background: red; /* For browsers that do not support gradients */
|
background: red; /* For browsers that do not support gradients */
|
||||||
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left top, red, green); /* For Safari 5.1 to 6.0 */
|
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left top, red, green); /* For Safari 5.1 to 6.0 */
|
||||||
background: -o-linear-gradient(bottom right, red, green); /* For Opera 11.1 to 12.0 */
|
background: -o-linear-gradient(bottom right, red, green); /* For Opera 11.1 to 12.0 */
|
||||||
background: -moz-linear-gradient(bottom right, red, green); /* For Firefox 3.6 to 15 */
|
background: -moz-linear-gradient(bottom right, red, green); /* For Firefox 3.6 to 15 */
|
||||||
background: linear-gradient(to bottom right, red, green); /* Standard syntax (must be last) */
|
background: linear-gradient(to bottom right, red, green); /* Standard syntax (must be last) */
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
</style>
|
</style>
|
||||||
</head>
|
</head>
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -21,9 +21,9 @@ The thought process should be:
|
|||||||
### The basic syntax
|
### The basic syntax
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) {
|
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) {
|
||||||
p {padding: 30px;}
|
p {padding: 30px;}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px width.</p>
|
The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px width.</p>
|
||||||
@@ -32,9 +32,9 @@ The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
@media only screen and (min-height: 768px) and (orientation: landscape) {
|
@media only screen and (min-height: 768px) and (orientation: landscape) {
|
||||||
p {padding: 30px;}
|
p {padding: 30px;}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px height and its orientation is landscape.
|
The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px height and its orientation is landscape.
|
||||||
@@ -42,9 +42,9 @@ The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px
|
|||||||
### The OR syntax
|
### The OR syntax
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px), (min-resolution: 150dpi) {
|
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px), (min-resolution: 150dpi) {
|
||||||
p {padding: 30px;}
|
p {padding: 30px;}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px width or its resolution reaches min 150dpi.
|
The `p` tag will have a padding of 30px as soon as the screen reaches min 768px width or its resolution reaches min 150dpi.
|
||||||
@@ -57,25 +57,25 @@ Beyond the core uses of media queries for mobile-first web design shown above, m
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
1. Adjusting for screen readers that convert website text to speech for the visually impaired (for example, ignoring non-essential text).
|
1. Adjusting for screen readers that convert website text to speech for the visually impaired (for example, ignoring non-essential text).
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
@media speech {
|
@media speech {
|
||||||
/* ... */
|
/* ... */
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
2. Allowing for more graceful zooming in for those with minor visual impairments, such as many elderly people.
|
2. Allowing for more graceful zooming in for those with minor visual impairments, such as many elderly people.
|
||||||
3. Allowing smoother experiences for those who prefer or need less animation to read a page.
|
3. Allowing smoother experiences for those who prefer or need less animation to read a page.
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
@media (prefers-reduced-motion: reduce) {
|
@media (prefers-reduced-motion: reduce) {
|
||||||
.animation {
|
.animation {
|
||||||
animation: none;
|
animation: none;
|
||||||
-webkit-animation: none;
|
-webkit-animation: none;
