* Moves eip-aggregator to Java 11 * Moves eip-message-channel to Java 11 * Moves eip-publish-subscribe to Java 11 * Moves eip-splitter to Java 11 * Moves eip-wire-tap to Java 11 * Moves event-aggregator to Java 11 * Moves event-asynchronous to Java 11 * Moves event-driven-architecture to Java 11 * Moves event-queue to Java 11 * Moves event-sourcing to Java 11 * Moves execute-around to Java 11 * Moves extension-objects to Java 11
layout, title, folder, permalink, categories, tags
| layout | title | folder | permalink | categories | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pattern | Extension objects | extension-objects | /patterns/extension-objects/ | Behavioral |
|
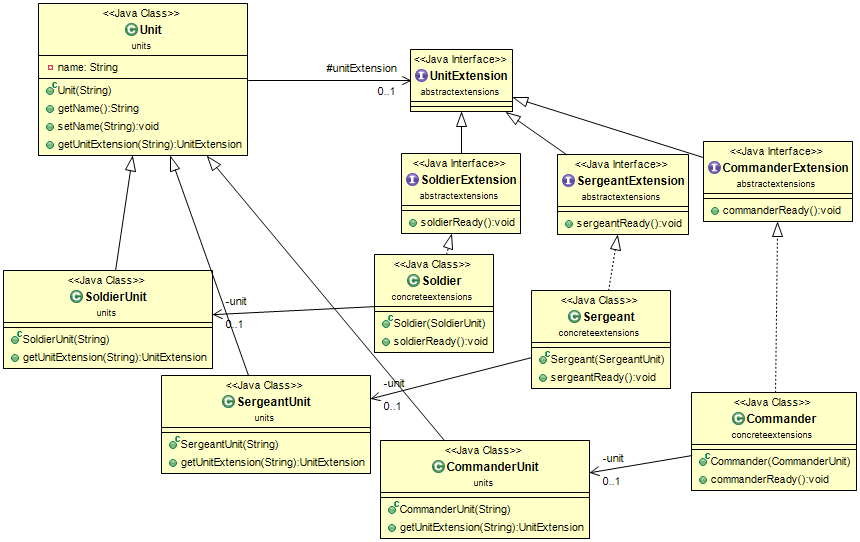
Intent
Anticipate that an object’s interface needs to be extended in the future. Additional interfaces are defined by extension objects.
Class diagram
Applicability
Use the Extension Objects pattern when:
- you need to support the addition of new or unforeseen interfaces to existing classes and you don't want to impact clients that don't need this new interface. Extension Objects lets you keep related operations together by defining them in a separate class
- a class representing a key abstraction plays different roles for different clients. The number of roles the class can play should be open-ended. There is a need to preserve the key abstraction itself. For example, a customer object is still a customer object even if different subsystems view it differently.
- a class should be extensible with new behavior without subclassing from it.