chore(i18n,docs): processed translations (#44446)
This commit is contained in:
@ -2,63 +2,63 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Leia nosso ["Guia de como contribuir com código aberto"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). É uma referência ampla para quem contribui com projetos pela primeira vez. E inclui muitas dicas de como contribuir para código aberto.
|
||||
|
||||
### What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
|
||||
### O que eu preciso saber para contribuir com a base de código?
|
||||
|
||||
freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
|
||||
O freeCodeCamp é executado em uma stack de JavaScript moderna. Se estiver interessado em contribuir com a nossa base de código, você precisará ter alguma familiaridade com JavaScript e com algumas das tecnologias que usamos como o Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby e Webpack.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
|
||||
### Posso traduzir os recursos do freeCodeCamp?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
|
||||
Sim. Você pode contribuir com qualquer um dos mais de 30 idiomas disponíveis em nossa plataforma de tradução.
|
||||
|
||||
We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/world-language-translation-effort).
|
||||
Temos traduções enviadas por usuários ao vivo em alguns idiomas. Pretendemos traduzir o freeCodeCamp para vários idiomas. Você pode ler mais sobre isso em nosso [anúncio aqui](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/world-language-translation-effort).
|
||||
|
||||
If you are interested in contributing to translations please makes sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files.md) first.
|
||||
Se você está interessado em contribuir com as traduções, certifique-se de [ler este guia](how-to-translate-files.md) primeiro.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
|
||||
### Posso contribuir com artigos para o editorial do freeCodeCamp ou com vídeos para o canal do YouTube do CodeCamp?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
|
||||
Sim - você pode contribuir com o nosso blog de publicação e com o canal do YouTube.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
|
||||
Se estiver interessado em escrever artigos para o editorial do freeCodeCamp, visite este [guia de publicação](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). Além disso, leia nosso [guia de estilo](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) pois ele ajudará você a escrever artigos mais sólidos e eficazes.
|
||||
|
||||
To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
|
||||
Para nos ajudar a fazer vídeos educacionais para nosso canal do YouTube, você pode seguir o [guia do canal do YouTube aqui](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I report a new bug?
|
||||
### Como posso relatar um novo erro?
|
||||
|
||||
If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["Help I've Found a Bug"](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/how-to-report-a-bug/19543) article and follow its instructions.
|
||||
Se você acha que encontrou um erro, primeiro leia o artigo ["Socorro, encontrei um erro"](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/how-to-report-a-bug/19543) e siga suas instruções.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
|
||||
Se você está confiante de que é um novo erro, vá em frente e crie uma nova issue no GitHub. Certifique-se de incluir o máximo de informações possível para que possamos reproduzir o erro. Temos um modelo predefinido de issue para ajudar você.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
|
||||
Observe que essas issues do GitHub são para discussões e questões relacionadas ao código – não para obter ajuda sobre como aprender a programar. Sempre que houver dúvidas, você deve [procurar por assistência no fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) antes de criar uma issue no GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I report a security issue?
|
||||
### Como posso relatar um problema de segurança?
|
||||
|
||||
Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please send an email to `security@freecodecamp.org` and we'll look into it immediately.
|
||||
Não crie issues no GitHub para problemas de segurança. Em vez disso, envie um e-mail para `security@freecodecamp.org` e nós vamos investigar isso imediatamente.
|
||||
|
||||
### I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
|
||||
### Eu sou estudante. Posso trabalhar em um recurso para créditos acadêmicos?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
|
||||
Sim. Note, porém, que não podemos nos comprometer com nenhum cronograma ou documentação que possa ser um requisito da sua faculdade ou universidade. Recebemos muitos pull-requests e contribuições em código de desenvolvedores voluntários e respeitamos o tempo e esforço deles. Em respeito a todos os outros contribuidores, não daremos nenhuma prioridade especial a nenhum PR só por ser relacionado à escola.
|
||||
|
||||
We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
|
||||
Pedimos que você planeje com antecedência e que trabalhe em suas contribuições de código tendo isso em mente.
