fix(guide): restructure curriculum guide articles (#36501)
* fix: restructure certifications guide articles * fix: added 3 dashes line before prob expl * fix: added 3 dashes line before hints * fix: added 3 dashes line before solutions
This commit is contained in:
@@ -2,36 +2,35 @@
|
||||
title: Find the Symmetric Difference
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
 Remember to use <a href="https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/how-to-get-help-when-you-are-stuck/" rel="help">**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program and write your own code
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation: ###
|
||||
# Find the Symmetric Difference
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
Symmetric difference (commonly denoted by Δ) of two sets is the set of elements which are in either of the two sets, but not in both.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, `sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4])` should yield `[3, 4, 5]`.
|
||||
|
||||
Following above definition, symmetric difference of three sets *A*, *B*, and *C* can be expressed as `(A Δ B) Δ C`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
* [Symmetric difference - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symmetric_difference)
|
||||
* [Symmetric difference - YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PxffSUQRkG4)
|
||||
* [Array.reduce()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/reduce)
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1 ##
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
The *arguments* object is *Array*-like object that only inherits `Array.length` property. Hence consider converting it to an actual *Array*.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2 ##
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
Deem writing a helper function that returns the symmetric difference of two arrays on each call instead of attempting to difference all sets simultaneously.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 3 ##
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 3
|
||||
Apply helper function against the created arguments array reducing its elements pairwise recursively to form the expected output.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**
|
||||
@@ -44,103 +43,95 @@ In the event of *odd number of sets* the symmetric difference will include ident
|
||||
(A ⋂ B) ⋂ C = {1, 4} &Intersection {3, 4, 5}
|
||||
A ⋂ B = {1, 3, 5}
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert! ##
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Solution Ahead!**
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution: ##
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
var args = [];
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
|
||||
args.push(arguments[i]);
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
var args = [];
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
|
||||
args.push(arguments[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function symDiff(arrayOne, arrayTwo) {
|
||||
var result = [];
|
||||
|
||||
arrayOne.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayTwo.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
function symDiff(arrayOne, arrayTwo) {
|
||||
var result = [];
|
||||
|
||||
arrayOne.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayTwo.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
arrayTwo.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayOne.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
arrayTwo.forEach(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrayOne.indexOf(item) < 0 && result.indexOf(item) < 0) {
|
||||
result.push(item);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply reduce method to args array, using the symDiff function
|
||||
return args.reduce(symDiff);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply reduce method to args array, using the symDiff function
|
||||
return args.reduce(symDiff);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation: ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
* `push()` is used to break down the *arguments* object to an array, *args*.
|
||||
* The `symDiff` function finds the symmetric difference between two sets. It is used as a callback function for the `reduce()` method called on *args*.
|
||||
* `arrayOne.forEach()` pushes the elements to *result* which are present only in *arrayOne* as well as not already a part of *result*.
|
||||
* `arrayTwo.forEach()` pushes the elements to *result* which are present only in *arrayTwo* as well as not already a part of *result*.
|
||||
* The *result*, which is the symmetric difference is returned. This solution works for any number of sets.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
* [Statement for](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/statements/for)
|
||||
* [Array.length](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/length)
|
||||
* [Array.push()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/push)
|
||||
* [Array.forEach()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/forEach)
|
||||
* [Array.indexOf()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/indexOf)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Intermediate Code Solution: ##
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
function sym() {
|
||||
// Convert the argument object into a proper array
|
||||
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert the argument object into a proper array
|
||||
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the symmetric difference of 2 arrays
|
||||
var getDiff = function(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns items in arr1 that don't exist in arr2
|
||||
function filterFunction(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
return arr1.filter(function(item) {
|
||||
return arr2.indexOf(item) === -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run filter function on each array against the other
|
||||
return filterFunction(arr1, arr2)
|
||||
.concat(filterFunction(arr2, arr1));
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Reduce all arguments getting the difference of them
|
||||
var summary = args.reduce(getDiff, []);
|
||||
|
||||
// Run filter function to get the unique values
|
||||
var unique = summary.filter(function(elem, index, self) {
|
||||
return index === self.indexOf(elem);
|
||||
});
|
||||
return unique;
|
||||
// Return the symmetric difference of 2 arrays
|
||||
var getDiff = function(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// Returns items in arr1 that don't exist in arr2
|
||||
function filterFunction(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
return arr1.filter(function(item) {
|
||||
return arr2.indexOf(item) === -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
// Run filter function on each array against the other
|
||||
return filterFunction(arr1, arr2).concat(filterFunction(arr2, arr1));
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Reduce all arguments getting the difference of them
|
||||
var summary = args.reduce(getDiff, []);
|
||||
|
||||
// Run filter function to get the unique values
|
||||
var unique = summary.filter(function(elem, index, self) {
|
||||
return index === self.indexOf(elem);
|
||||
});
|
||||
return unique;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation: ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
* The `slice()` method is used to break down the *arguments* object to an array, *args*.
