* Made minor changes in some patterns such as removed throws clause where not needed, changed incorrect order of arguments in assertEquals * Minor refactorings and code style changes. 1) Removed several use of raw types 2) Removed unnecessary throws clauses 3) Used lambda expressions wherever applicable 4) Used apt assertion methods for readability 5) Use of try with resources wherever applicable 6) Corrected incorrect order of assertXXX arguments * Removed unused import from Promise * Addressed review comments * Addressed checkstyle issue
layout, title, folder, permalink, categories, tags
| layout | title | folder | permalink | categories | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pattern | Null Object | null-object | /patterns/null-object/ | Behavioral |
|
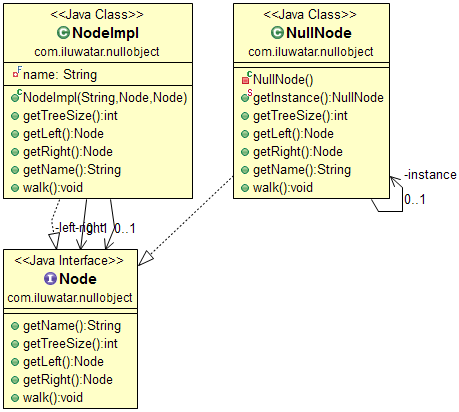
Intent
In most object-oriented languages, such as Java or C#, references may be null. These references need to be checked to ensure they are not null before invoking any methods, because methods typically cannot be invoked on null references. Instead of using a null reference to convey absence of an object (for instance, a non-existent customer), one uses an object which implements the expected interface, but whose method body is empty. The advantage of this approach over a working default implementation is that a Null Object is very predictable and has no side effects: it does nothing.
Applicability
Use the Null Object pattern when
- you want to avoid explicit null checks and keep the algorithm elegant and easy to read.