* Updated saga to JUnit 5 * Update fix for CI job in trampoline module * Updated update-method module to JUnit 5 * Upgraded to latest JUnit Jupiter JUnit 4 is not needed when using JUnit-Vintage * Reverted change to access modifier on Trampoline * Cleanup to resolve code smells * Formatting * Formatting * Migrating to JUnit5 and updating some Mockito patterns * Migrating to JUnit5 * Migrating to JUnit5 * Migrating to JUnit 5 * Formatting cleanup * Added missing scope for junit * Fixed tests that were not running previously. Co-authored-by: Subhrodip Mohanta <hello@subho.xyz>
layout, title, folder, permalink, categories, tags
| layout | title | folder | permalink | categories | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pattern | Registry | registry | /patterns/registry/ | Creational |
|
Intent
Stores the objects of a single class and provide a global point of access to them. Similar to Multiton pattern, only difference is that in a registry there is no restriction on the number of objects.
Explanation
In Plain Words
Registry is a well-known object that other objects can use to find common objects and services.
Programmatic Example
Below is a Customer Class
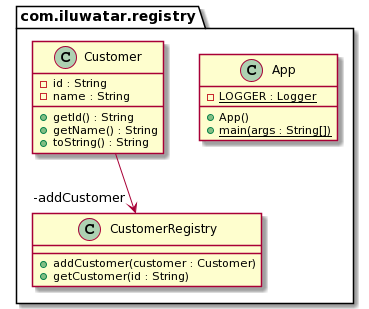
public class Customer {
private final String id;
private final String name;
public Customer(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
This registry of the Customer objects is CustomerRegistry
public final class CustomerRegistry {
private static final CustomerRegistry instance = new CustomerRegistry();
public static CustomerRegistry getInstance() {
return instance;
}
private final Map<String, Customer> customerMap;
private CustomerRegistry() {
customerMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
public Customer addCustomer(Customer customer) {
return customerMap.put(customer.getId(), customer);
}
public Customer getCustomer(String id) {
return customerMap.get(id);
}
}
Class diagram
Applicability
Use Registry pattern when
- client wants reference of some object, so client can lookup for that object in the object's registry.
Consequences
Large number of bulky objects added to registry would result in a lot of memory consumption as objects in the registry are not garbage collected.