|
||||
* The `getDiff` function finds the symmetric difference between two sets, *arr1* and *arr2*. It is used as a callback function for the `reduce()` method called on *args*.
|
||||
* The first `filterFunction()` returns elements in *arr1* that don't exist in *arr2*.
|
||||
@@ -148,41 +139,36 @@ In the event of *odd number of sets* the symmetric difference will include ident
|
||||
* *summary* consists of the reduced arguments.
|
||||
* `filter()` is used on *summary* to keep only the unique values and *unique* is returned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
* [Array.slice()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/slice)
|
||||
* [Array.filter()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/filter)
|
||||
* [Array.concat()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/concat)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Advanced Code Solution: ##
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 3 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const diff = (arr1, arr2) => (
|
||||
[
|
||||
...arr1.filter(e => !arr2.includes(e)),
|
||||
...arr2.filter(e => !arr1.includes(e)),
|
||||
]
|
||||
);
|
||||
const diff = (arr1, arr2) => [
|
||||
...arr1.filter(e => !arr2.includes(e)),
|
||||
...arr2.filter(e => !arr1.includes(e))
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
const sym = (...args) => [...new Set(args.reduce(diff))];
|
||||
const sym = (...args) => [...new Set(args.reduce(diff))];
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
sym([1, 2, 3], [5, 2, 1, 4]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation: ###
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* The main function *sym()* reduces given arrays utilising helper function *diff()* to a single array. Also, it temporary converts the result to *Set* to remove duplicates.
|
||||
|
||||
* The function *diff()* returns the symmetric difference of two arrays by picking out elements in parameterised arrays; *arr1* and *arr2*.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links ####
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
* [Set](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Set)
|
||||
* [Array.filter()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/filter)
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS: ##
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,48 +1,58 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Bubble Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Bubble Sort
|
||||
# Implement Bubble Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Bubble Sort is a sorting algorithm which sorts or *bubbles* the largest number as last element at the end of each pass.
|
||||
- We compare each element to the one ahead of it, if the element before is smaller, we swap their places.
|
||||
- Bubble Sort's time complexity is **O(n<sup>2</sup>)**.
|
||||
- It's a **stable** algorithm.
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Solution 1: Basic
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr){
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr) {
|
||||
let tmp = arr[a];
|
||||
arr[a] = arr[b];
|
||||
arr[b] = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function bubbleSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++){ // -i because the largest element will be bubbled at the end so we don't have to compare.
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j+1]){
|
||||
swap(j, j+1, array);
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
|
||||
// -i because the largest element will be bubbled at the end so we don't have to compare.
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
|
||||
swap(j, j + 1, array);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Solution 2: Advanced
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function bubbleSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++){
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j+1]) [array[j], array[j+1]] = [array[j+1], array[j]]; // Using ES6 array destructuring to swap
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
|
||||
for (let j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
|
||||
if (array[j] > array[j + 1])
|
||||
[array[j], array[j + 1]] = [array[j + 1], array[j]]; // Using ES6 array destructuring to swap
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [GeeksForGeeks](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bubble-sort/)
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bubble_sort)
|
||||
- Video by [HackerRank](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Gv8vg0kcHc)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
# Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Insertion Sort assumes that array is divided in two parts:
|
||||
1. Sorted (Initially the first element)
|
||||
2. Unsorted
|
||||
@@ -13,21 +14,27 @@ title: Implement Insertion Sort
|
||||
- Time comlexity of Insertion sort is of **O(n<sup>2</sup>)**.