|
||||
|
||||
### What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
|
||||
### O que significam estas etiquetas diferentes marcadas nas issues?
|
||||
|
||||
The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
|
||||
Os responsáveis pelo código fazem a [triagem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) das issues e pull requests tendo como base a prioridade, importância e outros fatores. Você pode [encontrar um glossário completo dos significados aqui](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
|
||||
|
||||
### Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
|
||||
### Por onde começar se quero ajudar em uma issue?
|
||||
|
||||
You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
|
||||
Você deve consultar issues [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) ou [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) para saber o que está disponível para ajuda.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] Você não precisa pedir permissão para ajudar com issues marcadas como **`help wanted`**. No entanto, issues com a etiqueta **`first timers only`** são issues especiais projetadas para pessoas que não contribuíram antes para a base de código freeCodeCamp.
|
||||
|
||||
### I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
|
||||
### Encontrei um erro de digitação. Devo relatar uma issue antes de poder fazer um pull request?
|
||||
|
||||
For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
|
||||
Para erros de digitação e outras mudanças em palavras, você pode diretamente abrir pull requests sem criar uma issue antes. Certifique-se de mencionar detalhes na descrição do pull request para nos ajudar a entender e revisar sua contribuição – mesmo se for uma mudança pequena.
|
||||
|
||||
Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
|
||||
Crie uma issue se quiser discutir grandes aspectos da base do código ou currículo.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I get an issue assigned to me?
|
||||
### Como posso receber uma issue atribuída a mim?
|
||||
|
||||
We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
|
||||
Tipicamente, não atribuímos issues para ninguém além de contribuidores de longo prazo. Ao invés disso, seguimos a política abaixo para sermos justos com todos:
|
||||
|
||||
1. É muito provável que façamos o merge do primeiro pull request que resolve a issue.
|
||||
2. No caso de vários colaboradores abrindo um pull request para a mesma issue, ao mesmo tempo, daremos prioridade ao pull request que melhor resolve a issue. Algumas coisas que consideramos:
|
||||
@ -69,19 +69,19 @@ We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. I
|
||||
- Você seguiu a checklist do pull request?
|
||||
- Você deu um título significativo ao seu pull request?
|
||||
|
||||
### I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
|
||||
### Estou com dificuldade em algo que não está incluído na documentação.
|
||||
|
||||
**Feel free to ask for help in:**
|
||||
**Fique à vontade para pedir ajuda em:**
|
||||
|
||||
- A categoria `Contributors` do [fórum da nossa comunidade](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
|
||||
- O canal `#Contributors` em nosso [servidor](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors).
|
||||
|
||||
We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
|
||||
Estamos animados em ajudar você a contribuir com qualquer tópico que desejar. Se você nos perguntar algo relacionado às issues, vamos ficar felizes em esclarecer. Certifique-se de pesquisar sua pergunta antes de postar uma nova.
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
|
||||
Agradecemos antecipadamente por ser educado(a) e paciente. Lembre-se – esta comunidade é feita principalmente de voluntários.
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional Assistance
|
||||
### Assistência adicional
|
||||
|
||||
If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
|
||||
Se você tiver dúvidas sobre a stack, a arquitetura do código, as traduções ou qualquer outra coisa, pode entrar em contato com nossa equipe [no fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
|
||||
|
||||
**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
|
||||
**Você pode enviar um e-mail para nossa equipe de desenvolvimento: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
|
||||
|
||||
87
docs/i18n/ukrainian/FAQ.md
Normal file
87
docs/i18n/ukrainian/FAQ.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
### Я лише починаю ознайомлення з GitHub та відкритим вихідним кодом. З чого мені варто почати?
|
||||
|
||||
Прочитайте нашу інструкцію ["Як зробити внесок до відкритого вихідного коду"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). Там є вичерпні вказівки для тих, хто вперше стикається з такими проєктами. Там також є багато порад для роботи з відкритим вихідним кодом.
|
||||
|
||||
### What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
|
||||
|
||||
freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
|
||||
|
||||
We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/world-language-translation-effort).
|
||||
|
||||
If you are interested in contributing to translations please makes sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files.md) first.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
|
||||
|
||||
To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I report a new bug?
|
||||
|
||||
If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["Help I've Found a Bug"](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/how-to-report-a-bug/19543) article and follow its instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I report a security issue?
|
||||
|
||||
Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please send an email to `security@freecodecamp.org` and we'll look into it immediately.
