Create article for autoencoder networks (#27107)
Started article in machine learning directory for autoencoder neural networks providing a brief overview of the motivation and ideas behind them
This commit is contained in:
committed by
 Randell Dawson
Randell Dawson
parent
4cd38be757
commit
b1a9ae7b65
23
guide/english/machine-learning/autoencoders/index.md
Normal file
23
guide/english/machine-learning/autoencoders/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Autoencoder Networks
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Autoencoder Networks
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
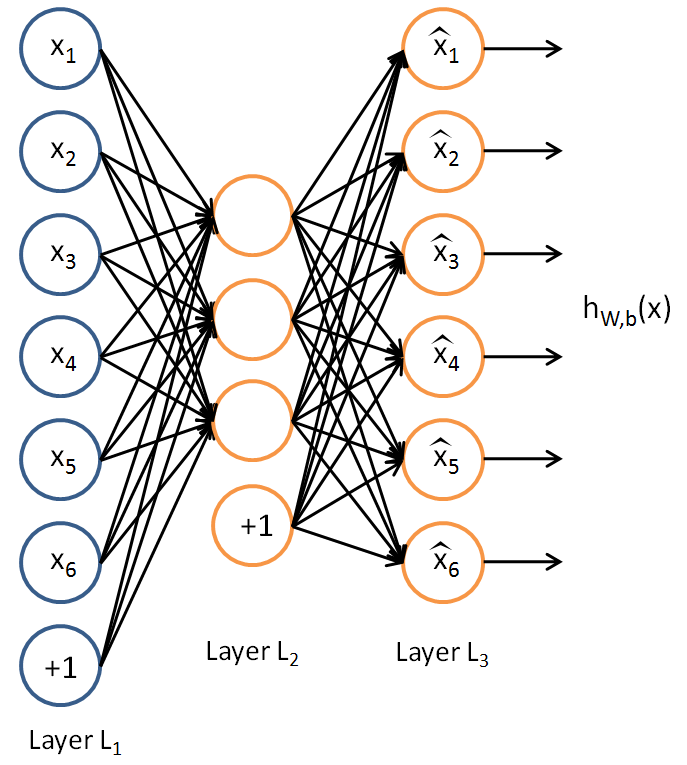
The Autoencoder is a type of neural network used to reduce the dimensionality of a set of data. The idea is to use a neural network whose structure is hourglass-shaped (many units on the input and output layers, but few units in the center layers) to encourage a network to represent the data in the smallest amount of information possible. The name, autoencoder, refers to the idea that the network is effectively learning efficient encodings for the type of data it is being trained upon.
|
||||
|
||||
Typically, when using neural networks as approximators for a set of data, one would have a training dataset which has some inputs that can be collected as data and some outputs which the aforementioned inputs are fed through the network to predict. When using autoencoders, the idea is to train a network to use the inputs to predict themselves. In other words, a perfect autoencoder would simply be an identity function; its outputs would be identical to its inputs in all cases.
|
||||
|
||||
If one were to use an autoencoder network which had the same number of hidden units throughout all of its layers, it would not be a very useful tool, as it would simply predict its inputs without reducing the spatial usage. However, the key idea of autoencoder networks is to reduce the dimensionality of the network gradually through the network structure to a minimum in the center. At this minimum-dimension central layer, if the network has been trained to accurately predict its own inputs, the input data itself is actually being fully represented in terms of far fewer units than there are inputs to the network. This effectively means that the data is "compressed" or encoded at this point in the network.
|
||||
|
||||
In real-world applications, by giving a distant party a copy of the trained network, one could transmit this encoded low-dimensional data from the network across the internet for a far smaller cost than transferring the original dataset. The party on the receiving end of the transmission would simply complete the data's forward-pass through the network to obtain the data which was encoded.
|
||||
|
||||
### Real-world applications
|
||||
* Compression
|
||||
* Dimensional reduction
|
||||
* Pretraining
|
||||
|
||||
### More Information:
|
||||
- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoencoder)
|
||||
- [Stanford University - Autoencoders](http://ufldl.stanford.edu/tutorial/unsupervised/Autoencoders/)
|
||||
- [Deng et al. - Encoding Speech Spectrograms using Autoencoders](https://www.isca-speech.org/archive/interspeech_2010/i10_1692.html)
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user