* #415 initial all componets * #415 add src and tests * #415 add diagram * #415 add README * #415 add README * #415 change pom.xml * #415 change pom.xml * #415 change pom.xml * #415 update pom.xml * #415 change some code smell * #415 change some code smell * #415 update test * #415 add javadoc * #415 remove author tag * #415 add lombok @AllArgsConstructor * #415 fix code converge * #415 fix code converge * #415 fix code converge * #415 add javadoc * #415 fix code smell * #415 fix code smell * #415 add log information * #415 remove unused import * #415 add javadoc and more test * #415 modify test * #415 fix checkstyle * #415 remove useless code and add more javadoc and test. * #415 add package-info.java. * #415 add package-info.java. * #415 add more test. * #415 fix code smell. * #415 fix code smell and increase code coverage. * #415 fix code smell. * #415 update README.md * #415 update README.md * #415 make this demo better * #415 satisfy checkstyle * #415 make some field static. * #415 make some fields static. * #415 rename some fields static. * Delete package-info.java Co-authored-by: Subhrodip Mohanta <subhrodipmohanta@gmail.com>
layout, title, folder, permalink, categories, tags
| layout | title | folder | permalink | categories | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pattern | Presentation | presentation | /patterns/presentation/ | Behavioral |
|
Also known as
Application Model
Intent
Presentation Model pulls the state and behavior of the view out into a model class that is part of the presentation.
Explanation
Real world example
When we need to write a program with GUI, there is no need for us to put all presentation behavior in the view class. Because it will test become harder. So we can use Presentation Model Pattern to separate the behavior and view. The view only need to load the data and states from other class and show these data on the screen according to the states.
In plain words
a pattern that used to divide the presentation and controlling.
Code Example
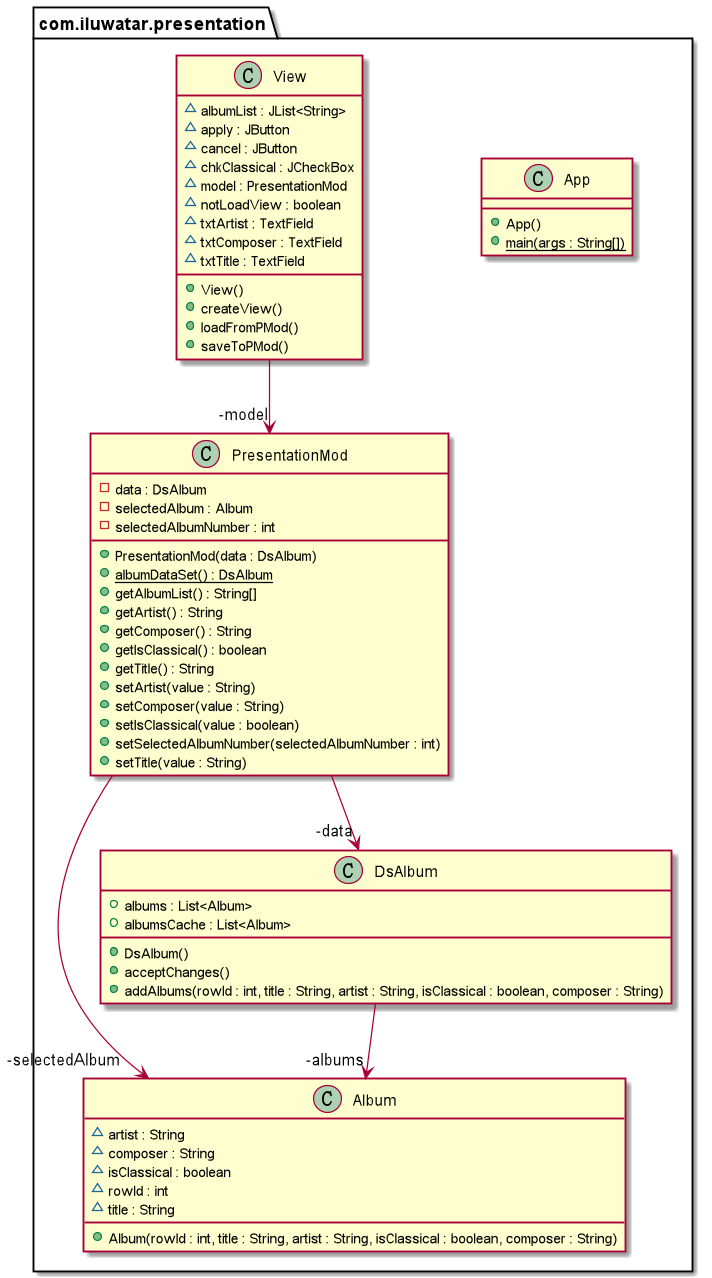
Class view is the GUI of albums. Methods saveToPMod and loadFromPMod are used to achieve synchronization.