|
||||
- It's a **stable** algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function insertionSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++){
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
|
||||
let curr = array[i];
|
||||
for (var j = i-1; j >= 0 && array[j] > curr; j--){
|
||||
array[j+1] = array[j];
|
||||
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && array[j] > curr; j--) {
|
||||
array[j + 1] = array[j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
array[j+1] = curr;
|
||||
array[j + 1] = curr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insertion_sort)
|
||||
- [Khan Academy](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lCzQvQr8Utw)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
# Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Merge Sort is a classic divide and conquer problem.
|
||||
- The following steps are involved:
|
||||
- Divide: We break the array from the middle using recusion until we're left with 1 element.
|
||||
@@ -14,19 +15,26 @@ title: Implement Merge Sort
|
||||
- It's a **stable** algorithm.
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//Merger function, which merges 2 sorted array into 1 sorted array
|
||||
function merger(arr1, arr2){
|
||||
let i = 0, j = 0, mergedArr = [];
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length){
|
||||
function merger(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
let i = 0,
|
||||
j = 0,
|
||||
mergedArr = [];
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length) {
|
||||
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) mergedArr.push(arr2[j++]);
|
||||
else mergedArr.push(arr1[i++]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length){
|
||||
while (i < arr1.length) {
|
||||
mergedArr.push(arr1[i++]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
while (j < arr2.length){
|
||||
while (j < arr2.length) {
|
||||
mergedArr.push(arr2[j++]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return mergedArr;
|
||||
@@ -34,17 +42,18 @@ function merger(arr1, arr2){
|
||||
function mergeSort(array) {
|
||||
//Array of length 1 is sorted so we return the same array back
|
||||
if (array.length == 1) return array;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Break down the array to half from middle into left and right
|
||||
let middle = Math.floor(array.length/2);
|
||||
let middle = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
|
||||
let left = mergeSort(array.slice(0, middle));
|
||||
let right = mergeSort(array.slice(middle));
|
||||
|
||||
let right = mergeSort(array.slice(middle));
|
||||
|
||||
//Return the merged sorted array
|
||||
return merger(left, right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort)
|
||||
- Video by [Hackerrank](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KF2j-9iSf4Q)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
# Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Quick sort is an efficient sorting algorithm. It's an in-place algorithm so it doesn't take any auxilary space.
|
||||
- First pick a random pivot point around which move all the smaller elements to it to the left of it and the bigger elements to the right of it.
|
||||
- After getting the pivotIndex which is essentially the fixed position of that element, we find other pivotIndex by recusirvely calling this function.
|
||||
@@ -12,40 +13,44 @@ title: Implement Quick Sort
|
||||
- It's an **unstable** algorithm.
|
||||
- 
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//Swapping array elements via ES6 array destructuring
|
||||
function swap(arr, x, y){
|
||||
//Swapping array elements via ES6 array destructuring
|
||||
function swap(arr, x, y) {
|
||||
[arr[x], arr[y]] = [arr[y], arr[x]];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//Pivot function returns the fixed pivot point
|
||||
function pivot(arr, left = 0, right = arr.length-1){
|
||||
function pivot(arr, left = 0, right = arr.length - 1) {
|
||||
let shift = left;
|
||||
for (let i = left+1; i <= right; i++){
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = left + 1; i <= right; i++) {
|
||||
//Move all the small elements on the left side
|
||||
if (arr[i] < arr[left]) swap(arr, i, ++shift);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Finally swapping the last element with the left
|
||||
swap(arr, left, shift);
|
||||
return shift;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function quickSort(array, left = 0, right = array.length-1) {
|
||||
if (left < right){
|
||||
function quickSort(array, left = 0, right = array.length - 1) {
|
||||
if (left < right) {
|
||||
let pivotIndex = pivot(array, left, right);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//Recusrively calling the function to the left of the pivot and to the right of the pivot
|
||||
quickSort(array, left, pivotIndex-1);
|
||||
quickSort(array, pivotIndex+1, right);
|
||||
quickSort(array, left, pivotIndex - 1);
|
||||
quickSort(array, pivotIndex + 1, right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return array;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Reference:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort)
|
||||
- [Khan Academy](https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-science/algorithms/quick-sort/a/overview-of-quicksort)
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,10 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
# Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
|
||||
### Method:
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
- Selection Sort is one of the easier sorting algorithm to understand and implement.
|
||||
- This algorithm splits the array in two parts:
|
||||
1. Sorted
|
||||
@@ -12,17 +13,21 @@ title: Implement Selection Sort
|
||||
- Each pass, initially we assume the first element to be the smallest then we loop through the whole array and *select* the smallest element. At the end of the pass we swap smallest element to the sorted array.
|
||||
- It has **O(n<sup>2</sup>)** time complexity.
