fix(guide): restructure curriculum guide articles (#36501)
* fix: restructure certifications guide articles * fix: added 3 dashes line before prob expl * fix: added 3 dashes line before hints * fix: added 3 dashes line before solutions
This commit is contained in:
@@ -2,36 +2,35 @@
|
||||
title: Find the Symmetric Difference
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
 Remember to use <a href="https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/how-to-get-help-when-you-are-stuck/" rel="help">**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program and write your own code
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation: ###
|
||||
# Find the Symmetric Difference
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
Symmetric difference (commonly denoted by Δ) of two sets is the set of elements which are in either of the two sets, but not in both.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, `sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4])` should yield `[3, 4, 5]`.
|
||||
|
||||
Following above definition, symmetric difference of three sets *A*, *B*, and *C* can be expressed as `(A Δ B) Δ C`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
* [Symmetric difference - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symmetric_difference)
|
||||
* [Symmetric difference - YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PxffSUQRkG4)
|
||||
* [Array.reduce()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/reduce)
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1 ##
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
The *arguments* object is *Array*-like object that only inherits `Array.length` property. Hence consider converting it to an actual *Array*.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2 ##
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
Deem writing a helper function that returns the symmetric difference of two arrays on each call instead of attempting to difference all sets simultaneously.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 3 ##
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 3
|
||||
Apply helper function against the created arguments array reducing its elements pairwise recursively to form the expected output.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**
|
||||
@@ -44,103 +43,95 @@ In the event of *odd number of sets* the symmetric difference will include ident
|
||||
(A ⋂ B) ⋂ C = {1, 4} &Intersection {3, 4, 5}
|
||||
A ⋂ B = {1, 3, 5}
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert! ##
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Solution Ahead!**
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution: ##
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
var args = [];
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
|
||||
args.push(arguments[i]);
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
var args = [];
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
|
||||
args.push(arguments[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function symDiff(arrayOne, arrayTwo) {
|
||||
var result = [];
|
||||
|
||||
arrayOne.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayTwo.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
function symDiff(arrayOne, arrayTwo) {
|
||||
var result = [];
|
||||
|
||||
arrayOne.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayTwo.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
arrayTwo.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayOne.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
arrayTwo.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayOne.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply reduce method to args array, using the symDiff function
|
||||
return args.reduce(symDiff);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply reduce method to args array, using the symDiff function
|
||||
return args.reduce(symDiff);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation: ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
* `push()` is used to break down the *arguments* object to an array, *args*.
|
||||
* The `symDiff` function finds the symmetric difference between two sets. It is used as a callback function for the `reduce()` method called on *args*.
|
||||
* `arrayOne.forEach()` pushes the elements to *result* which are present only in *arrayOne* as well as not already a part of *result*.
|
||||
* `arrayTwo.forEach()` pushes the elements to *result* which are present only in *arrayTwo* as well as not already a part of *result*.
|
||||
* The *result*, which is the symmetric difference is returned. This solution works for any number of sets.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
* [Statement for](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/statements/for)
|
||||
* [Array.length](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/length)
|
||||
* [Array.push()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/push)
|
||||
* [Array.forEach()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/forEach)
|
||||
* [Array.indexOf()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/indexOf)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Intermediate Code Solution: ##
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
// Convert the argument object into a proper array
|
||||
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert the argument object into a proper array
|
||||
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the symmetric difference of 2 arrays
|
||||
var getDiff = function(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns items in arr1 that don't exist in arr2
|
||||
function filterFunction(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
return arr1.filter(function(item) {
|
||||
return arr2.indexOf(item) === -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run filter function on each array against the other
|
||||
return filterFunction(arr1, arr2)
|
||||
.concat(filterFunction(arr2, arr1));
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Reduce all arguments getting the difference of them
|
||||
var summary = args.reduce(getDiff, []);
|
||||
|
||||
// Run filter function to get the unique values
|
||||
var unique = summary.filter(function(elem, index, self) {
|
||||
return index === self.indexOf(elem);
|
||||
});
|
||||
return unique;
|
||||
// Return the symmetric difference of 2 arrays
|
||||
var getDiff = function(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// Returns items in arr1 that don't exist in arr2
|
||||
function filterFunction(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
return arr1.filter(function(item) {
|
||||
return arr2.indexOf(item) === -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
// Run filter function on each array against the other
|
||||
return filterFunction(arr1, arr2).concat(filterFunction(arr2, arr1));
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Reduce all arguments getting the difference of them
|
||||
var summary = args.reduce(getDiff, []);
|
||||
|
||||
// Run filter function to get the unique values
|
||||
var unique = summary.filter(function(elem, index, self) {
|
||||
return index === self.indexOf(elem);
|
||||
});
|
||||
return unique;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation: ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
* The `slice()` method is used to break down the *arguments* object to an array, *args*.
|
||||
* The `getDiff` function finds the symmetric difference between two sets, *arr1* and *arr2*. It is used as a callback function for the `reduce()` method called on *args*.
|
||||
* The first `filterFunction()` returns elements in *arr1* that don't exist in *arr2*.
|
||||
@@ -148,41 +139,36 @@ In the event of *odd number of sets* the symmetric difference will include ident
|
||||
* *summary* consists of the reduced arguments.
|
||||
* `filter()` is used on *summary* to keep only the unique values and *unique* is returned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
* [Array.slice()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/slice)
|
||||
* [Array.filter()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/filter)
|
||||
* [Array.concat()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/concat)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Advanced Code Solution: ##
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 3 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const diff = (arr1, arr2) => (
|
||||
[
|
||||
...arr1.filter(e => !arr2.includes(e)),
|
||||
...arr2.filter(e => !arr1.includes(e)),
|
||||
]
|
||||
);
|
||||
const diff = (arr1, arr2) => [
|
||||
...arr1.filter(e => !arr2.includes(e)),
|
||||
...arr2.filter(e => !arr1.includes(e))
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
const sym = (...args) => [...new Set(args.reduce(diff))];
|
||||
const sym = (...args) => [...new Set(args.reduce(diff))];
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation: ###
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* The main function *sym()* reduces given arrays utilising helper function *diff()* to a single array. Also, it temporary converts the result to *Set* to remove duplicates.
|
||||
|
||||
* The function *diff()* returns the symmetric difference of two arrays by picking out elements in parameterised arrays; *arr1* and *arr2*.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
* [Set](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Set)
|
||||
* [Array.filter()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/filter)
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS: ##
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,48 +1,58 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Bubble Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Bubble Sort
|
||||
# Implement Bubble Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Bubble Sort is a sorting algorithm which sorts or *bubbles* the largest number as last element at the end of each pass.
|
||||
- We compare each element to the one ahead of it, if the element before is smaller, we swap their places.
|
||||
- Bubble Sort's time complexity is **O(n<sup>2</sup>)**.
|
||||
- It's a **stable** algorithm.
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Solution 1: Basic
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr){
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr) {
|
||||
let tmp = arr[a];
|
||||
arr[a] = arr[b];
|
||||
arr[b] = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function bubbleSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++){ // -i because the largest element will be bubbled at the end so we don't have to compare.
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j+1]){
|
||||
swap(j, j+1, array);
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
|
||||
// -i because the largest element will be bubbled at the end so we don't have to compare.
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
|
||||
swap(j, j + 1, array);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Solution 2: Advanced
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function bubbleSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++){
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j+1]) [array[j], array[j+1]] = [array[j+1], array[j]]; // Using ES6 array destructuring to swap
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j + 1])
|
||||
[array[j], array[j + 1]] = [array[j + 1], array[j]]; // Using ES6 array destructuring to swap
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [GeeksForGeeks](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bubble-sort/)
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bubble_sort)
|
||||
- Video by [HackerRank](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Gv8vg0kcHc)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
# Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Insertion Sort assumes that array is divided in two parts:
|
||||
1. Sorted (Initially the first element)
|
||||
2. Unsorted
|
||||
@@ -13,21 +14,27 @@ title: Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
- Time comlexity of Insertion sort is of **O(n<sup>2</sup>)**.
|
||||
- It's a **stable** algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function insertionSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++){
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
|
||||
let curr = array[i];
|
||||
for (var j = i-1; j >= 0 && array[j] > curr; j--){
|
||||
array[j+1] = array[j];
|
||||
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && array[j] > curr; j--) {
|
||||
array[j + 1] = array[j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
array[j+1] = curr;
|
||||
array[j + 1] = curr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insertion_sort)
|
||||
- [Khan Academy](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lCzQvQr8Utw)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
# Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Merge Sort is a classic divide and conquer problem.
|
||||
- The following steps are involved:
|
||||
- Divide: We break the array from the middle using recusion until we're left with 1 element.
|
||||
@@ -14,19 +15,26 @@ title: Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
- It's a **stable** algorithm.