|
||||
|
||||
### I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
|
||||
|
||||
We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
|
||||
|
||||
### What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
|
||||
|
||||
The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
|
||||
|
||||
### Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
|
||||
|
||||
You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] Проблеми в **`потрібна допомога`** загальнодоступні, тож вам не треба отримувати дозволи на роботу з ними. А ось проблеми з позначкою **`лише новачкам`** — це спеціальні проблеми для людей, які ще не робили внесок до кодової бази freeCodeCamp.
|
||||
|
||||
### I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
|
||||
|
||||
For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
|
||||
|
||||
Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I get an issue assigned to me?
|
||||
|
||||
We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Скоріш за все ми об'єднаємо перший пул реквест з подальшими, які стосуються цієї проблеми.
|
||||
2. Якщо декілька користувачів одночасно відкривають пул реквести для однієї проблеми, ми надаватимемо пріоритет тому, який найкраще її вирішує. На що ми звертаємо увагу:
|
||||
- Чи входять туди тести?
|
||||
- Чи враховані всі сценарії використання?
|
||||
- Чи ви переконалися, що всі тести виконуються і працюють локально?
|
||||
3. Також ми даємо пріоритет тим пул реквестам, які дотримуються наших рекомендацій.
|
||||
- Ви стежили за списком пул реквестів?
|
||||
- Чи змістовна назва у вашого пул реквеста?
|
||||
|
||||
### I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
**Feel free to ask for help in:**
|
||||
|
||||
- Розділу `Співавтори` на [форумі спільноти](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
|
||||
- Каналу `#Contributors` на [чаті серверу](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors).
|
||||
|
||||
We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional Assistance
|
||||
|
||||
If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
|
||||
|
||||
**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
|
||||
36
docs/i18n/ukrainian/_sidebar.md
Normal file
36
docs/i18n/ukrainian/_sidebar.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
- **Початок роботи**
|
||||
- [Вступ](index.md "Зробіть свій внесок у спільноту freeCodeCamp.org")
|
||||
- [Поширені питання](FAQ.md)
|
||||
- **Внесок у переклад**
|
||||
- [Робота над перекладом матеріалів](how-to-translate-files.md)
|
||||
- [Робота над вичиткою перекладів](how-to-proofread-files.md)
|
||||
- **Як зробити внесок до коду**
|
||||
- [Встановити freeCodeCamp локально](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md)
|
||||
- [Дотримання кращих практик написання коду](codebase-best-practices.md)
|
||||
- [Відкрити пул реквест](how-to-open-a-pull-request.md)
|
||||
- [Робота над завданнями з кодом](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md)
|
||||
- [Робота над практичними проєктами](how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md)
|
||||
- [Робота над туторіалами з CodeRoad](how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md)
|
||||
- [Робота над локалізованим вебзастосунком](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md)
|
||||
- [Робота з Cypress тестами](how-to-add-cypress-tests.md)
|
||||
- [Робота над завданнями з відео](how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md)
|
||||
- [Робота над новинами](how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md)
|
||||
- [Робота з документацією](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md)
|
||||
- **Додаткові інструкції**
|
||||
- [Тестуйте переклади локально](how-to-test-translations-locally.md)
|
||||
- [Ознайомлення зі структурою файлів навчальної програми](curriculum-file-structure.md)
|
||||
- [Налагоджуйте вихідні електронні листи локально](how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md)
|
||||
- [Встановіть freeCodeCamp на Windows (WSL)](how-to-setup-wsl.md)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
- **Посібники** (для персоналу & модераторів)
|
||||
- [Довідник модератора](moderator-handbook.md)
|
||||
- [Довідник DevOps](devops.md)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
- **Наша спільнота**
|
||||
- [**GitHub**](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp)
|
||||
- [**Форум**](https://freecodecamp.org/forum/c/contributors)
|
||||
- [**Чат**](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/home)
|
||||
134
docs/i18n/ukrainian/codebase-best-practices.md
Normal file
134
docs/i18n/ukrainian/codebase-best-practices.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
||||
# Найкращі практики кодової бази
|
||||
|
||||
## Загальний JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
In most cases, our [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) will warn of any formatting which goes against this codebase's preferred practice.
|
||||
|
||||
Рекомендується використовувати функціональні компоненти замість класових компонентів.