public class View {
/**
* the model that controls this view.
*/
private final PresentationModel model;
private TextField txtTitle;
private TextField txtArtist;
private JCheckBox chkClassical;
private TextField txtComposer;
private JList<String> albumList;
private JButton apply;
private JButton cancel;
public View() {
model = new PresentationModel(PresentationModel.albumDataSet());
}
/**
* save the data to PresentationModel.
*/
public void saveToPMod() {
LOGGER.info("Save data to PresentationModel");
model.setArtist(txtArtist.getText());
model.setTitle(txtTitle.getText());
model.setIsClassical(chkClassical.isSelected());
model.setComposer(txtComposer.getText());
}
/**
* load the data from PresentationModel.
*/
public void loadFromPMod() {
LOGGER.info("Load data from PresentationModel");
txtArtist.setText(model.getArtist());
txtTitle.setText(model.getTitle());
chkClassical.setSelected(model.getIsClassical());
txtComposer.setEditable(model.getIsClassical());
txtComposer.setText(model.getComposer());
}
public void createView() {
// the detail of GUI information like size, listenser and so on.
}
}
Class Album is to store information of a album.
public class Album {
private String title;
private String artist;
private boolean isClassical;
/**
* only when the album is classical,
* composer can have content.
*/
private String composer;
}
Class DisplatedAlbums is store the information of all the albums that will be displayed on GUI.
public class DisplayedAlbums {
private final List<Album> albums;
public DisplayedAlbums() {
this.albums = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addAlbums(final String title,
final String artist, final boolean isClassical,
final String composer) {
if (isClassical) {
this.albums.add(new Album(title, artist, true, composer));
} else {
this.albums.add(new Album(title, artist, false, ""));
}
}
}
Class PresentationMod is used to control all the action of GUI.
public class PresentationModel {
private final DisplayedAlbums data;
private int selectedAlbumNumber;
private Album selectedAlbum;
public PresentationModel(final DisplayedAlbums dataOfAlbums) {
this.data = dataOfAlbums;
this.selectedAlbumNumber = 1;
this.selectedAlbum = this.data.getAlbums().get(0);
}
/**
* Changes the value of selectedAlbumNumber.
*
* @param albumNumber the number of album which is shown on the view.
*/
public void setSelectedAlbumNumber(final int albumNumber) {
LOGGER.info("Change select number from {} to {}",
this.selectedAlbumNumber, albumNumber);
this.selectedAlbumNumber = albumNumber;
this.selectedAlbum = data.getAlbums().get(this.selectedAlbumNumber - 1);
}
public String getTitle() {
return selectedAlbum.getTitle();
}
// other get methods are like this, which are used to get information of selected album.
public void setTitle(final String value) {
LOGGER.info("Change album title from {} to {}",
selectedAlbum.getTitle(), value);
selectedAlbum.setTitle(value);
}
// other set methods are like this, which are used to get information of selected album.
/**
* Gets a list of albums.
*
* @return the names of all the albums.
*/
public String[] getAlbumList() {
var result = new String[data.getAlbums().size()];
for (var i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = data.getAlbums().get(i).getTitle();
}
return result;
}
}
We can run class App to start this demo. the checkbox is the album classical; the first text field is the name of album artist; the second is the name of album title; the last one is the name of the composer:
Class diagram
Applicability
Use the Presentation Model Pattern when
- Testing a presentation through a GUI window is often awkward, and in some cases impossible.
- Do not determine which GUI will be used.