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr){
|
||||
function swap(a, b, arr) {
|
||||
let tmp = arr[a];
|
||||
arr[a] = arr[b];
|
||||
arr[b] = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
function selectionSort(array) {
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++){
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
|
||||
let min = i;
|
||||
for (let j = i+1; j < array.length; j++){
|
||||
for (let j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
|
||||
if (array[min] > array[j]) min = j;
|
||||
}
|
||||
swap(i, min, array);
|
||||
@@ -31,6 +36,8 @@ function selectionSort(array) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### References:
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- Read about Selection Sort at [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selection_sort)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Algorithms
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Algorithms
|
||||
# Algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/mathematics/quadratic-equations/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Inventory Update
|
||||
---
|
||||
 Remember to use <a>**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program  and write your own code 
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation:
|
||||
# Inventory Update
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
In this problem, you've to compare and update the inventory stored in a 2D array against a second 2D array of a fresh delivery. Update the current existing inventory item quantities (in `arr1`). If an item cannot be found, add the new item and quantity into the inventory array. The returned inventory array should be in alphabetical order by item.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,100 +15,92 @@ The current as well as new inventory will be in this format: `[[2, "item-0"], [3
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
You need to work through each item of the new inventory to see if it exists in the current inventory or not. Remember that the product name is stored as the second element of each sub-array: `array[0][1] = "item-name"`.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
|
||||
If the item exists, you need to add the quantity from the new inventory. If the item doesn't exist, you need to add the entire item.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 3
|
||||
### Hint 3
|
||||
|
||||
Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Solution ahead!**
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution:
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// Variable for location of product
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
|
||||
// Variable for location of product
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
|
||||
// A helper method to return the index of a specified product (undefined if not found)
|
||||
var getProductIndex = function (name) {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (this[i][1] === name) {
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return undefined;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// For each item of the new Inventory
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Invoke our helper function using arr1 as this
|
||||
index = getProductIndex.call(arr1, arr2[i][1]);
|
||||
|
||||
// If the item doesn't exist
|
||||
if (index === undefined) {
|
||||
// Push the entire item
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[i]);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Add the new quantity of the current item
|
||||
arr1[index][0] += arr2[i][0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sort alphabetically, by the product name of each item
|
||||
arr1.sort(function (a, b) {
|
||||
if (a[1] > b[1]) {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (a[1] < b[1]) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
// A helper method to return the index of a specified product (undefined if not found)
|
||||
var getProductIndex = function(name) {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
|
||||
if (this[i][1] === name) {
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return undefined;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// For each item of the new Inventory
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
// Invoke our helper function using arr1 as this
|
||||
index = getProductIndex.call(arr1, arr2[i][1]);
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// If the item doesn't exist
|
||||
if (index === undefined) {
|
||||
// Push the entire item
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[i]);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Add the new quantity of the current item
|
||||
arr1[index][0] += arr2[i][0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
// Sort alphabetically, by the product name of each item
|
||||
arr1.sort(function(a, b) {
|
||||
if (a[1] > b[1]) {
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (a[1] < b[1]) {
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* The variable **index** stores the location (index) of a product.
|
||||
* The helper function `getProductIndex()` returns the index of a specified product. It iterates through each element of the array that it is called on until it can find the name parameter. If the product is not found in the inventory, `undefined` is returned.
|
||||
@@ -124,74 +118,75 @@ Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-push/14298' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.push()</a>
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-sort/14306' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.sort()</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Intermediate Code Solution:
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 2 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
var arrCurInvName = []; // Names of arr1's items
|
||||
var arrNeInvName = []; // Names of arr2's items
|
||||
var index;
|
||||
var arrCurInvName = []; // Names of arr1's items
|
||||
var arrNeInvName = []; // Names of arr2's items
|
||||
|
||||
// Same as using two for loops, this takes care of increasing the number of stock quantity.