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//Merger function, which merges 2 sorted array into 1 sorted array
|
||||
function merger(arr1, arr2){
|
||||
let i = 0, j = 0, mergedArr = [];
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length){
|
||||
function merger(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
let i = 0,
|
||||
j = 0,
|
||||
mergedArr = [];
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length) {
|
||||
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) mergedArr.push(arr2[j++]);
|
||||
else mergedArr.push(arr1[i++]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length){
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length) {
|
||||
mergedArr.push(arr1[i++]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (j < arr2.length){
|
||||
while (j < arr2.length) {
|
||||
mergedArr.push(arr2[j++]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return mergedArr;
|
||||
@@ -34,17 +42,18 @@ function merger(arr1, arr2){
|
||||
function mergeSort(array) {
|
||||
//Array of length 1 is sorted so we return the same array back
|
||||
if (array.length == 1) return array;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Break down the array to half from middle into left and right
|
||||
let middle = Math.floor(array.length/2);
|
||||
let middle = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
|
||||
let left = mergeSort(array.slice(0, middle));
|
||||
let right = mergeSort(array.slice(middle));
|
||||
|
||||
let right = mergeSort(array.slice(middle));
|
||||
|
||||
//Return the merged sorted array
|
||||
return merger(left, right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort)
|
||||
- Video by [Hackerrank](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KF2j-9iSf4Q)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
# Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Quick sort is an efficient sorting algorithm. It's an in-place algorithm so it doesn't take any auxilary space.
|
||||
- First pick a random pivot point around which move all the smaller elements to it to the left of it and the bigger elements to the right of it.
|
||||
- After getting the pivotIndex which is essentially the fixed position of that element, we find other pivotIndex by recusirvely calling this function.
|
||||
@@ -12,40 +13,44 @@ title: Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
- It's an **unstable** algorithm.
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//Swapping array elements via ES6 array destructuring
|
||||
function swap(arr, x, y){
|
||||
//Swapping array elements via ES6 array destructuring
|
||||
function swap(arr, x, y) {
|
||||
[arr[x], arr[y]] = [arr[y], arr[x]];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//Pivot function returns the fixed pivot point
|
||||
function pivot(arr, left = 0, right = arr.length-1){
|
||||
function pivot(arr, left = 0, right = arr.length - 1) {
|
||||
let shift = left;
|
||||
for (let i = left+1; i <= right; i++){
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = left + 1; i <= right; i++) {
|
||||
//Move all the small elements on the left side
|
||||
if (arr[i] < arr[left]) swap(arr, i, ++shift);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Finally swapping the last element with the left
|
||||
swap(arr, left, shift);
|
||||
return shift;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function quickSort(array, left = 0, right = array.length-1) {
|
||||
if (left < right){
|
||||
function quickSort(array, left = 0, right = array.length - 1) {
|
||||
if (left < right) {
|
||||
let pivotIndex = pivot(array, left, right);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Recusrively calling the function to the left of the pivot and to the right of the pivot
|
||||
quickSort(array, left, pivotIndex-1);
|
||||
quickSort(array, pivotIndex+1, right);
|
||||
quickSort(array, left, pivotIndex - 1);
|
||||
quickSort(array, pivotIndex + 1, right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Reference:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort)
|
||||
- [Khan Academy](https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-science/algorithms/quick-sort/a/overview-of-quicksort)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
# Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Selection Sort is one of the easier sorting algorithm to understand and implement.
|
||||
- This algorithm splits the array in two parts:
|
||||
1. Sorted
|
||||
@@ -12,17 +13,21 @@ title: Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
- Each pass, initially we assume the first element to be the smallest then we loop through the whole array and *select* the smallest element. At the end of the pass we swap smallest element to the sorted array.
|
||||
- It has **O(n<sup>2</sup>)** time complexity.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr){
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr) {
|
||||
let tmp = arr[a];
|
||||
arr[a] = arr[b];
|
||||
arr[b] = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function selectionSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++){
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
|
||||
let min = i;
|
||||
for (let j = i+1; j < array.length; j++){
|
||||
for (let j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
|
||||
if (array[min] > array[j]) min = j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
swap(i, min, array);
|
||||
@@ -31,6 +36,8 @@ function selectionSort(array) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- Read about Selection Sort at [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selection_sort)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Algorithms
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Algorithms
|
||||
# Algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/mathematics/quadratic-equations/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Inventory Update
|
||||
---
|
||||
 Remember to use <a>**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program  and write your own code 
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation:
|
||||
# Inventory Update
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
In this problem, you've to compare and update the inventory stored in a 2D array against a second 2D array of a fresh delivery. Update the current existing inventory item quantities (in `arr1`). If an item cannot be found, add the new item and quantity into the inventory array. The returned inventory array should be in alphabetical order by item.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,100 +15,92 @@ The current as well as new inventory will be in this format: `[[2, "item-0"], [3
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
You need to work through each item of the new inventory to see if it exists in the current inventory or not. Remember that the product name is stored as the second element of each sub-array: `array[0][1] = "item-name"`.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
|
||||
If the item exists, you need to add the quantity from the new inventory. If the item doesn't exist, you need to add the entire item.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 3
|
||||
### Hint 3
|
||||
|
||||
Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Solution ahead!**
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution:
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// Variable for location of product
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
|
||||
// Variable for location of product
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
|
||||
// A helper method to return the index of a specified product (undefined if not found)
|
||||
var getProductIndex = function (name) {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (this[i][1] === name) {
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return undefined;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// For each item of the new Inventory
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Invoke our helper function using arr1 as this
|
||||
index = getProductIndex.call(arr1, arr2[i][1]);
|
||||
|
||||
// If the item doesn't exist
|
||||
if (index === undefined) {
|
||||
// Push the entire item
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[i]);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Add the new quantity of the current item
|
||||
arr1[index][0] += arr2[i][0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sort alphabetically, by the product name of each item
|
||||
arr1.sort(function (a, b) {
|
||||
if (a[1] > b[1]) {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (a[1] < b[1]) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
// A helper method to return the index of a specified product (undefined if not found)
|
||||
var getProductIndex = function(name) {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (this[i][1] === name) {
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return undefined;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// For each item of the new Inventory
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
// Invoke our helper function using arr1 as this
|
||||
index = getProductIndex.call(arr1, arr2[i][1]);
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// If the item doesn't exist
|
||||
if (index === undefined) {
|
||||
// Push the entire item
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[i]);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Add the new quantity of the current item
|
||||
arr1[index][0] += arr2[i][0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
// Sort alphabetically, by the product name of each item
|
||||
arr1.sort(function(a, b) {
|
||||
if (a[1] > b[1]) {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (a[1] < b[1]) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* The variable **index** stores the location (index) of a product.
|
||||
* The helper function `getProductIndex()` returns the index of a specified product. It iterates through each element of the array that it is called on until it can find the name parameter. If the product is not found in the inventory, `undefined` is returned.
|
||||
@@ -124,74 +118,75 @@ Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-push/14298' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.push()</a>
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-sort/14306' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.sort()</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Intermediate Code Solution:
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
var arrCurInvName = []; // Names of arr1's items
|
||||
var arrNeInvName = []; // Names of arr2's items
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
var arrCurInvName = []; // Names of arr1's items
|
||||
var arrNeInvName = []; // Names of arr2's items
|
||||
|
||||
// Same as using two for loops, this takes care of increasing the number of stock quantity.
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item1) {
|
||||
return arr2.map(function(item2) {
|
||||
if (item1[1] === item2[1]) {
|
||||
item1[0] = item1[0] + item2[0]; //Increase number of stock
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
// Same as using two for loops, this takes care of increasing the number of stock quantity.