|
||||
|
||||
## Specific TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
### Migrating a JavaScript File to TypeScript
|
||||
|
||||
#### Збереження історії файлів Git
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes changing the file from `<filename>.js` to `<filename>.ts` (or `.tsx`) causes the original file to be deleted, and a new one created, and other times the filename just changes - in terms of Git. Ideally, we want the file history to be preserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Найкращі умови для досягнення цього:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Перейменувати файл
|
||||
2. Commit with the flag `--no-verify` to prevent Husky from complaining about the lint errors
|
||||
3. Refactor to TypeScript for migration, in a separate commit
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Такі редактори, як VSCode, все одно показуватимуть, що файл видалено та створено новий. Якщо ви використовуєте `git add .`, тоді VSCode покаже файл як перейменований в процесі
|
||||
|
||||
### Naming Conventions
|
||||
|
||||
#### Інтерфейси та типи
|
||||
|
||||
For the most part, it is encouraged to use interface declarations over type declarations.
|
||||
|
||||
React Component Props - суфікс `Props`
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
interface MyComponentProps {}
|
||||
// type MyComponentProps = {};
|
||||
const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
React Stateful Components - суфікс `State`
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
interface MyComponentState {}
|
||||
// type MyComponentState = {};
|
||||
class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
За замовчуванням - ім'я об'єкта в PascalCase
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
interface MyObject {}
|
||||
// type MyObject = {};
|
||||
const myObject: MyObject = {};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
|
||||
|
||||
## Redux
|
||||
|
||||
### Визначення дій
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
enum AppActionTypes = {
|
||||
actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export const actionFunction = (
|
||||
arg: Arg
|
||||
): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
|
||||
type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
|
||||
payload: arg
|
||||
});
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Як підключити Reduce
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
// Base reducer action without payload
|
||||
type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
|
||||
// Logic for handling optional payloads
|
||||
type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
|
||||
T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
|
||||
? ReducerBase<T> & {
|
||||
payload: AppState['property'];
|
||||
}
|
||||
: ReducerBase<T>;
|
||||
|
||||
// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
|
||||
export const reducer = (
|
||||
state: AppState = initialState,
|
||||
action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
|
||||
): AppState => {
|
||||
switch (action.type) {
|
||||
case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
|
||||
return { ...state, property: action.payload };
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return state;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Dispatch
|
||||
|
||||
Усередині компонента імпортуйте необхідні дії та селектори.
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
// Add type definition
|
||||
interface MyComponentProps {
|
||||
actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Connect to Redux store
|
||||
const mapDispatchToProps = {
|
||||
actionFunction
|
||||
};
|
||||
// Example React Component connected to store
|
||||
const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
|
||||
const handleClick = () => {
|
||||
// Dispatch function
|
||||
actionFunction();
|
||||
};
|
||||
return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
|
||||
<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
|
||||
|
||||
## Додаткова література
|
||||
|
||||
- [Документація по TypeScript](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
|
||||
- [Підказки по TypeScript з React](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
|
||||
106
docs/i18n/ukrainian/curriculum-file-structure.md
Normal file
106
docs/i18n/ukrainian/curriculum-file-structure.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
# Структура навчальної програми
|
||||
|
||||
Наш основний навчальний контент знаходиться у каталозі під назвою `навчальна програма`. На цій сторінці буде детально описано, як ці файли організовані.
|
||||
|
||||
## Термінологія
|
||||
|
||||
При обговоренні навчальної програми важливо знати декілька термінів.
|
||||
|
||||
- `certification` : Коли йдеться про сертифікацію, мається на увазі сертифікати, які отримують користувачі. Це не те саме, що й superBlock.
|
||||
- `superBlock` : superBlock — це збірка найскладніших завдань. Кожен суперблок відповідає сертифікату в навчальній програмі (наприклад, Адаптивний вебдизайн).