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
4. Restyling a page for when it's printed as opposed to read on a screen.
|
4. Restyling a page for when it's printed as opposed to read on a screen.
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
@media print {
|
@media print {
|
||||||
/* ... */
|
/* ... */
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### More Information
|
### More Information
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -87,48 +87,48 @@ You need the separate div classes to create the button, and another div to separ
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
#myNav1 {
|
#myNav1 {
|
||||||
height: 0;
|
height: 0;
|
||||||
width: 50%;
|
width: 50%;
|
||||||
position: fixed;
|
position: fixed;
|
||||||
z-index: 6;
|
z-index: 6;
|
||||||
top: 0;
|
top: 0;
|
||||||
left: 0;
|
left: 0;
|
||||||
background-color: #ffff;
|
background-color: #ffff;
|
||||||
overflow: hidden;
|
overflow: hidden;
|
||||||
transition: 0.3s;
|
transition: 0.3s;
|
||||||
opacity: 0.85;
|
opacity: 0.85;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#myNav2 {
|
#myNav2 {
|
||||||
height: 0;
|
height: 0;
|
||||||
width: 50%;
|
width: 50%;
|
||||||
position: fixed;
|
position: fixed;
|
||||||
z-index: 6;
|
z-index: 6;
|
||||||
bottom: 0;
|
bottom: 0;
|
||||||
right: 0;
|
right: 0;
|
||||||
background-color: #ffff;
|
background-color: #ffff;
|
||||||
overflow: hidden;
|
overflow: hidden;
|
||||||
transition: 0.3s;
|
transition: 0.3s;
|
||||||
opacity: 0.85;
|
opacity: 0.85;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.overlay-content {
|
.overlay-content {
|
||||||
position: relative;
|
position: relative;
|
||||||
width: 100%;
|
width: 100%;
|
||||||
text-align: center;
|
text-align: center;
|
||||||
margin-top: 30px;
|
margin-top: 30px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#myNav1-content{
|
#myNav1-content{
|
||||||
top: 12%;
|
top: 12%;
|
||||||
left: 5%;
|
left: 5%;
|
||||||
display: none;
|
display: none;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#myNav2-content{
|
#myNav2-content{
|
||||||
top: 12%;
|
top: 12%;
|
||||||
right: 10%;
|
right: 10%;
|
||||||
display: none;
|
display: none;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ It works with a *fallback* system, meaning if your browser does not support the
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
p {
|
p {
|
||||||
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
|
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
In the above example, "Times New Roman" is the *family-name* of the font, while "serif" is the *generic-name*. Generic names are used as a fallback mechanism for preserving style if the family-name is unavailable. A generic name should always be the last item in the list of font family names.
|
In the above example, "Times New Roman" is the *family-name* of the font, while "serif" is the *generic-name*. Generic names are used as a fallback mechanism for preserving style if the family-name is unavailable. A generic name should always be the last item in the list of font family names.
|
||||||
@@ -42,15 +42,15 @@ This property has 3 values:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.normal {
|
.normal {
|
||||||
font-style: normal;
|
font-style: normal;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.italic {
|
.italic {
|
||||||
font-style: italic;
|
font-style: italic;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.oblique {
|
.oblique {
|
||||||
font-style: oblique;
|
font-style: oblique;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -67,19 +67,19 @@ There are different types of font size values:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.with-pixels {
|
.with-pixels {
|
||||||
font-size: 14px;
|
font-size: 14px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.with-ems {
|
.with-ems {
|
||||||
font-size: 0.875em;
|
font-size: 0.875em;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.with-absolute {
|
.with-absolute {
|
||||||
font-size: large;
|
font-size: large;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.with-percentage {
|
.with-percentage {
|
||||||
font-size: 80%;
|
font-size: 80%;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ The `font-weight`property specifies the weight (or boldness) of the font. Accept
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
p {
|
p {
|
||||||
font-weight: bold
|
font-weight: bold
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -10,24 +10,24 @@ You can use CSS to create you own image galleries.
|
|||||||
<head>
|
<head>
|
||||||
<style>
|
<style>
|
||||||
div.gallery {
|
div.gallery {
|
||||||
margin: 5px;
|
margin: 5px;
|
||||||
border: 1px solid #ccc;
|
border: 1px solid #ccc;
|
||||||
float: left;
|
float: left;
|
||||||
width: 180px;
|
width: 180px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
div.gallery:hover {
|
div.gallery:hover {
|
||||||
border: 1px solid #777;
|
border: 1px solid #777;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
div.gallery img {
|
div.gallery img {
|
||||||
width: 100%;
|
width: 100%;
|
||||||
height: 150px;
|
height: 150px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
div.desc {
|
div.desc {
|
||||||
padding: 15px;
|
padding: 15px;
|
||||||
text-align: center;
|
text-align: center;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
</style>
|
</style>
|
||||||
</head>
|
</head>
|
||||||
@@ -69,4 +69,3 @@ div.desc {
|
|||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
||||||
https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_image_gallery.asp
|
https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_image_gallery.asp
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -12,15 +12,15 @@ The ```opacity``` property allows you to make an image transparent by lowering h
|
|||||||
Example:
|
Example:
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
opacity: 0.3;
|
opacity: 0.3;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Include ```filter: alpha(opacity=x)``` for IE8 and earlier. `x` takes a value from 0-100.
|
Include ```filter: alpha(opacity=x)``` for IE8 and earlier. The x takes a value from 0-100.
