---
layout: pattern
title: Metadata Mapping
folder: metadata-mapping
permalink: /patterns/metadata-mapping/
categories: Architectural
language: en
tags:
- Data access
---
## Intent
Holds details of object-relational mapping in the metadata.
## Explanation
Real world example
> Hibernate ORM Tool uses Metadata Mapping Pattern to specify the mapping between classes and tables either using XML or annotations in code.
In plain words
> Metadata Mapping specifies the mapping between classes and tables so that we could treat a table of any database like a Java class.
Wikipedia says
> Create a "virtual [object database](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Object_database)" that can be used from within the programming language.
**Programmatic Example**
We give an example about visiting the information of `USER` table in `h2` database. Firstly, we create `USER` table with `h2`:
```java
@Slf4j
public class DatabaseUtil {
private static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:h2:mem:metamapping";
private static final String CREATE_SCHEMA_SQL = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;"
+ "CREATE TABLE `user` (\n"
+ " `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,\n"
+ " `username` varchar(255) NOT NULL,\n"
+ " `password` varchar(255) NOT NULL,\n"
+ " PRIMARY KEY (`id`)\n"
+ ");";
/**
* Create database.
*/
static {
LOGGER.info("create h2 database");
var source = new JdbcDataSource();
source.setURL(DB_URL);
try (var statement = source.getConnection().createStatement()) {
statement.execute(CREATE_SCHEMA_SQL);
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOGGER.error("unable to create h2 data source", e);
}
}
}
```
Correspondingly, here's the basic `User` entity.
```java
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
/**
* Get a user.
* @param username user name
* @param password user password
*/
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
}
```
Then we write a `xml` file to show the mapping between the table and the object:
```xml
```
We use `Hibernate` to resolve the mapping and connect to our database, here's its configuration:
```xml
jdbc:h2:mem:metamapping
org.h2.Driver
1
org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
false
create-drop
```
Then we can get access to the table just like an object with `Hibernate`, here's some CRUDs:
```java
@Slf4j
public class UserService {
private static final SessionFactory factory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
/**
* List all users.
* @return list of users
*/
public List listUser() {
LOGGER.info("list all users.");
List users = new ArrayList<>();
try (var session = factory.openSession()) {
var tx = session.beginTransaction();
List userIter = session.createQuery("FROM User").list();
for (var iterator = userIter.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
users.add(iterator.next());
}
tx.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
LOGGER.debug("fail to get users", e);
}
return users;
}
// other CRUDs ->
...
public void close() {
HibernateUtil.shutdown();
}
}
```
## Class diagram
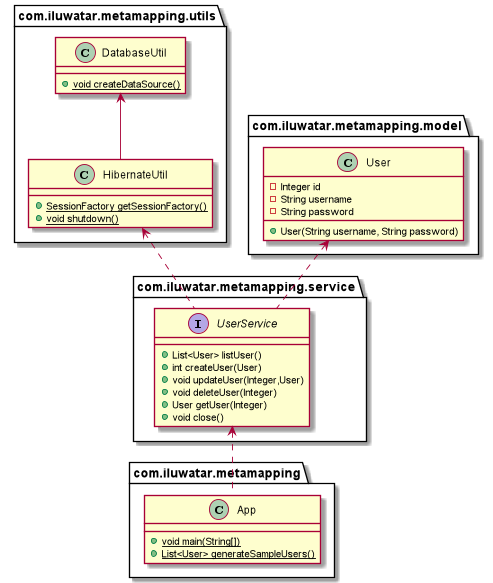
## Applicability
Use the Metadata Mapping when:
- you want reduce the amount of work needed to handle database mapping.
## Known uses
[Hibernate](https://hibernate.org/), [EclipseLink](https://www.eclipse.org/eclipselink/), [MyBatis](https://blog.mybatis.org/)......
## Credits
- [J2EE Design Patterns](https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/0596004273/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=9325&creativeASIN=0596004273&linkCode=as2&tag=javadesignpat-20&linkId=48d37c67fb3d845b802fa9b619ad8f31)