|
||||
- `block` : Блок — це розділ у межах superblock. Блок відповідає групі завдань у даній сертифікації (наприклад, Базовий HTML та HTML5)
|
||||
- `challenge` : Завдання — це окремий урок у навчальній програмі (наприклад, Ознайомтесь з HTML елементами)
|
||||
|
||||
## Дерево файлів
|
||||
|
||||
Ось як буде виглядати структура файлів з цими термінами:
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- prettier-ignore -->
|
||||
```md
|
||||
|
||||
curriculum/
|
||||
├─ _meta/
|
||||
│ ├─ {block}/
|
||||
│ │ ├─ meta.json
|
||||
├─ {language}/
|
||||
│ ├─ {superBlock}/
|
||||
│ │ ├─ {block}/
|
||||
│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Каталог `_meta`
|
||||
|
||||
Каталог `_meta` — це особливий каталог, який містить `.json` файли. Ці файли відповідають кожному окремому блоку в навчальній програмі та використовуються, щоб визначити до якого суперблоку належить блок та порядок завдань у цьому блоці.
|
||||
|
||||
## Перейменування файлів
|
||||
|
||||
Інколи вам потрібно перейменувати сертифікат, суперблок, блок чи завдання. У цьому розділі будуть описані важливі кроки, які допоможуть вам уникнути помилок збірки.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!УВАГА] Перейменування файлів у структурі навчальної програми часто змінює шлях (або URL-адресу) контенту на головній вебсторінці. Робити це слід з обережністю, оскільки перенаправлення потрібно налаштовувати для кожної внесеної зміни.
|
||||
|
||||
### Перейменування сертифікату
|
||||
|
||||
Під час перейменування сертифікату ви, ймовірно, захочете перейменувати пов’язаний із ним суперблок. Виконуйте наступні дії, щоб перейменувати лише сертифікат:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Оберіть нову назву для теки `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate`.
|
||||
1. У файлі `meta.json` тієї теки, змініть значення в `name`, `dashedName` і `challengeOrder` на нову назву.
|
||||
1. У `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate`, перейменуйте теку `{superBlock}-certificate` і YAML файл у ній.
|
||||
1. У YAML файлі, змініть `title` на нову назву.
|
||||
1. Перейменуйте файл і теку з третього кроку для інших мов навчальної програми.
|
||||
1. Оновіть `client/src/redux/index.ts`, щоб використовувати правильний `title`.
|
||||
1. За бажанням оновіть і `certSlug` для суперблока в цьому ж файлі. **Зауважте**, що перейменування `certSlug` змінить URL-адресу для сертифікатів, тому це слід робити обачно.
|
||||
1. Оновіть `title` в `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` до нових значень. **Зверніть увагу**, що зміна `title` тут **зруйнує** superBlock сторінку для відповідної сертифікації. Це пов'язано із тим, що назва superBlock має відповідати назві сертифікації. Бажано одночасно змінити й назву суперблоку.
|
||||
1. Якщо Ви перейменували `certSlug` у сьомому кроці, змініть його тут для сертифіката і вкладених `projects` значень.
|
||||
1. У `config/certification-settings.js`, оновіть значення `certTypeTitleMap` на нову назву.
|
||||
1. Якщо Ви перейменували `certSlug` у сьомому кроці, оновіть ключ доступу `certSlugTypeMap` в цьому ж файлі.
|
||||
1. За необхідності оновіть ім'я сертифікату в масиві `legacyCerts` з `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx`.
|
||||
1. Оновіть основний файл `README.md` до нового імені.
|
||||
|
||||
### Перейменування суперблоку
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Під час перейменування суперблоку, нове ім’я теки використовується як шлях і його слід вважати «вірним» ім’ям. Усі інші значення слід оновити, щоб показати цю зміну.
|
||||
|
||||
Крім того, ви, ймовірно, захочете перейменувати сертифікат та блок `{superBlock}-projects` одночасно із superBlock, оскільки всі вони мають спільну назву. Виконайте наступні кроки, щоб перейменувати лише superBlock:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Перейменуйте теку superBlock у каталозі `curriculum/challenges/english`.
|
||||
1. Перейменуйте теку superBlock у _всіх_ інших каталогах `curriculum/challenges/{language}`.
|
||||
1. Для кожного блоку в цьому суперблоці оновіть значення `superBlock` в `meta.json` файлі на його ж dashedName. Вам не потрібно перейменовувати теки тут. Зробіть це при перейменуванні блоку.
|
||||
1. Перейменуйте теку суперблоку в `client/src/pages/learn`.