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item1) {
|
||||
return arr2.map(function(item2) {
|
||||
if (item1[1] === item2[1]) {
|
||||
item1[0] = item1[0] + item2[0]; //Increase number of stock
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Get item's name for new Inventory
|
||||
arr2.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrNeInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
// Get item's name for new Inventory
|
||||
arr2.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrNeInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Get item's name for Current Inventory
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrCurInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
// Get item's name for Current Inventory
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrCurInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Add new inventory items to current inventory.
|
||||
arrNeInvName.map(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrCurInvName.indexOf(item) === -1) {
|
||||
index = arrNeInvName.indexOf(item);
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[index]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Sort the array alphabetically using the second element of the array as base.
|
||||
arr1.sort(function(currItem, nextItem) {
|
||||
|
||||
//Ternary function to avoid using if else
|
||||
return currItem[1] > nextItem[1] ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
// Add new inventory items to current inventory.
|
||||
arrNeInvName.map(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrCurInvName.indexOf(item) === -1) {
|
||||
index = arrNeInvName.indexOf(item);
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[index]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// Sort the array alphabetically using the second element of the array as base.
|
||||
arr1.sort(function(currItem, nextItem) {
|
||||
//Ternary function to avoid using if else
|
||||
return currItem[1] > nextItem[1] ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* The variable **index** stores the location (index) of a product.
|
||||
* **arrCurInvName** has the names of **arr1**'s items.
|
||||
@@ -207,66 +202,64 @@ Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-indexof/14291' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.indexOf()</a>
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-ternary-operator/15973' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Ternary Operator</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Advanced Code Solution:
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 3 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
|
||||
// convert current inventory (arr1) to an one-dimensional array
|
||||
const inventory = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arr1);
|
||||
// convert current inventory (arr1) to an one-dimensional array
|
||||
const inventory = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arr1);
|
||||
|
||||
// loop through new delivery (arr2)
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
// loop through new delivery (arr2)
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
// extract item properties for easy reference
|
||||
const item = arr2[i][1];
|
||||
const quantity = arr2[i][0];
|
||||
|
||||
// extract item properties for easy reference
|
||||
const item = arr2[i][1];
|
||||
const quantity = arr2[i][0];
|
||||
|
||||
// check if item already exists in inventory
|
||||
const position = inventory.indexOf(item);
|
||||
|
||||
// exsisting item: update quantity
|
||||
if (position !== -1) {
|
||||
const row = Math.floor(position / 2);
|
||||
arr1[row][0] += quantity;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// alien item: add to inventory
|
||||
arr1.push([quantity, item]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// sort inventory in alphabetical order
|
||||
arr1.sort((previous, next) => (previous[1] > [next[1]]) ? 1 : -1);
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
// check if item already exists in inventory
|
||||
const position = inventory.indexOf(item);
|
||||
|
||||
// exsisting item: update quantity
|
||||
if (position !== -1) {
|
||||
const row = Math.floor(position / 2);
|
||||
arr1[row][0] += quantity;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// alien item: add to inventory
|
||||
arr1.push([quantity, item]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// sort inventory in alphabetical order
|
||||
arr1.sort((previous, next) => (previous[1] > [next[1]] ? 1 : -1));
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* Convert current inventory array **arr1** to an one-dimensional array in order that `indexOf()` method could be used to check existance of new delivery items in current inventory.
|
||||
* Check if item already exists in current inventory using `indexOf()`.
|
||||
@@ -279,9 +272,5 @@ Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function/apply'>JS Function.prototype.apply()</a>
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/continue' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS continue</a>
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/sort' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.sort()</a>
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +1,19 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: No Repeats Please
|
||||
---
|
||||
 Remember to use <a>**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program  and write your own code 
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation:
|
||||
# No Repeats Please
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
This task requires us to return the number of total permutations of the provided string that don't have repeated consecutive letters. It is to be assumed that all characters in the provided string are each unique. For example, `aab` should return 2 because it has 6 total permutations (`aab`, `aab`, `aba`, `aba`, `baa`, `baa`), but only 2 of them (`aba` and `aba`) don't have the same letter (in this case `a`) repeating.
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve that, we'll have to look at each possible permutation of a string. There are several ways to do that. A common interview question is building a function that collects all permutations of a string. There are several tutorials available on the internet on how to do that.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Potential Methods Used As Solution
|
||||
**Potential Methods Used As Solution**
|
||||
|
||||
##### Recursive Method
|
||||
**Recursive Method**
|
||||
|
||||
This task can be daunting even after watching a tutorial. To write a recursive solution, you will want to send each new use of the function three inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,6 +23,7 @@ This task can be daunting even after watching a tutorial. To write a recursive s
|
||||
|
||||
The pseudo code will look something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
var str = ???;
|
||||
permAlone(current position in original string, characters used already in original string, created string) {
|
||||
if (current string is finished) {
|
||||
@@ -37,13 +40,15 @@ The pseudo code will look something like this:
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
permAlone(0, nothing used yet, empty new string (or array the same size as str));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to think about this problem is to start from an empty space. Introduce the first letter to the space. This space will now contain the first sub-permutation. Here's a diagram illustrating the idea:
|
||||
|
||||
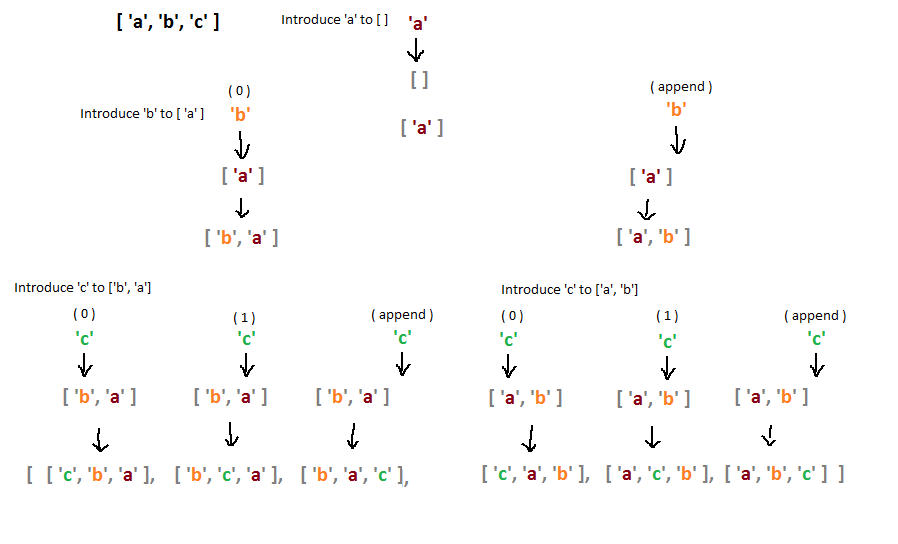
|
||||
|
||||
##### Non-Recursive Method
|
||||
**Non-Recursive Method**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
// An approach to introduce a new character to a permutation
|
||||
var ch = '?';
|
||||
var source = ['?', '?', '?']; // Current sub-permutation
|
||||
@@ -54,6 +59,7 @@ Another way to think about this problem is to start from an empty space. Introdu
|
||||
temp.splice(i, 0, ch); // Insert the new character
|
||||
dest.push(temp); // Store the new sub-permutation
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finding each permutation could then be done non-recursively by including the above in a function taking a source array and returning a destination array. For each letter of the input string, pass that character, as well as the array returned from the previous call of the function.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,81 +74,76 @@ A way to visualize this is by considering a tree that starts with the first char
|
||||
* <a>JS Regex Resources</a>
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/String' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS String object</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
* The easiest way is to use Heap's algorithm to recursively get a list of all the permutations.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
|
||||
* Once you have the list then just create a regular expression to catch the repeating characters.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 3
|
||||
### Hint 3
|
||||
|
||||
* You will want to have the permutations as an array of joined strings instead of separated characters.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert!
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
```js
|
||||
function permAlone(str) {
|
||||
// Create a regex to match repeated consecutive characters.
|
||||
var regex = /(.)\1+/;
|
||||
|
||||
**Solution ahead!**
|
||||
// Split the string into an array of characters.
|
||||
var arr = str.split("");
|
||||
var permutations = [];
|
||||
var tmp;
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution:
|
||||
// Return 0 if str contains same character.
|
||||
if (str.match(regex) !== null && str.match(regex)[0] === str) return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
function permAlone(str) {
|
||||
// Function to swap variables' content.
|
||||
function swap(index1, index2) {
|
||||
tmp = arr[index1];
|
||||
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
|
||||
arr[index2] = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Create a regex to match repeated consecutive characters.
|
||||
var regex = /(.)\1+/;
|
||||
|
||||
// Split the string into an array of characters.
|
||||
var arr = str.split('');
|
||||
var permutations = [];
|
||||
var tmp;
|
||||
|
||||
// Return 0 if str contains same character.
|
||||
if (str.match(regex) !== null && str.match(regex)[0] === str) return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// Function to swap variables' content.
|
||||
function swap(index1, index2) {
|
||||
tmp = arr[index1];
|
||||
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
|
||||
arr[index2] = tmp;
|
||||
// Generate arrays of permutations using the algorithm.
|
||||
function generate(int) {
|
||||
if (int === 1) {
|
||||
// Make sure to join the characters as we create the permutation arrays
|
||||
permutations.push(arr.join(""));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i != int; ++i) {
|
||||
generate(int - 1);
|
||||
swap(int % 2 ? 0 : i, int - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate arrays of permutations using the algorithm.
|
||||
function generate(int) {
|
||||
if (int === 1) {
|
||||
// Make sure to join the characters as we create the permutation arrays
|
||||
permutations.push(arr.join(''));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i != int; ++i) {
|
||||
generate(int - 1);
|
||||
swap(int % 2 ? 0 : i, int - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
generate(arr.length);
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter the array of repeated permutations.
|
||||
var filtered = permutations.filter(function(string) {
|
||||
return !string.match(regex);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Return how many have no repetitions.
|
||||
return filtered.length;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Test here.
|
||||
permAlone('aab');
|
||||
generate(arr.length);
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter the array of repeated permutations.
