diff --git a/guide/english/logic/algebra-of-logic/index.md b/guide/english/logic/algebra-of-logic/index.md
index c372e75df6..9d535b8581 100644
--- a/guide/english/logic/algebra-of-logic/index.md
+++ b/guide/english/logic/algebra-of-logic/index.md
@@ -5,15 +5,21 @@ title: Algebra of Logic
_Algebra of Logic_ or _Boolean algebra_ is a branch of mathematics. It deals with variables and their truth value. The variables have two possible states – `true` or `false`.
-It was first introduced by George Boole in his book The Mathematical Analysis of Logic (1847).
+It was first introduced by George Boole in his book The Mathematical Analysis of Logic (1847), and was subsequently developed by C.S. Peirce, P.S. Poretskii, B. Russell, D. Hilbert, and others. The development of the algebra of logic was an attempt to solve traditional logical problems by algebraic methods.
Boolean algebra is fundamental to the development of digital electronics. It is responsible for making possible all modern computing.
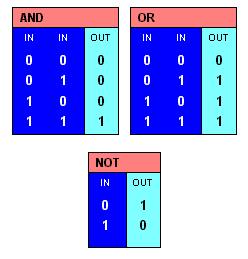
-The three basic operations in Boolean Algebra are `AND`, `OR`, and `NOT`. Consider two boolean variables `x` and `y`:
+The three basic operations in Boolean Algebra are `AND`, `OR`, and `NOT`.
+Most often
+ `AND` is also represented by `.`(dot)
+ `OR` is also represented by `+`(plus)
+ `NOT` is also represented by `~`(tilde)
+Consider two boolean variables `x` and `y`:
- `x AND y` is true if and only if both `x` and `y` are true
- `x OR y` is true if either of `x` or `y` are true
- `NOT x` is true if and only if `x` is false and vice versa
+ `NOT` of boolean statements can be refactored to apply directly to each variable. Consider the following :
- `NOT (x AND y) = NOT x OR NOT y`
`NOT` of boolean statements can be refactored to apply directly to each variable. Consider the following :
- `NOT (x AND y) = NOT x OR NOT y`
 `NOT` of boolean statements can be refactored to apply directly to each variable. Consider the following :
- `NOT (x AND y) = NOT x OR NOT y`
`NOT` of boolean statements can be refactored to apply directly to each variable. Consider the following :
- `NOT (x AND y) = NOT x OR NOT y`