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
opacity: 0.3;
|
opacity: 0.3;
|
||||||
filter: alpha(opacity=30);
|
filter: alpha(opacity=30);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -34,12 +34,12 @@ You can pair ```opacity``` with ```:hover``` to create a dynamic mouse-over effe
|
|||||||
Example:
|
Example:
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
opacity: 0.3;
|
opacity: 0.3;
|
||||||
filter: alpha(opacity=30);
|
filter: alpha(opacity=30);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
img:hover {
|
img:hover {
|
||||||
opacity: 1.0;
|
opacity: 1.0;
|
||||||
filter: alpha(opacity=100);
|
filter: alpha(opacity=100);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
[Here's a codepen example to show a transparent image turning opaque on hover](https://codepen.io/lvcoulter/full/JrzxXa/)
|
[Here's a codepen example to show a transparent image turning opaque on hover](https://codepen.io/lvcoulter/full/JrzxXa/)
|
||||||
@@ -50,8 +50,8 @@ You can create the opposite effect with less code since the image is 1.0 opacity
|
|||||||
Example:
|
Example:
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
img:hover {
|
img:hover {
|
||||||
opacity: 0.3;
|
opacity: 0.3;
|
||||||
filter: alpha(opacity=30);
|
filter: alpha(opacity=30);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
[Here's a codepen example to show transparency on mouse-over](https://codepen.io/lvcoulter/full/xXBQoR/)
|
[Here's a codepen example to show transparency on mouse-over](https://codepen.io/lvcoulter/full/xXBQoR/)
|
||||||
@@ -59,8 +59,4 @@ img:hover {
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
- w3schools.com: [CSS Opacity/Transparency](https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_image_transparency.asp)
|
- w3schools.com: [CSS Opacity/Transparency](https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_image_transparency.asp)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- MDN Web Docs: [Opacity](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/opacity)
|
- MDN Web Docs: [Opacity](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/opacity)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -22,15 +22,15 @@ The `display` property specifies the type of box used for an HTML element. There
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.myBox {
|
.myBox {
|
||||||
display: block;
|
display: block;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.myContainer {
|
.myContainer {
|
||||||
display: flex;
|
display: flex;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.inlineList ul > li {
|
.inlineList ul > li {
|
||||||
display: inline;
|
display: inline;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ In its simplest use, the `float` property can be used to wrap text around images
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
float: right;
|
float: right;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
This example specifies that an image should float to the right in a page:
|
This example specifies that an image should float to the right in a page:
|
||||||
@@ -31,14 +31,14 @@ This example specifies that an image should float to the right in a page:
|
|||||||

|

|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
float: left;
|
float: left;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
This example specifies that an image should float to the left in a page:
|
This example specifies that an image should float to the left in a page:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
float: none;
|
float: none;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ When clearing floats, you should match the `clear` to the `float`. If an element
|
|||||||
Source: CSS-TRICS
|
Source: CSS-TRICS
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
div {
|
div {
|
||||||
clear: left;
|
clear: left;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ Ideally, when you build a site, you'd design it with Grid and use Flex as a fall
|
|||||||
To make any element a grid, you need to assign its `display` property to `grid`, like so:
|
To make any element a grid, you need to assign its `display` property to `grid`, like so:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.conatiner {
|
.container {
|
||||||
display: grid;
|
display: grid;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ title: The Position Property
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element (static, relative, fixed, absolute or sticky).
|
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element (static, relative, fixed, absolute or sticky).
|
||||||
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element.
|
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element.