|
||||
var filtered = permutations.filter(function(string) {
|
||||
return !string.match(regex);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
// Return how many have no repetitions.
|
||||
return filtered.length;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Test here.
|
||||
permAlone("aab");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* **regex** contains the regular expression to match repeated consecutive characters.
|
||||
* The string **str** is split into an array of characters, **arr**.
|
||||
@@ -162,8 +163,5 @@ A way to visualize this is by considering a tree that starts with the first char
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/length' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>array.length</a>
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-filter/14289' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array Prototype Filter</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Pairwise
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Pairwise
|
||||
# Pairwise
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/algorithms/pairwise/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Add a New Element to a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Add a New Element to a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Add a New Element to a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/add-a-new-element-to-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Add Elements at a Specific Index in a Linked List
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Add Elements at a Specific Index in a Linked List
|
||||
# Add Elements at a Specific Index in a Linked List
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/add-elements-at-a-specific-index-in-a-linked-list/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,50 +1,44 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Adjacency List
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Adjacency List
|
||||
 Remember to use <a>**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program  and write your own code 
|
||||
# Adjacency List
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
To solve this problem, you have to create a Javascript Object to emulate an undirected graph in the form of an adjacency list.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
Create keys with the names James, Jill, Jenny and Jeff.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
|
||||
Read the presentation and try to understand what it means to be an undirected graph.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var undirectedAdjList = {
|
||||
James: ["Jeff"],
|
||||
Jill: ["Jenny"],
|
||||
Jenny: ["Jill", "Jeff"],
|
||||
Jeff: ["Jenny", "James"]
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Solution ahead!**
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
var undirectedAdjList = {
|
||||
James: ["Jeff"],
|
||||
Jill: ["Jenny"],
|
||||
Jenny: ["Jill", "Jeff"],
|
||||
Jeff: ["Jenny", "James"]
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* The undirected graph is created using a Javascript Object. Each unique name is a key and the each person who has a relationship with the name is in the unique name's array value. e.g. if James and Jeff have a relationship, Jeff will be in James's array value and James will be in Jeff's array value.
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Adjacency Matrix
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Adjacency Matrix
|
||||
# Adjacency Matrix
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/adjacency-matrix/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,56 +1,46 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Breadth-First Search
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Breadth-First Search
|
||||
# Breadth-First Search
|
||||
|
||||
Let's first define the `Tree` class to be used for the implementation of the Breadth First Search algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Tree:
|
||||
def __init__(self, x):
|
||||
self.val = x
|
||||
self.left = None
|
||||
self.right = None
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function bfs(graph, root) {
|
||||
// Distance object returned
|
||||
var nodesLen = {};
|
||||
// Set all distances to infinity
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
|
||||
nodesLen[i] = Infinity;
|
||||
}
|
||||
nodesLen[root] = 0; // ...except root node
|
||||
var queue = [root]; // Keep track of nodes to visit
|
||||
var current; // Current node traversing
|
||||
// Keep on going until no more nodes to traverse
|
||||
while (queue.length !== 0) {
|
||||
current = queue.shift();
|
||||
// Get adjacent nodes from current node
|
||||
var curConnected = graph[current]; // Get layer of edges from current
|
||||
var neighborIdx = []; // List of nodes with edges
|
||||
var idx = curConnected.indexOf(1); // Get first edge connection
|
||||
while (idx !== -1) {
|
||||
neighborIdx.push(idx); // Add to list of neighbors
|
||||
idx = curConnected.indexOf(1, idx + 1); // Keep on searching
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Loop through neighbors and get lengths
|
||||
for (var j = 0; j < neighborIdx.length; j++) {
|
||||
// Increment distance for nodes traversed
|
||||
if (nodesLen[neighborIdx[j]] === Infinity) {
|
||||
nodesLen[neighborIdx[j]] = nodesLen[current] + 1;
|
||||
queue.push(neighborIdx[j]); // Add new neighbors to queue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nodesLen;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The breadth first search algorithm moves from one level to another starting from the root of the tree. We will make use of a `queue` for this.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
def bfs(root_node):
|
||||
queue = [root_node]
|
||||
|
||||
while queue:
|
||||
top_element = queue.pop()
|
||||
print("Node processed: ",top_element)
|
||||
|
||||
if top_element.left:
|
||||
queue.append(top_element.left)
|
||||
|
||||
if top_element.right:
|
||||
queue.append(top_element.right)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can easily modify the above code to print the level of each node as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
def bfs(root_node):
|
||||
queue = [(root_node, 0)]
|
||||
|
||||
while queue:
|
||||
top_element, level = queue.pop()
|
||||
print("Node processed: {} at level {}".format(top_element, level))
|
||||
|
||||
if top_element.left:
|
||||
queue.append((top_element.left, level + 1))
|
||||
|
||||
if top_element.right:
|
||||
queue.append((top_element.right, level + 1))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| Complexity | Time | Space |
|
||||
| ----- | ------ | ------ |
|
||||
| BFS | n | n |
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Check if an Element is Present in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Check if an Element is Present in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Check if an Element is Present in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/check-if-an-element-is-present-in-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,81 +1,88 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Circular Queue
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Circular Queue
|
||||
# Create a Circular Queue
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- In this challenge we create a Circular Queue data structure.
|
||||
- First, we need to create an array of `size` with all elements set to `null`.
|
||||
- Then we create an equeue method, which moves the write pointer but doesnt exceed the read pointer.
|
||||
- The dequeue method on the other hand, moves the read pointer but doesnt exceed the write pointer.
|
||||
- Example:
|
||||
|
||||
- First, we create an array of length 5:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
```
|
||||
[null, null, null, null, null]
|
||||
^Read @ 0
|
||||
^Write @ 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Then we enqueue `a`, `b`, and `c`:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Then we enqueue `a`, `b`, and `c`:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[a, b, c, null, null]
|
||||
^Read @ 0
|
||||
^Write @ 3
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Now we dequeue all the enqueued items:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[null, null, null, null, null]
|
||||
^Read @ 3
|
||||
^Write @ 3
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Finally, we enqueue `d`, `e` and `f`:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
```
|
||||
[f, null, null, d, e]
|
||||
^Read @ 3
|
||||
^Write @ 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
class CircularQueue {
|
||||
constructor(size) {
|
||||
|
||||
this.queue = [];
|
||||
this.read = 0;
|
||||
this.write = 0;
|
||||
this.max = size - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (size > 0) {
|
||||
this.queue.push(null);
|
||||
size--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
constructor(size) {
|
||||
this.queue = [];
|
||||
this.read = 0;
|
||||
this.write = 0;
|
||||
this.max = size - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
while (size > 0) {
|
||||
this.queue.push(null);
|
||||
size--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
print() {
|
||||
return this.queue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
print() {
|
||||
return this.queue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
enqueue(item) {
|
||||
if (this.queue[this.write] === null) {
|
||||
this.queue[this.write++] = item;
|
||||
|
||||
if (this.write > this.max) this.write = 0;
|
||||
return item;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
enqueue(item) {
|
||||
if (this.queue[this.write] === null){
|
||||
this.queue[this.write++] = item;
|
||||
|
||||
if (this.write > this.max) this.write = 0;
|
||||
return item;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dequeue() {
|
||||
if (this.queue[this.read] != null) {
|
||||
let item = this.queue[this.read];
|
||||
this.queue[this.read++] = null;
|
||||
if (this.read > this.max) this.read = 0;
|
||||
return item;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dequeue() {
|
||||
if (this.queue[this.read] != null){
|
||||
let item = this.queue[this.read];
|
||||
this.queue[this.read++] = null;
|
||||
if (this.read > this.max) this.read = 0;
|
||||
return item;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circular_buffer)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Doubly Linked List
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Doubly Linked List
|
||||
# Create a Doubly Linked List
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/create-a-doubly-linked-list/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Hash Table
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Hash Table
|
||||
# Create a Hash Table
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/create-a-hash-table/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Linked List Class
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Linked List Class
|
||||
# Create a Linked List Class
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/create-a-linked-list-class/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Map Data Structure
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Map Data Structure
|
||||
# Create a Map Data Structure
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/create-a-map-data-structure/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Priority Queue Class
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Priority Queue Class
|
||||
# Create a Priority Queue Class
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Priority Queue is an Abstract Data Type.
|
||||
- It can be implemented using other Data Structures but is commonly implemented using a Heap.
|
||||
- Each node contains a priority. When we enqueue a node to the queue, it's "bubbled up" to its place in the queue.