|
||||
1. Оновіть файл `index.md` у вищевказаній теці, змінивши `title` та `superBlock` значення на нове ім'я.
|
||||
1. Для кожної вищезазначеної теки у блоці, оновіть `index.md`, щоб використовувати її за правильним `superBlock` значенням.
|
||||
1. У файлі `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`, оновіть алгоритм дій до сертифіката на початку файлу і значення `title` для цього суперблоку. **Зверніть увагу:** зміна `title` тут **забере у Вас** можливість переглядати дійсні сертифікати для цього суперблоку. Це пов'язано із тим, що назва superBlock має відповідати назві сертифікації. Бажано одночасно змінити й назву сертифіката.
|
||||
1. Оновіть `superBlockCertTypeMap` ключ у `config/certification-settings.js` до нової назви суперблоку.
|
||||
1. Оновіть значення шляху в `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
|
||||
1. Оновіть `intro.json` файл для кожної мови в `client/i18n/locales`, щоб мати змогу використати новий суперблок `dashedName`. В англійському файлі також оновіть `title`.
|
||||
1. Перевірте `config/i18n/all-langs.js` файл, щоб побачити чи надав суперблок можливість конвертації. Оновіть усі значення, де він використовується.
|
||||
1. Оновіть назву головного `README.md` файлу.
|
||||
|
||||
### Перейменування блоку
|
||||
|
||||
При перейменуванні блоку навчальної програми, вам варто:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Змінити назву теки блоку в каталозі `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}`.
|
||||
1. Змінити назву тієї ж самої теки блоку в _усіх_ іншомовних каталогах, аби вони збігалися. Вони повинні бути такі ж самі як і в англійській теці, інакше буде помилка збірки.
|
||||
1. Змінити назву теки блоку в `_meta` каталозі.
|
||||
1. Оновити властивості `name` та `dashedName` для `meta.json` файлу цього блоку.
|
||||
1. Оновити `client/utils/help-category-map.json`, щоб використати нову назву блоку як основну.
|
||||
1. Оновити теку блоку в `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
|
||||
1. Оновити `block` значення в титульному елементі в файлі `index.md` з вищезгаданої теки.
|
||||
1. У файлах `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json` оновіть назву блоку до нової для всіх мов. В англійському файлі `intro.json` також оновіть `title`.
|
||||
1. Оновити основний `README.md` файл до нового імені.
|
||||
|
||||
### Перейменування завдання
|
||||
|
||||
Під час перейменування окремого файлу завдання Вам необхідно:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Змінити назву файлу завдання в каталозі `curriculum/challenges/english`.
|
||||
1. Змінити назву `title` і `dashedName` у цьому файлі.
|
||||
1. Змінити назву файлу та `dashedName` у цих файлах для _всіх_ каталогів мов так, щоб вони збігалися.
|
||||
1. Оновити назву завдання у відповідному файлі `meta.json`. Ці назви завдань не використовуються у збірці, але забезпечують зручний спосіб ідентифікації порядку завдань.
|
||||
1. Якщо за це завдання передбачений сертифікат, то оновіть назву файлу YAML у `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>`.
|
||||
1. Якщо за це завдання передбачений сертифікат, оновіть `title` та `link` в `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
|
||||
1. Якщо за це завдання передбачений сертифікат, оновіть основний файл `README.md` до нового імені.
|
||||
|
||||
## Властивість `dashedName`
|
||||
|
||||
The `dashedName` property is used to generate the URL path for the superblock, block, or challenge. These should generally match what the `/utils/slugs.js` helper would output for the file name.
|
||||
962
docs/i18n/ukrainian/devops.md
Normal file
962
docs/i18n/ukrainian/devops.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,962 @@
|
||||
# Довідник з DevOps
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will help you understand our infrastructure stack and how we maintain our platforms. While this guide does not have exhaustive details for all operations, it could be used as a reference for your understanding of the systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us know, if you have feedback or queries, and we will be happy to clarify.
|
||||
|
||||
# Посібник - Розгортання коду
|
||||
|
||||
This repository is continuously built, tested and deployed to **separate sets of infrastructure (Servers, Databases, CDNs, etc.)**.
|
||||
|
||||
This involves three steps to be followed in sequence:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Нові зміни (виправлення і функціонал) зливаються у нашу основну гілку розробки (`main`) через pull запити.