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item1) {
|
||||
return arr2.map(function(item2) {
|
||||
if (item1[1] === item2[1]) {
|
||||
item1[0] = item1[0] + item2[0]; //Increase number of stock
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
// Same as using two for loops, this takes care of increasing the number of stock quantity.
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item1) {
|
||||
return arr2.map(function(item2) {
|
||||
if (item1[1] === item2[1]) {
|
||||
item1[0] = item1[0] + item2[0]; //Increase number of stock
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Get item's name for new Inventory
|
||||
arr2.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrNeInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
// Get item's name for new Inventory
|
||||
arr2.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrNeInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Get item's name for Current Inventory
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrCurInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
// Get item's name for Current Inventory
|
||||
arr1.map(function(item) {
|
||||
arrCurInvName.push(item[1]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Add new inventory items to current inventory.
|
||||
arrNeInvName.map(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrCurInvName.indexOf(item) === -1) {
|
||||
index = arrNeInvName.indexOf(item);
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[index]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Sort the array alphabetically using the second element of the array as base.
|
||||
arr1.sort(function(currItem, nextItem) {
|
||||
|
||||
//Ternary function to avoid using if else
|
||||
return currItem[1] > nextItem[1] ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
// Add new inventory items to current inventory.
|
||||
arrNeInvName.map(function(item) {
|
||||
if (arrCurInvName.indexOf(item) === -1) {
|
||||
index = arrNeInvName.indexOf(item);
|
||||
arr1.push(arr2[index]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// Sort the array alphabetically using the second element of the array as base.
|
||||
arr1.sort(function(currItem, nextItem) {
|
||||
//Ternary function to avoid using if else
|
||||
return currItem[1] > nextItem[1] ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* The variable **index** stores the location (index) of a product.
|
||||
* **arrCurInvName** has the names of **arr1**'s items.
|
||||
@@ -207,66 +202,64 @@ Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-indexof/14291' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.indexOf()</a>
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-ternary-operator/15973' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Ternary Operator</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Advanced Code Solution:
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 3 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
function updateInventory(arr1, arr2) {
|
||||
// All inventory must be accounted for or you're fired!
|
||||
|
||||
// convert current inventory (arr1) to an one-dimensional array
|
||||
const inventory = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arr1);
|
||||
// convert current inventory (arr1) to an one-dimensional array
|
||||
const inventory = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arr1);
|
||||
|
||||
// loop through new delivery (arr2)
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
// loop through new delivery (arr2)
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
|
||||
// extract item properties for easy reference
|
||||
const item = arr2[i][1];
|
||||
const quantity = arr2[i][0];
|
||||
|
||||
// extract item properties for easy reference
|
||||
const item = arr2[i][1];
|
||||
const quantity = arr2[i][0];
|
||||
|
||||
// check if item already exists in inventory
|
||||
const position = inventory.indexOf(item);
|
||||
|
||||
// exsisting item: update quantity
|
||||
if (position !== -1) {
|
||||
const row = Math.floor(position / 2);
|
||||
arr1[row][0] += quantity;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// alien item: add to inventory
|
||||
arr1.push([quantity, item]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// sort inventory in alphabetical order
|
||||
arr1.sort((previous, next) => (previous[1] > [next[1]]) ? 1 : -1);
|
||||
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
// check if item already exists in inventory
|
||||
const position = inventory.indexOf(item);
|
||||
|
||||
// exsisting item: update quantity
|
||||
if (position !== -1) {
|
||||
const row = Math.floor(position / 2);
|
||||
arr1[row][0] += quantity;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// alien item: add to inventory
|
||||
arr1.push([quantity, item]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
// sort inventory in alphabetical order
|
||||
arr1.sort((previous, next) => (previous[1] > [next[1]] ? 1 : -1));
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
return arr1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
// test here
|
||||
// Example inventory lists
|
||||
var curInv = [
|
||||
[21, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[2, "Dirty Sock"],
|
||||
[1, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[5, "Microphone"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
var newInv = [
|
||||
[2, "Hair Pin"],
|
||||
[3, "Half-Eaten Apple"],
|
||||
[67, "Bowling Ball"],
|
||||
[7, "Toothpaste"]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
updateInventory(curInv, newInv);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* Convert current inventory array **arr1** to an one-dimensional array in order that `indexOf()` method could be used to check existance of new delivery items in current inventory.
|
||||
* Check if item already exists in current inventory using `indexOf()`.
|
||||
@@ -279,9 +272,5 @@ Return the completed inventory in alphabetical order.