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +19,11 @@ title: Create a Priority Queue Class
|
||||
| Priority Queue | 1 | 1 | logn | logn |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//function which swaps elements in array, using ES6 syntax
|
||||
function swap(arr, i, j) {
|
||||
@@ -121,5 +126,7 @@ class PriorityQueue {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,10 +1,11 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Queue Class
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Queue Class
|
||||
# Create a Queue Class
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- A Queue is an abstract Data Structure.
|
||||
- A Queue folow FIFO/LILO principle.
|
||||
- In this challenge we nede to implement `enqueue()`, `dequeue()`, `front()`, `size()`, `isEmpty()` methods.
|
||||
@@ -20,61 +21,69 @@ title: Create a Queue Class
|
||||
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Basic:
|
||||
##### Note:
|
||||
- This solution is not exactly a queue, the shift() method used in the dequeue() method is of complexity `O(n)` and not `O(1)`. However, the advanced solution rectifies this and uses Object(HashTables) instead of Array to implement Queue.
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** This solution is not exactly a queue, the shift() method used in the dequeue() method is of complexity `O(n)` and not `O(1)`. However, the advanced solution rectifies this and uses Object(HashTables) instead of Array to implement Queue.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function Queue () {
|
||||
var collection = [];
|
||||
this.print = function() {
|
||||
console.log(collection);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.enqueue = function(val){
|
||||
collection.push(val);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.dequeue = function(){
|
||||
return collection.shift();
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.front = function(){
|
||||
return collection[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.size = function(){
|
||||
return collection.length;
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.isEmpty = function(){
|
||||
return collection.length === 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function Queue() {
|
||||
var collection = [];
|
||||
this.print = function() {
|
||||
console.log(collection);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.enqueue = function(val) {
|
||||
collection.push(val);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.dequeue = function() {
|
||||
return collection.shift();
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.front = function() {
|
||||
return collection[0];
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.size = function() {
|
||||
return collection.length;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.isEmpty = function() {
|
||||
return collection.length === 0;
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Advanced - ES6 class syntax:
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
class Queue {
|
||||
constructor(){
|
||||
this.collection = {};
|
||||
this.start = 0;
|
||||
this.end = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
print(){
|
||||
console.log(this.collection);
|
||||
}
|
||||
enqueue(val){
|
||||
this.collection[this.end++] = val;
|
||||
}
|
||||
dequeue(){
|
||||
return this.collection[this.start++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
front(){
|
||||
return this.collection[this.start];
|
||||
}
|
||||
size(){
|
||||
return this.end - this.start;
|
||||
}
|
||||
isEmpty(){
|
||||
return this.size() === 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
this.collection = {};
|
||||
this.start = 0;
|
||||
this.end = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
print() {
|
||||
console.log(this.collection);
|
||||
}
|
||||
enqueue(val) {
|
||||
this.collection[this.end++] = val;
|
||||
}
|
||||
dequeue() {
|
||||
return this.collection[this.start++];
|
||||
}
|
||||
front() {
|
||||
return this.collection[this.start];
|
||||
}
|
||||
size() {
|
||||
return this.end - this.start;
|
||||
}
|
||||
isEmpty() {
|
||||
return this.size() === 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Queue_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,32 +1,39 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Set Class
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Set Class
|
||||
# Create a Set Class
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- A Set is an abstract data structure.
|
||||
- It can store unique value and the collection is unordered.
|
||||
- In this challenge, we have to implement `.add()` method. This method should only add unique values to `collection`.
|
||||
- The method should return `true`, if the value is sucessfully added to the collection, otherwise it should return `false`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function Set() {
|
||||
// the var collection will hold our set
|
||||
var collection = [];
|
||||
// this method will check for the presence of an element and return true or false
|
||||
this.has = function(element) {
|
||||
return (collection.indexOf(element) !== -1);
|
||||
};
|
||||
// this method will return all the values in the set
|
||||
this.values = function() {
|
||||
return collection;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.add = function(el) {
|
||||
return this.has(el) ? false : Boolean(collection.push(el));
|
||||
}
|
||||
// the var collection will hold our set
|
||||
var collection = [];
|
||||
// this method will check for the presence of an element and return true or false
|
||||
this.has = function(element) {
|
||||
return collection.indexOf(element) !== -1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
// this method will return all the values in the set
|
||||
this.values = function() {
|
||||
return collection;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.add = function(el) {
|
||||
return this.has(el) ? false : Boolean(collection.push(el));
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Resources:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Set_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Stack Class
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Stack Class
|
||||
# Create a Stack Class
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Stack is an abstract data structure.
|
||||
- Stack follows LIFO/FILO principle.
|
||||
- In this challenge, we need to add `.push()`, `.pop()`, `.peek()`, `.isEmpty()` and `.clear()` methods to the class.
|
||||
@@ -18,58 +19,65 @@ title: Create a Stack Class
|
||||
| ----- | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
|
||||
| Stack | n | n | 1 | 1 |
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
#### Basic:
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function Stack() {
|
||||
var collection = [];
|
||||
this.print = function() {
|
||||
console.log(collection);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.push = function(val){
|
||||
return collection.push(val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.pop = function(){
|
||||
return collection.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.peek = function(){
|
||||
return collection[collection.length-1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.isEmpty = function(){
|
||||
return collection.length === 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.clear = function(){
|
||||
collection.length = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Advanced - ES6 Class syntax:
|
||||
```js
|
||||
|
||||
class Stack {
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
this.collection = [];
|
||||
}
|
||||
print(){
|
||||
console.log(this.collection);
|
||||
}
|
||||
push(val){
|
||||
retiurn this.collection.push(val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
pop(){
|
||||
return this.collection.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
peek(){
|
||||
return this.collection[this.collection.length-1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
isEmpty(){
|
||||
return this.collection.length === 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
clear(){
|
||||
return this.collection.length = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function Stack() {
|
||||
var collection = [];
|
||||
this.print = function() {
|
||||
console.log(collection);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.push = function(val) {
|
||||
return collection.push(val);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.pop = function() {
|
||||
return collection.pop();
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.peek = function() {
|
||||
return collection[collection.length - 1];
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.isEmpty = function() {
|
||||
return collection.length === 0;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.clear = function() {
|
||||
collection.length = 0;
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Resources:
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
class Stack {
|
||||
constructor() {
|
||||
this.collection = [];
|
||||
}
|
||||
print() {
|
||||
console.log(this.collection);
|
||||
}
|
||||
push(val) {
|
||||
return this.collection.push(val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
pop() {
|
||||
return this.collection.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
peek() {
|
||||
return this.collection[this.collection.length - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
isEmpty() {
|
||||
return this.collection.length === 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
clear() {
|
||||
return (this.collection.length = 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stack_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create a Trie Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create a Trie Search Tree
|
||||
# Create a Trie Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/create-a-trie-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create an ES6 JavaScript Map
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create an ES6 JavaScript Map
|
||||
# Create an ES6 JavaScript Map
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/create-an-es6-javascript-map/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,37 +1,31 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Create and Add to Sets in ES6
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Create and Add to Sets in ES6
|
||||
# Create and Add to Sets in ES6
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
 Remember to use <a>**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program  and write your own code 
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
To solve this problem, you have to add an array of items to the set.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
Use the add function to add an array of strings to the set.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
|
||||
Use the length attribute on the values of the Set.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Solution ahead!**
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution:
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function checkSet() {
|
||||
@@ -46,13 +40,10 @@ function checkSet() {
|
||||
checkSet();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* Creating a set object as shown in pre-written code will create the set without duplicate objects.
|
||||
* Therefore, by using the add function, we can add items to the set and they will not be duplicated, and will still be represented in the array.
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Delete a Leaf Node in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Delete a Leaf Node in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Delete a Leaf Node in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/delete-a-leaf-node-in-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Delete a Node with One Child in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Delete a Node with One Child in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Delete a Node with One Child in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/delete-a-node-with-one-child-in-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Delete a Node with Two Children in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Delete a Node with Two Children in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Delete a Node with Two Children in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/delete-a-node-with-two-children-in-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Depth-First Search
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Depth-First Search
|
||||
# Depth-First Search
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/depth-first-search/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,87 +1,88 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Find the Minimum and Maximum Height of a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Find the Minimum and Maximum Height of a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Find the Minimum and Maximum Height of a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var displayTree = (tree) => console.log(JSON.stringify(tree, null, 2));
|
||||
var displayTree = tree => console.log(JSON.stringify(tree, null, 2));
|
||||
function Node(value) {
|
||||
this.value = value;
|
||||
this.left = null;
|
||||
this.right = null;
|
||||
this.value = value;
|
||||
this.left = null;
|
||||
this.right = null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function BinarySearchTree() {
|
||||
this.root = null;
|
||||
// change code below this line
|
||||
// change code above this line
|
||||
this.findMinHeight = function(root = this.root) {
|
||||
// empty tree.
|
||||
if(root === null) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// leaf node.
|
||||
if(root.left === null && root.right === null) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(root.left === null){
|
||||
return this.findMinHeight(root.right) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(root.right === null){
|
||||
return this.findMinHeight(root.left) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const lHeight = this.findMinHeight(root.left);
|
||||
const rHeight = this.findMinHeight(root.right);
|
||||
return Math.min(lHeight, rHeight) + 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.findMaxHeight = function(root = this.root) {
|
||||
// empty tree.