|
||||||
The position proprty isn't generally used to create layouts, but instead it is used to position elements that somehow stand out from the page flow.
|
The position property isn't generally used to create layouts, but instead it is used to position elements that somehow stand out from the page flow.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
There are five different position values:
|
There are five different position values:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -20,5 +20,3 @@ Elements are then positioned using the top, bottom, left, and right properties.
|
|||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
||||||
<a href="https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_positioning.asp" target="_blank">The is a good article</a> to read up to understand more about the position property.
|
<a href="https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_positioning.asp" target="_blank">The is a good article</a> to read up to understand more about the position property.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Margin values are set using lengths or percentages or `auto` or `inherit` keywor
|
|||||||
## Syntax
|
## Syntax
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.element {
|
.element {
|
||||||
margin: margin-top || margin-right || margin-bottom || margin-left;
|
margin: margin-top || margin-right || margin-bottom || margin-left;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -10,9 +10,9 @@ Navigation Bars are mostly made up of `<ul>` lists that are horizontally arrange
|
|||||||
While styling the navigation bars, it's common to remove the extra spacing created by the `<ul>` and `<li>` tags as well as the bulletpoints that are automatically inserted:
|
While styling the navigation bars, it's common to remove the extra spacing created by the `<ul>` and `<li>` tags as well as the bulletpoints that are automatically inserted:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
list-style-type: none;
|
list-style-type: none;
|
||||||
margin: 0px;
|
margin: 0px;
|
||||||
padding: 0px;
|
padding: 0px;
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Example:**
|
**Example:**
|
||||||
@@ -21,41 +21,41 @@ There are two parts to any navigation: the HTML and the CSS. This is just a quic
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```html
|
```html
|
||||||
<nav class="myNav"> <!-- Any element can be used here -->
|
<nav class="myNav"> <!-- Any element can be used here -->
|
||||||
<ul>
|
<ul>
|
||||||
<li><a href="index.html">Home</a></li>
|
<li><a href="index.html">Home</a></li>
|
||||||
<li><a href="about.html">About</a></li>
|
<li><a href="about.html">About</a></li>
|
||||||
<li><a href="contact.html">Contact</a></li>
|
<li><a href="contact.html">Contact</a></li>
|
||||||
</ul>
|
</ul>
|
||||||
</nav>
|
</nav>
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
/* Define the main Navigation block */
|
/* Define the main Navigation block */
|
||||||
.myNav {
|
.myNav {
|
||||||
display: block;
|
display: block;
|
||||||
height: 50px;
|
height: 50px;
|
||||||
line-height: 50px;
|
line-height: 50px;
|
||||||
background-color: #333;
|
background-color: #333;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
/* Remove bullets, margin and padding */
|
/* Remove bullets, margin and padding */
|
||||||
.myNav ul {
|
.myNav ul {
|
||||||
list-style: none;
|
list-style: none;
|
||||||
padding: 0;
|
padding: 0;
|
||||||
margin: 0;
|
margin: 0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
.myNav li {
|
.myNav li {
|
||||||
float: left;
|
float: left;
|
||||||
/* Or you can use display: inline; */
|
/* Or you can use display: inline; */
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
/* Define the block styling for the links */
|
/* Define the block styling for the links */
|
||||||
.myNav li a {
|
.myNav li a {
|
||||||
display: inline-block;
|
display: inline-block;
|
||||||
text-align: center;
|
text-align: center;
|
||||||
padding: 14px 16px;
|
padding: 14px 16px;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
/* This is optional, however if you want to display the active link differently apply a background to it */
|
/* This is optional, however if you want to display the active link differently apply a background to it */
|
||||||
.myNav li a.active {
|
.myNav li a.active {
|
||||||
background-color: #3786E1;
|
background-color: #3786E1;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -64,5 +64,3 @@ There are two parts to any navigation: the HTML and the CSS. This is just a quic
|
|||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
||||||
More Navigation Examples: [W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_navbar.asp)
|
More Navigation Examples: [W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_navbar.asp)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ Basically we use the `object-fit` property to define how it stretch or squish an
|
|||||||
## Syntax
|
## Syntax
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.element {
|
.element {
|
||||||
object-fit: fill || contain || cover || none || scale-down;
|
object-fit: fill || contain || cover || none || scale-down;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -50,10 +50,10 @@ For example, a given block-level element (`<div>`) set to 300px wide, that conta
|
|||||||
* `overflow-y`: Allows the user to scroll through the content that extends beyond the width of the box.