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function/apply'>JS Function.prototype.apply()</a>
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/continue' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS continue</a>
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/sort' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array.prototype.sort()</a>
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +1,19 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: No Repeats Please
|
||||
---
|
||||
 Remember to use <a>**`Read-Search-Ask`**</a> if you get stuck. Try to pair program  and write your own code 
|
||||
|
||||
###  Problem Explanation:
|
||||
# No Repeats Please
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
This task requires us to return the number of total permutations of the provided string that don't have repeated consecutive letters. It is to be assumed that all characters in the provided string are each unique. For example, `aab` should return 2 because it has 6 total permutations (`aab`, `aab`, `aba`, `aba`, `baa`, `baa`), but only 2 of them (`aba` and `aba`) don't have the same letter (in this case `a`) repeating.
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve that, we'll have to look at each possible permutation of a string. There are several ways to do that. A common interview question is building a function that collects all permutations of a string. There are several tutorials available on the internet on how to do that.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Potential Methods Used As Solution
|
||||
**Potential Methods Used As Solution**
|
||||
|
||||
##### Recursive Method
|
||||
**Recursive Method**
|
||||
|
||||
This task can be daunting even after watching a tutorial. To write a recursive solution, you will want to send each new use of the function three inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,6 +23,7 @@ This task can be daunting even after watching a tutorial. To write a recursive s
|
||||
|
||||
The pseudo code will look something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
var str = ???;
|
||||
permAlone(current position in original string, characters used already in original string, created string) {
|
||||
if (current string is finished) {
|
||||
@@ -37,13 +40,15 @@ The pseudo code will look something like this:
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
permAlone(0, nothing used yet, empty new string (or array the same size as str));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to think about this problem is to start from an empty space. Introduce the first letter to the space. This space will now contain the first sub-permutation. Here's a diagram illustrating the idea:
|
||||
|
||||
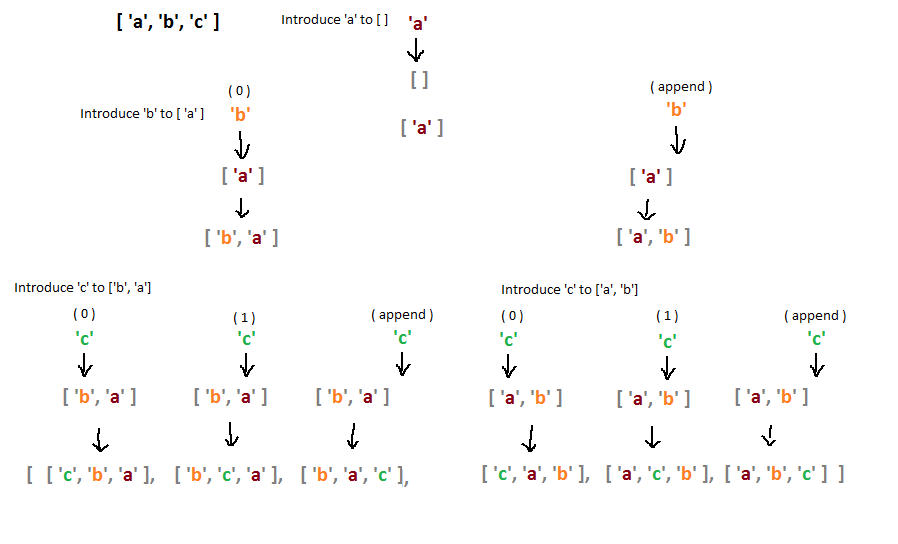
|
||||
|
||||
##### Non-Recursive Method
|
||||
**Non-Recursive Method**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
// An approach to introduce a new character to a permutation
|
||||
var ch = '?';
|
||||
var source = ['?', '?', '?']; // Current sub-permutation
|
||||
@@ -54,6 +59,7 @@ Another way to think about this problem is to start from an empty space. Introdu
|
||||
temp.splice(i, 0, ch); // Insert the new character
|
||||
dest.push(temp); // Store the new sub-permutation
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finding each permutation could then be done non-recursively by including the above in a function taking a source array and returning a destination array. For each letter of the input string, pass that character, as well as the array returned from the previous call of the function.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,81 +74,76 @@ A way to visualize this is by considering a tree that starts with the first char
|
||||
* <a>JS Regex Resources</a>
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/String' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS String object</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 1
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
* The easiest way is to use Heap's algorithm to recursively get a list of all the permutations.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 2
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
|
||||
* Once you have the list then just create a regular expression to catch the repeating characters.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
##  Hint: 3
|
||||
### Hint 3
|
||||
|
||||
* You will want to have the permutations as an array of joined strings instead of separated characters.