|
||||
if(root === null) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// leaf node.
|
||||
if(root.left === null && root.right === null) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(root.left === null){
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.right) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(root.right === null){
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.left) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const lHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.left);
|
||||
const rHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.right);
|
||||
return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.isBalanced = function(root = this.root) {
|
||||
this.root = null;
|
||||
// change code below this line
|
||||
// change code above this line
|
||||
this.findMinHeight = function(root = this.root) {
|
||||
// empty tree.
|
||||
if (root === null) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// leaf node.
|
||||
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (root.left === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMinHeight(root.right) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (root.right === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMinHeight(root.left) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const lHeight = this.findMinHeight(root.left);
|
||||
const rHeight = this.findMinHeight(root.right);
|
||||
return Math.min(lHeight, rHeight) + 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.findMaxHeight = function(root = this.root) {
|
||||
// empty tree.
|
||||
if (root === null) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// leaf node.
|
||||
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (root.left === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.right) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (root.right === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.left) + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
const lHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.left);
|
||||
const rHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.right);
|
||||
return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.isBalanced = function(root = this.root) {
|
||||
if (root === null) {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(root === null) {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(root.left === null && root.right === null){
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (root.left === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.right) <= 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(root.left === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.right) <= 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (root.right === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.left) <= 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(root.right === null) {
|
||||
return this.findMaxHeight(root.left) <= 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const lHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.left);
|
||||
const rHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.right);
|
||||
if(Math.abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1){
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return this.isBalanced(root.left) && this.isBalanced(root.right);
|
||||
};
|
||||
const lHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.left);
|
||||
const rHeight = this.findMaxHeight(root.right);
|
||||
if (Math.abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return this.isBalanced(root.left) && this.isBalanced(root.right);
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Find the Minimum and Maximum Value in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Find the Minimum and Maximum Value in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Find the Minimum and Maximum Value in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/find-the-minimum-and-maximum-value-in-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Heap Sort with a Min Heap
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Heap Sort with a Min Heap
|
||||
# Implement Heap Sort with a Min Heap
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/implement-heap-sort-with-a-min-heap/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Incidence Matrix
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Incidence Matrix
|
||||
# Incidence Matrix
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/incidence-matrix/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Data Structures
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Data Structures
|
||||
# Data Structures
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/mathematics/quadratic-equations/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Insert an Element into a Max Heap
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Insert an Element into a Max Heap
|
||||
# Insert an Element into a Max Heap
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/insert-an-element-into-a-max-heap/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,33 +1,28 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Invert a Binary Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Invert a Binary Tree
|
||||
# Invert a Binary Tree
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
## Hint: 1
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
Create a invert(node = this.root) method in the BinarySearchTree constructor function.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Hint: 2
|
||||
|
||||
Try to use recursion and think of a base case.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert!
|
||||
|
||||
**Solution ahead!**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Basic Code Solution:
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var displayTree = (tree) => console.log(JSON.stringify(tree, null, 2));
|
||||
var displayTree = tree => console.log(JSON.stringify(tree, null, 2));
|
||||
function Node(value) {
|
||||
this.value = value;
|
||||
this.left = null;
|
||||
@@ -45,15 +40,13 @@ function BinarySearchTree() {
|
||||
this.invert(node.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// change code above this line
|
||||
};
|
||||
// change code above this line
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a href='https://repl.it/repls/SereneScholarlyAnalyst' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Run Code</a>
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
* Using recursion will allow you to traverse each node once and the only extra memory used is the auxiliary temp variable that enables you to swap. You keep swapping the left and right pointers of a node until you reach the leaves which will not do anything as the left and right of them are null references.
|
||||
## NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
|
||||
**DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**.
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,23 +1,30 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Learn how a Stack Works
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Learn how a Stack Works
|
||||
# Learn how a Stack Works
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Stacks are an abstract data structures.
|
||||
- They follow LIFO (Last In First Out) or FILO (First In Last Out) principle.
|
||||
- Stack's insertion and deletion operations are of **O(1)** time complexity.
|
||||
- In JavaScript, arrays can be treated as a Stack since `.push()` and `.pop()` methods have time complexity of **O(1)**.
|
||||
- In this challenge we need to `.pop()` and then `.push()` into the stack.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var homeworkStack = ["BIO12","HIS80","MAT122","PSY44"];
|
||||
var homeworkStack = ["BIO12", "HIS80", "MAT122", "PSY44"];
|
||||
|
||||
homeworkStack.pop();
|
||||
homeworkStack.push("CS50");
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Reference:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stack_(abstract_data_type))
|
||||
- Video by [Hackerrank](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjI1WNcIntg)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Perform a Difference on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Perform a Difference on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
# Perform a Difference on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/perform-a-difference-on-two-sets-of-data/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Perform a Subset Check on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Perform a Subset Check on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
# Perform a Subset Check on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/perform-a-subset-check-on-two-sets-of-data/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Perform a Union on Two Sets
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Perform a Union on Two Sets
|
||||
# Perform a Union on Two Sets
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/perform-a-union-on-two-sets/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Perform an Intersection on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Perform an Intersection on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
# Perform an Intersection on Two Sets of Data
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/perform-an-intersection-on-two-sets-of-data/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Remove an Element from a Max Heap
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Remove an Element from a Max Heap
|
||||
# Remove an Element from a Max Heap
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/remove-an-element-from-a-max-heap/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Remove Elements from a Linked List by Index
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Remove Elements from a Linked List by Index
|
||||
# Remove Elements from a Linked List by Index
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/remove-elements-from-a-linked-list-by-index/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Remove Elements from a Linked List
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Remove Elements from a Linked List
|
||||
# Remove Elements from a Linked List
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/remove-elements-from-a-linked-list/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Remove items from a set in ES6
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Remove items from a set in ES6
|
||||
# Remove items from a set in ES6
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/remove-items-from-a-set-in-es6/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,15 +2,20 @@
|
||||
title: Reverse a Doubly Linked List
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Reverse a Doubly Linked List
|
||||
# Reverse a Doubly Linked List
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Reverse the doubly linked list, and update previous and next variables for each member node accordingly.
|
||||
- Define privileged methods add() and reverse().
|
||||
- add() will find the end of the list and append new entries at this location.
|
||||
- reverse() will swap entries one pair at a time using a temporary variable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var Node = function(data, prev) {
|
||||
@@ -31,32 +36,32 @@ var DoublyLinkedList = function() {
|
||||
this.head = node;
|
||||
this.tail = node;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
while (currentNode.next) {
|
||||
previousNode = currentNode;
|
||||
while (currentNode.next) {
|
||||
previousNode = currentNode;
|
||||
currentNode = currentNode.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
node.prev = currentNode;
|
||||
currentNode.next = node;
|
||||
this.tail = node;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.reverse = function() {
|
||||
let temp = null;
|
||||
let currentNode = this.head;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (this.head === null) {
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
this.tail = currentNode;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while (currentNode) {
|
||||
temp = currentNode.prev;
|
||||
temp = currentNode.prev;
|
||||
currentNode.prev = currentNode.next;
|
||||
currentNode.next = temp;
|
||||
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (temp != null) {
|
||||
this.head = temp.prev;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -65,5 +70,7 @@ var DoublyLinkedList = function() {
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Reference:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Search within a Linked List
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Search within a Linked List
|
||||
# Search within a Linked List
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/search-within-a-linked-list/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,13 +1,19 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Typed Arrays
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Typed Arrays
|
||||
# Typed Arrays
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- In this challenge, first we need to create a buffer of 64 bytes. We can use `ArrayBuffer()` constructor.
