diff --git a/guide/english/mathematics/roman-numerals/index.md b/guide/english/mathematics/roman-numerals/index.md
index 6611907ae5..860f58897c 100644
--- a/guide/english/mathematics/roman-numerals/index.md
+++ b/guide/english/mathematics/roman-numerals/index.md
@@ -2,11 +2,46 @@
title: Roman Numerals
---
## Roman Numerals
+
+I = 1
+V = 5
+X = 10
+L = 50
+C = 100
+D = 500
+M = 1000
-The [numeric system](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Numeric_system) represented by **Roman numerals** originated in [ancient Rome](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient_Rome) and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the [Late Middle Ages](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Late_Middle_Ages). Numbers in this system are represented by combinations of letters from the [Latin alphabet](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latin_alphabet). Roman numerals, as used today, are based on seven symbols.
+How to Remember:
+"M e D i C a L X a V I e r".
+It has the roman numerals in descending order from 1000 to 1.
-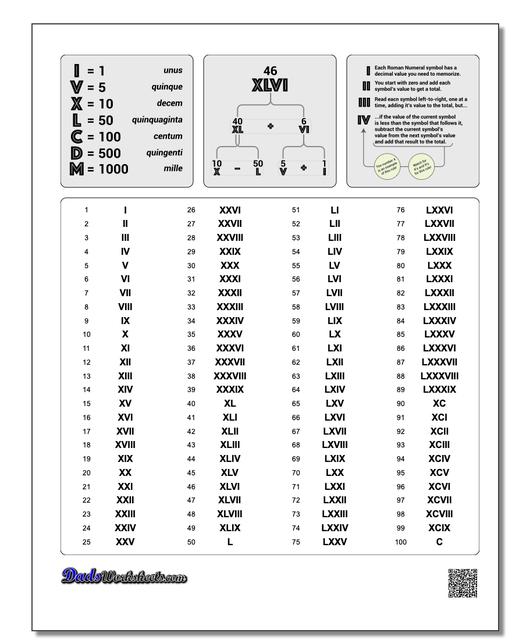 +When a symbol appears after a larger (or equal) symbol, it is added:
+
+When a symbol appears after a larger (or equal) symbol, it is added:
+
+Example:
+II = 2, (1 + 1 = 2)
+VI = 6, (5 + 1 = 6)
+XI = 11, (10 + 1 = 11)
+
+
+But if a symbol appears before a larger symbol, it is subtracted:
+
+Example:
+IV = 4, (5 - 1 = 4)
+IX = 9, (10 - 1 = 9)
+
+
+Don't use the same symbol more than three times in a row:
+
+Example:
+III = 3
+VIII = 8
+XXX = 30
+LXXX = 80
+CCC = 300
+DCCC = 800
+MMM = 3000
+
#### More Information:
-
+
[Wikipedia: Roman numerals](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roman_numerals)
 +When a symbol appears after a larger (or equal) symbol, it is added:
+
+When a symbol appears after a larger (or equal) symbol, it is added:
+