|
||||
|
||||
> _try to solve the problem now_
|
||||
|
||||
## Spoiler Alert!
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
```js
|
||||
function permAlone(str) {
|
||||
// Create a regex to match repeated consecutive characters.
|
||||
var regex = /(.)\1+/;
|
||||
|
||||
**Solution ahead!**
|
||||
// Split the string into an array of characters.
|
||||
var arr = str.split("");
|
||||
var permutations = [];
|
||||
var tmp;
|
||||
|
||||
##  Basic Code Solution:
|
||||
// Return 0 if str contains same character.
|
||||
if (str.match(regex) !== null && str.match(regex)[0] === str) return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
function permAlone(str) {
|
||||
// Function to swap variables' content.
|
||||
function swap(index1, index2) {
|
||||
tmp = arr[index1];
|
||||
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
|
||||
arr[index2] = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Create a regex to match repeated consecutive characters.
|
||||
var regex = /(.)\1+/;
|
||||
|
||||
// Split the string into an array of characters.
|
||||
var arr = str.split('');
|
||||
var permutations = [];
|
||||
var tmp;
|
||||
|
||||
// Return 0 if str contains same character.
|
||||
if (str.match(regex) !== null && str.match(regex)[0] === str) return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// Function to swap variables' content.
|
||||
function swap(index1, index2) {
|
||||
tmp = arr[index1];
|
||||
arr[index1] = arr[index2];
|
||||
arr[index2] = tmp;
|
||||
// Generate arrays of permutations using the algorithm.
|
||||
function generate(int) {
|
||||
if (int === 1) {
|
||||
// Make sure to join the characters as we create the permutation arrays
|
||||
permutations.push(arr.join(""));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i != int; ++i) {
|
||||
generate(int - 1);
|
||||
swap(int % 2 ? 0 : i, int - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate arrays of permutations using the algorithm.
|
||||
function generate(int) {
|
||||
if (int === 1) {
|
||||
// Make sure to join the characters as we create the permutation arrays
|
||||
permutations.push(arr.join(''));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i != int; ++i) {
|
||||
generate(int - 1);
|
||||
swap(int % 2 ? 0 : i, int - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
generate(arr.length);
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter the array of repeated permutations.
|
||||
var filtered = permutations.filter(function(string) {
|
||||
return !string.match(regex);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// Return how many have no repetitions.
|
||||
return filtered.length;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Test here.
|
||||
permAlone('aab');
|
||||
generate(arr.length);
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter the array of repeated permutations.
|
||||
var filtered = permutations.filter(function(string) {
|
||||
return !string.match(regex);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Explanation:
|
||||
// Return how many have no repetitions.
|
||||
return filtered.length;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Test here.
|
||||
permAlone("aab");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
* **regex** contains the regular expression to match repeated consecutive characters.
|
||||
* The string **str** is split into an array of characters, **arr**.
|
||||
@@ -162,8 +163,5 @@ A way to visualize this is by considering a tree that starts with the first char
|
||||
* <a href='https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/length' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>array.length</a>
|
||||
* <a href='http://forum.freecodecamp.com/t/javascript-array-prototype-filter/14289' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>JS Array Prototype Filter</a>
|
||||
|
||||
##  NOTES FOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
|
||||
|
||||
*  **DO NOT** add solutions that are similar to any existing solutions. If you think it is **_similar but better_**, then try to merge (or replace) the existing similar solution.
|
||||
* Add an explanation of your solution.
|
||||
* Categorize the solution in one of the following categories — **Basic**, **Intermediate** and **Advanced**. 
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Pairwise
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Pairwise
|
||||
# Pairwise
|
||||
|
||||
This is a stub. <a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/certifications/coding-interview-prep/algorithms/pairwise/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Help our community expand it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user