|
||||
- After creating a buffer we need to create an Int32Array, for that we can use `Int32Array()` constructor.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//Create a buffer of 64 bytes
|
||||
var buffer = new ArrayBuffer(64);
|
||||
@@ -16,6 +22,8 @@ var buffer = new ArrayBuffer(64);
|
||||
var i32View = new Int32Array(buffer);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [ArrayBuffer](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/ArrayBuffer)
|
||||
- [TypedArray](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Typed_arrays)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Use .has and .size on an ES6 Set
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Use .has and .size on an ES6 Set
|
||||
# Use .has and .size on an ES6 Set
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/use-.has-and-.size-on-an-es6-set/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Use Breadth First Search in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Use Breadth First Search in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Use Breadth First Search in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/use-breadth-first-search-in-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Use Depth First Search in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Use Depth First Search in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
# Use Depth First Search in a Binary Search Tree
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/use-depth-first-search-in-a-binary-search-tree/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Use Spread and Notes for ES5 Set() Integration
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Use Spread and Notes for ES5 Set() Integration
|
||||
# Use Spread and Notes for ES5 Set() Integration
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/use-spread-and-notes-for-es5-set-integration/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Work with Nodes in a Linked List
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Work with Nodes in a Linked List
|
||||
# Work with Nodes in a Linked List
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/data-structures/work-with-nodes-in-a-linked-list/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Coding Interview Prep
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Coding Interview Prep
|
||||
# Coding Interview Prep
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we can start with the premise and the fact that almost all companies leave to the applicant's choice to choose their preferable programming language for the interview. Since you have this advantage, you should pick the language you are most familiar with. If you are a rookie in this domain and you want to apply for your first job, it's recommended to start with the language which seems more interesting to you and makes you comfortable when you write code.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
title: Project Euler
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Project Euler
|
||||
# Project Euler
|
||||
[Project Euler](https://projecteuler.net/), named for mathematician Leonard Euler, is a popular resource for practicing writing efficient algorithms. It is inspired by the shared goal of mathematicians and programmers to compose elegant and efficient solutions to complex problems. Project Euler is language agnostic. Rather than testing coded solutions, it presents a question to users and asks them only to input the correct answer. For this reason it is a popular platform for people who are learning new languages as well as those who want to practice writing more efficient solutions. The challenges presented by Project Euler are math problems of increasing complexity. Although all of these challenges can be solved by an algorithm that runs in less than a minute, the most obvious may take hours or even days to complete. The Project Euler platform does not run your algorithm and does not grade you based on its efficiency, but once you have solved the problem to arrive at a correct solution you will be granted access to a discussion forum of the challenge where you can get community help on how to improve your approach.
|
||||
|
||||
#### More Information:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,19 +1,26 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Multiples of 3 and 5
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 1: Multiples of 3 and 5
|
||||
# Problem 1: Multiples of 3 and 5
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- We can find if a number is divisble by another number with the help of `%` modulo operator.
|
||||
- `num1 % num2` returns `0` if there's no remainder while doing `num1/num2`.
|
||||
- Starting from `i = 3` because that's the first number that's divisble by 3 or 5, we loop through till the `number` provided.
|
||||
- If the number is divisible either by 3 or 5, we add that to the variable `sum` and finally return it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function multiplesOf3and5(number) {
|
||||
let sum = 0, i = 3;
|
||||
while (i < number){
|
||||
let sum = 0,
|
||||
i = 3;
|
||||
while (i < number) {
|
||||
if (i % 3 == 0 || i % 5 == 0) sum += i;
|
||||
i++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -22,5 +29,7 @@ function multiplesOf3and5(number) {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Reference:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Modulo operator](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Arithmetic_Operators#Remainder_())
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +1,20 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Summation of primes
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 10: Summation of primes
|
||||
# Problem 10: Summation of primes
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- In this challenge we need to find sum of all prime numbers up to `n`.
|
||||
- Example:
|
||||
- If `n = 10` then prime numbers before it are `2, 3, 5, 7` and their sum is `17`.
|
||||
- We've used Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm to find prime numbers in the below solution.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function primeSummation(n) {
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,5 +55,6 @@ function primeSummation(n) {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- Sieve of Eratosthenes [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Eratosthenes)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Even Fibonacci Numbers
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 2: Even Fibonacci Numbers
|
||||
# Problem 2: Even Fibonacci Numbers
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- A fibonacci sequence is a sequence where `fib(n) = fib(n-1) + fib(n-1)`.
|
||||
- In this challenge we have to sum all the even numbers upto `nth` term in the sequence.
|
||||
- Example for `fiboEvenSum(10)`:
|
||||
@@ -13,34 +14,51 @@ title: Even Fibonacci Numbers
|
||||
+ Sum of all even number in the above sequence is:
|
||||
2 + 8 + 34 = 44
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Basic Solution - Iterative:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
Iterative
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function fiboEvenSum(n) {
|
||||
let first = 1, second = 2, sum = 2, fibNum; // declaring and initializing variables
|
||||
let first = 1,
|
||||
second = 2,
|
||||
sum = 2,
|
||||
fibNum; // declaring and initializing variables
|
||||
if (n <= 1) return sum; // edge case
|
||||
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++){ // looping till n
|
||||
fibNum = first + second; // getting the ith fibonacci number
|
||||
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
// looping till n
|
||||
fibNum = first + second; // getting the ith fibonacci number
|
||||
first = second;
|
||||
second = fibNum;
|
||||
if (fibNum%2 == 0) sum+=fibNum; // If even add to the sum variable
|
||||
if (fibNum % 2 == 0) sum += fibNum; // If even add to the sum variable
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Advanced Solution - Recursive:
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
Recursive
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// We use memoization technique to save ith fibonacci number to the fib array
|
||||
function fiboEvenSum(n){
|
||||
const fib = [1, 1, 2];
|
||||
// We use memoization technique to save ith fibonacci number to the fib array
|
||||
function fiboEvenSum(n) {
|
||||
const fib = [1, 1, 2];
|
||||
let sumEven = fib[2];
|
||||
function fibonacci(n){
|
||||
if (n <= 1) return fib[n]; // base condition
|
||||
else if (fib[n]) return fib[n]; // if the number exists in the array we cache it and return
|
||||
function fibonacci(n) {
|
||||
if (n <= 1) return fib[n];
|
||||
// base condition
|
||||
else if (fib[n]) return fib[n];
|
||||
// if the number exists in the array we cache it and return
|
||||
else {
|
||||
fib[n] = fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2); // otherwise calculcate and save it to the array
|
||||
if (fib[n]%2 == 0) sumEven+=fib[n]; //if the number is even, add it to the sumEven variable
|
||||
fib[n] = fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2); // otherwise calculcate and save it to the array
|
||||
if (fib[n] % 2 == 0) sumEven += fib[n]; //if the number is even, add it to the sumEven variable
|
||||
return fib[n];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -48,6 +66,6 @@ function fiboEvenSum(n){
|
||||
return sumEven;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,29 +1,35 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Largest prime factor
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 3: Largest prime factor
|
||||
# Problem 3: Largest prime factor
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- To find the largest prime factor of a number, we start from the smallest prime factor 2 and divide the number with it.
|
||||
- If the remainder is 0 that means the number is divisible by that prime number, we keep dividing the number by same prime number until that number is no more divisible by that prime number.
|
||||
- After that, we incrememnt the prime factor by 1 and repeat this process till the number becomes 1.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function largestPrimeFactor(number) {
|
||||
let prime = 2, max = 1;
|
||||
while (prime <= number){
|
||||
let prime = 2,
|
||||
max = 1;
|
||||
while (prime <= number) {
|
||||
if (number % prime == 0) {
|
||||
max = prime;
|
||||
number = number/prime;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else prime++; //Only increment the prime number if the number isn't divisible by it
|
||||
number = number / prime;
|
||||
} else prime++; //Only increment the prime number if the number isn't divisible by it
|
||||
}
|
||||
return max;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Resources:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prime_number)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,51 +1,54 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Largest palindrome product
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 4: Largest palindrome product
|
||||
# Problem 4: Largest palindrome product
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- A palindromic number is the one that when reversed reads the same.
|
||||
- The largest number obtained from product of two 3 digit number is `999 * 999`, so we can make a loop that starts by producting the largest number and check if that number is palindromic or not.
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function largestPalindromeProduct(n) {
|
||||
|
||||
//To get the maximum n digit number, + operator type castes String to Number type
|
||||
let max = +[...Array(n)].reduce((a, c) => a+=9, "");
|
||||
|
||||
let max = +[...Array(n)].reduce((a, c) => (a += 9), "");
|
||||
|
||||
//Next we get minimum n digit number from the max
|
||||
let min = (max+1)/10;
|
||||
|
||||
let min = (max + 1) / 10;
|
||||
|
||||
//To store the result
|
||||
let res = [];
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Starting the loop from max to min
|
||||
for (let i = max; i >= min; i--){
|
||||
|
||||
//Another loop
|
||||
for (let j = max; j >= min; j--){
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = max; i >= min; i--) {
|
||||
//Another loop
|
||||
for (let j = max; j >= min; j--) {
|
||||
//Getting the product
|
||||
let num = i*j;
|
||||
|
||||
let num = i * j;
|
||||
|
||||
//Reversing the number
|
||||
let numReverse = [...String(num)].reverse().join('');
|
||||
|
||||
let numReverse = [...String(num)].reverse().join("");
|
||||
|
||||
//Checking for palindromic number
|
||||
if (num == numReverse) {
|
||||
|
||||
//Pushing the number into array and breaking the loop for efficiency
|
||||
res.push(num);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Returning the maximum of the result array
|
||||
return Math.max(...res);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palindromic_number)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,39 +1,45 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Smallest multiple
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 5: Smallest multiple
|
||||
# Problem 5: Smallest multiple
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- In this challenge we need to find the LCM of 1 to n numbers.
|
||||
- To find LCM of a number we use the following formula:
|
||||
- 
|
||||
- To find GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two number we use Euclidean algorithm.