|
* `overflow-y`: Allows the user to scroll through the content that extends beyond the width of the box.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.box-element {
|
.box-element {
|
||||||
overflow-x: scroll;
|
overflow-x: scroll;
|
||||||
overflow-y: auto;
|
overflow-y: auto;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
And the `.box-element` will look like this:
|
And the `.box-element` will look like this:
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Padding values are set using lengths, percentages, or the `inherit` keyword, and
|
|||||||
## Syntax
|
## Syntax
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.element {
|
.element {
|
||||||
padding: [padding-top] || [padding-right] || [padding-bottom] || [padding-left];
|
padding: [padding-top] || [padding-right] || [padding-bottom] || [padding-left];
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -9,15 +9,15 @@ You use the `background-color` property to set the background color of an elemen
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
body {
|
body {
|
||||||
background-color: crimson;
|
background-color: crimson;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
div {
|
div {
|
||||||
background-color: #ffffff;
|
background-color: #ffffff;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
.myClass {
|
.myClass {
|
||||||
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
|
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -35,5 +35,3 @@ div {
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
#### More Information:
|
#### More Information:
|
||||||
<a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/background-color?v=b' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>MDN web docs</a>
|
<a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/background-color?v=b' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>MDN web docs</a>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -30,15 +30,15 @@ Examples:
|
|||||||
For repeating the image both horizontally and vertically
|
For repeating the image both horizontally and vertically
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
body {
|
body {
|
||||||
background-image:url(smiley.gif);
|
background-image:url(smiley.gif);
|
||||||
background-repeat:repeat;
|
background-repeat:repeat;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
For repeat the image horizontally
|
For repeat the image horizontally
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
body {
|
body {
|
||||||
background-image:url(smiley.gif);
|
background-image:url(smiley.gif);
|
||||||
background-repeat:repeat-x;
|
background-repeat:repeat-x;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ You can use several methods to declare a color such as:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
h1{
|
h1{
|
||||||
color: blue;
|
color: blue;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ h1{
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
h1{
|
h1{
|
||||||
color: #0000ff;
|
color: #0000ff;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ h1{
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
h1{
|
h1{
|
||||||
color: rgb(0, 0, 255);
|
color: rgb(0, 0, 255);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ h1{
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
h1{
|
h1{
|
||||||
color: rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.5);
|
color: rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.5);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ h1{
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
h1{
|
h1{
|
||||||
color: hsl(240, 100%, 50%);
|
color: hsl(240, 100%, 50%);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ h1{
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
h1{
|
h1{
|
||||||
color: hsl(240, 100%, 50%, 0.5);
|
color: hsl(240, 100%, 50%, 0.5);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
## CSS Color Properties explained
|
## CSS Color Properties explained
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ text-shadow : X-offset Y-offset blur-radius color
|
|||||||
**Example :**
|
**Example :**
|
||||||
``` css
|
``` css
|
||||||
p {
|
p {
|
||||||
text-shadow : 2px 2px 8px #FF0000;
|
text-shadow : 2px 2px 8px #FF0000;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ title: Vertical Align CSS
|
|||||||
For example, you can use ```vertical-align``` like this to align an image:
|
For example, you can use ```vertical-align``` like this to align an image:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
img {
|
img {
|
||||||
vertical-align: top;
|
vertical-align: top;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
These are the valid values for ```vertical-align```:
|
These are the valid values for ```vertical-align```:
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ The will-change property allows you to tell the browser what manipulations will
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
```css
|
```css
|
||||||
.container {
|
.container {
|
||||||
will-change: transform;
|
will-change: transform;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user