Minor grammar and structure changes (#23370)
This commit is contained in:
committed by
 Christopher McCormack
Christopher McCormack
parent
2e64c17b34
commit
ca3c57bde5
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ title: Neural Networks
|
|||||||
## Neural Networks
|
## Neural Networks
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
An artificial neural network is a computing system. They are like biological neural networks that constitute animal brains.
|
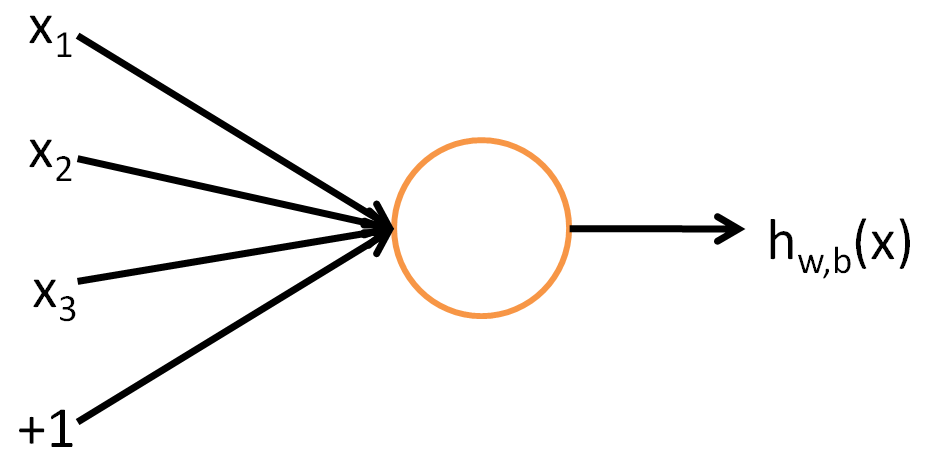
An artificial neural network is a computing system based on biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. The most basic element of a neural network is a neuron. Its input is a vector, say `x`, and its output is a real valued variable, say `y`. The neuron acts as a mapping between the vector `x` and a real number `y`.
|
||||||
To train a neural network, we need an input vector and a corresponding output vector.
|
To train a neural network, we need an input vector and a corresponding output vector.
|
||||||
The training works by minimizing an error term. This error can be the squared difference between the predicted output and the original output.
|
The training works by minimizing an error term. This error can be the squared difference between the predicted output and the original output.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -13,8 +13,6 @@ The basic principle which underlies the remarkable success of neural networks is
|
|||||||
Neural networks initially became popular in the 1980s, but limitations in computational power prohibited their widespread acceptance until the past decade.
|
Neural networks initially became popular in the 1980s, but limitations in computational power prohibited their widespread acceptance until the past decade.
|
||||||
Innovations in CPU size and power allow for neural network implementation at scale, though other machine learning paradigms still outrank neural networks in terms of efficiency.
|
Innovations in CPU size and power allow for neural network implementation at scale, though other machine learning paradigms still outrank neural networks in terms of efficiency.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The most basic element of a neural network is a neuron. It's input is a vector, say `x`, and its output is a real valued variable, say `y`. Thus, we can conclude that the neuron acts as a mapping between the vector `x` and a real number `y`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Neural networks perform regression iteratively across multiple layers, resulting in a more nuanced prediction model.
|
Neural networks perform regression iteratively across multiple layers, resulting in a more nuanced prediction model.
|
||||||
A single node in a neural network computes the exact same function as [logistic regression](../logistic-regression/index.md).
|
A single node in a neural network computes the exact same function as [logistic regression](../logistic-regression/index.md).
|
||||||
All these layers, aside from the input and output, are hidden, that is, the specific traits represented by these layers are not chosen or modified by the programmer.
|
All these layers, aside from the input and output, are hidden, that is, the specific traits represented by these layers are not chosen or modified by the programmer.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user