|
||||
- Once we get LCM of two numbers, we can get LCM of the numbers from 1 to n.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//LCM of two numbers
|
||||
function lcm(a, b){
|
||||
return (a*b)/gcd(a, b);
|
||||
function lcm(a, b) {
|
||||
return (a * b) / gcd(a, b);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//Euclidean recursive algorithm
|
||||
function gcd(a, b){
|
||||
//Euclidean recursive algorithm
|
||||
function gcd(a, b) {
|
||||
if (b === 0) return a;
|
||||
return gcd(b, a%b);
|
||||
return gcd(b, a % b);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function smallestMult(n){
|
||||
function smallestMult(n) {
|
||||
let maxLCM = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Getting the LCM in the range
|
||||
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++){
|
||||
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
maxLCM = lcm(maxLCM, i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return maxLCM;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Euclidean algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_algorithm)
|
||||
- [LCM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Least_common_multiple)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Sum square difference
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 6: Sum square difference
|
||||
# Problem 6: Sum square difference
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Sum of first n natural numbers can be calculated by using this formula:
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +13,11 @@ title: Sum square difference
|
||||
|
||||
- We can calculate the values using the above formula and subtract them to get the result.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function sumSquareDifference(n) {
|
||||
const sumOfN = (n*(n+1))/2;
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +28,9 @@ function sumSquareDifference(n) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Sum of n numbers - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1_%2B_2_%2B_3_%2B_4_%2B_%E2%8B%AF)
|
||||
- [Sum of n square numbers - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Square_pyramidal_number)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,49 +1,54 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 10001st prime
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 7: 10001st prime
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
# Problem 7: 10001st prime
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- A prime number is a number which is divided by 1 and itself.
|
||||
- We can find a number is prime if it's not divisible by other prime numbers smaller than itself.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function nthPrime(n) {
|
||||
|
||||
//Primes array which will store all the prime numbers
|
||||
const primes = [2];
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Num is the number we want to check
|
||||
let num = 3, isPrime = true;
|
||||
|
||||
let num = 3,
|
||||
isPrime = true;
|
||||
|
||||
//Looping until primes array is equal to n
|
||||
while (primes.length < n){
|
||||
|
||||
while (primes.length < n) {
|
||||
//All the primes numbers of a number is always <= its square root
|
||||
let max = Math.ceil(Math.sqrt(num));
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; primes[i] <= max; i++){
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; primes[i] <= max; i++) {
|
||||
if (num % primes[i] == 0) {
|
||||
|
||||
//Looping till we find the prime
|
||||
isPrime = false;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//if Prime found, push it to the array
|
||||
if (isPrime) primes.push(num);
|
||||
isPrime = true;
|
||||
|
||||
//An optimization technique, since we know of all even numbers only 2 is a prime number, we can skip the rest
|
||||
num+=2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//Returning the last number
|
||||
return primes[primes.length-1];
|
||||
|
||||
//An optimization technique, since we know of all even numbers only 2 is a prime number, we can skip the rest
|
||||
num += 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//Returning the last number
|
||||
return primes[primes.length - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prime_number)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@@ -1,32 +1,39 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Special Pythagorean triplet
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem 9: Special Pythagorean triplet
|
||||
# Problem 9: Special Pythagorean triplet
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- In this challenge we need to find the pythagorean triple.
|
||||
- We have the following information - `a < b < c`
|
||||
- Based on this, we can make a loop starting from `a = 0` and `b = a` since `a < b` always.
|
||||
- We also know that `a + b + c = n` and `a^2 + b^2 = c^2`, since we have `a`, `b` and `n`. We can find `c` and see if it satisfies the triplet theorem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function specialPythagoreanTriplet(n) {
|
||||
let sumOfabc = n;
|
||||
for (let a = 1; a < n; a++){
|
||||
for (let b = a; b < n; b++){
|
||||
let c = n - a- b;
|
||||
if (c > 0){
|
||||
if (c**2 == a**2 + b**2){
|
||||
return a*b*c;
|
||||
for (let a = 1; a < n; a++) {
|
||||
for (let b = a; b < n; b++) {
|
||||
let c = n - a - b;
|
||||
if (c > 0) {
|
||||
if (c ** 2 == a ** 2 + b ** 2) {
|
||||
return a * b * c;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
specialPythagoreanTriplet(1000);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pythagorean_triple)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 100 doors
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 100 doors
|
||||
# 100 doors
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/100-doors/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 24 game
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 24 game
|
||||
# 24 game
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/24-game/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 9 billion names of God the integer
|
||||
---
|
||||
## 9 billion names of God the integer
|
||||
# 9 billion names of God the integer
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/9-billion-names-of-god-the-integer/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: ABC Problem
|
||||
---
|
||||
## ABC Problem
|
||||
# ABC Problem
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/abc-problem/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Abundant, deficient and perfect number classifications
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Abundant, deficient and perfect number classifications
|
||||
# Abundant, deficient and perfect number classifications
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/abundant-deficient-and-perfect-number-classifications/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Accumulator factory
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Accumulator factory
|
||||
# Accumulator factory
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/accumulator-factory/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Ackermann function
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Ackermann function
|
||||
# Ackermann function
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/ackermann-function/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Align columns
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Align columns
|
||||
# Align columns
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/align-columns/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Amicable pairs
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Amicable pairs
|
||||
# Amicable pairs
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/amicable-pairs/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Averages/Mode
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Averages/Mode
|
||||
# Averages/Mode
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/averagesmode/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Averages/Pythagorean means
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Averages/Pythagorean means
|
||||
# Averages/Pythagorean means
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/averagespythagorean-means/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Averages/Root mean square
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Averages/Root mean square
|
||||
# Averages/Root mean square
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/averagesroot-mean-square/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Babbage problem
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Babbage problem
|
||||
# Babbage problem
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/babbage-problem/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,25 +1,24 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Balanced brackets
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Balanced brackets
|
||||
# Balanced brackets
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/balanced-brackets/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
<a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/blob/master/README.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>This quick style guide will help ensure your pull request gets accepted</a>.
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- The article goes here, in GitHub-flavored Markdown. Feel free to add YouTube videos, images, and CodePen/JSBin embeds -->
|
||||
<details><summary>### Solution #1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Solution
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function isBalanced(str) {
|
||||
if (str === '') return true;
|
||||
if (str === "") return true;
|
||||
|
||||
str = str.split('');
|
||||
str = str.split("");
|
||||
let stack = [];
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (str[i] === '[') {
|
||||
stack.push('[');
|
||||
} else if (str[i] === ']' && stack[stack.length - 1] === '[') {
|
||||
if (str[i] === "[") {
|
||||
stack.push("[");
|
||||
} else if (str[i] === "]" && stack[stack.length - 1] === "[") {
|
||||
stack.pop();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -32,3 +31,5 @@ function isBalanced(str) {
|
||||
- Push every `[` into a stack.
|
||||
- Check if the item stored on the stack is `[` when a `]` occurs. This makes it a pair & `[` can be removed from the stack.
|
||||
- The brackets are balanced if there is no item present in the stack.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Circles of given radius through two points
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Circles of given radius through two points
|
||||
# Circles of given radius through two points
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/circles-of-given-radius-through-two-points/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Closest-pair problem
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Closest-pair problem
|
||||
# Closest-pair problem
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/closest-pair-problem/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Combinations
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Combinations
|
||||
# Combinations
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/combinations/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Comma quibbling
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Comma quibbling
|
||||
# Comma quibbling
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/comma-quibbling/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Compare a list of strings
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Compare a list of strings
|
||||
# Compare a list of strings
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/compare-a-list-of-strings/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Convert seconds to compound duration
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Convert seconds to compound duration
|
||||
# Convert seconds to compound duration
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/convert-seconds-to-compound-duration/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Count occurrences of a substring
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Count occurrences of a substring
|
||||
# Count occurrences of a substring
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/count-occurrences-of-a-substring/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Count the coins
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Count the coins
|
||||
# Count the coins
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/count-the-coins/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Cramer's rule
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Cramer's rule
|
||||
# Cramer's rule
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/cramers-rule/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Date format
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Date format
|
||||
# Date format
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/date-format/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Date manipulation
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Date manipulation
|
||||
# Date manipulation
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/date-manipulation/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Day of the week
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Day of the week
|
||||
# Day of the week
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/day-of-the-week/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Deal cards for FreeCell
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Deal cards for FreeCell
|
||||
# Deal cards for FreeCell
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/deal-cards-for-freecell/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Deepcopy
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Deepcopy
|
||||
# Deepcopy
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/deepcopy/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Define a primitive data type
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Define a primitive data type
|
||||
# Define a primitive data type
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/define-a-primitive-data-type/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Department Numbers
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Department Numbers
|
||||
# Department Numbers
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/department-numbers/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Discordian date
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Discordian date
|
||||
# Discordian date
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/discordian-date/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Element-wise operations
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Element-wise operations
|
||||
# Element-wise operations
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/rosetta-code/element-wise-operations/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user