|
||||
2. Ці зміни проходять через ряд автоматизованих тестів.
|
||||
3. Once the tests pass we release the changes (or update them if needed) to deployments on our infrastructure.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Building the codebase - Mapping Git Branches to Deployments.
|
||||
|
||||
Typically, [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (the default development branch) is merged into the [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) branch once a day and is released into an isolated infrastructure.
|
||||
|
||||
This is an intermediate release for our developers and volunteer contributors. Він також відомий як наш "staging" або "бета" реліз.
|
||||
|
||||
It is identical to our live production environment at `freeCodeCamp.org`, other than it using a separate set of databases, servers, web-proxies, etc. This isolation lets us test ongoing development and features in a "production" like scenario, without affecting regular users of freeCodeCamp.org's main platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the developer team [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) is happy with the changes on the staging platform, these changes are moved every few days to the [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) branch.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the final release that moves changes to our production platforms on freeCodeCamp.org.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Testing changes - Integration and User Acceptance Testing.
|
||||
|
||||
We employ various levels of integration and acceptance testing to check on the quality of the code. Всі наші тести виконуються за допомогою таких програм, як [Github Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) та [Azure pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp).
|
||||
|
||||
We have unit tests for testing our challenge solutions, Server APIs and Client User interfaces. These help us test the integration between different components.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] We are also in the process of writing end user tests which will help in replicating real world scenarios like updating an email or making a call to the API or third-party services.
|
||||
|
||||
Together these tests help in preventing issues from repeating themselves and ensure we do not introduce a bug while working on another bug or a feature.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Розгортання змін - відправлення змін до серверів.
|
||||
|
||||
Ми налаштували безперервне програмне забезпечення доставки для внесення змін до наших серверів розробки і виробництва.
|
||||
|
||||
Після того, як зміни будуть відправлені в захищені гілки релізу, конвеєр збірки автоматично запускається для гілки. Гарбопроводи відповідають за будівництво артефактів та збереження їх у холодному сховищі для подальшого використання.
|
||||
|
||||
The build pipeline goes on to trigger a corresponding release pipeline if it completes a successful run. The release pipelines are responsible for collecting the build artifacts, moving them to the servers and going live.
|
||||
|
||||
Status of builds and releases are [available here](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
|
||||
|
||||
## Trigger a build, test and deploy
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, only members on the developer team can push to the production branches. The changes to the `production-*` branches can land only via fast-forward merge to the [`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] In the upcoming days we would improve this flow to be done via pull-requests, for better access management and transparency.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pushing changes to Staging Applications.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Configure your remotes correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
git remote -v
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Results:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
|
||||
origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
|
||||
upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
|
||||
upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Make sure your `main` branch is pristine and in sync with the upstream.
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
git checkout main
|
||||
git fetch --all --prune
|
||||
git reset --hard upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Check that the GitHub CI is passing on the `main` branch for upstream.
|
||||
|
||||
The [continuous integration](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) tests should be green and PASSING for the `main` branch. Click the green check mark next to the commit hash when viewing the `main` branch code.
|
||||
|
||||
<details> <summary> Checking status on GitHub Actions (screenshot) </summary>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||

|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
If this is failing you should stop and investigate the errors.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Confirm that you are able to build the repository locally.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
npm run clean-and-develop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Move changes from `main` to `prod-staging` via a fast-forward merge
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git checkout prod-staging
|
||||
git merge main
|
||||
git push upstream
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in anyway these commands will error out.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If they do, you may have done something incorrectly and you should just start over.
|
||||
|
||||
The above steps will automatically trigger a run on the build pipeline for the `prod-staging` branch. Once the build is complete, the artifacts are saved as `.zip` files in a cold storage to be retrieved and used later.
|
||||
|
||||
The release pipeline is triggered automatically when a fresh artifact is available from the connected build pipeline. For staging platforms, this process does not involve manual approval and the artifacts are pushed to the Client CDN and API servers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pushing changes to Production Applications.
|
||||
|
||||
The process is mostly the same as the staging platforms, with a few extra checks in place. This is just to make sure, we do not break anything on freeCodeCamp.org which can see hundreds of users using it at any moment.
|
||||
|
||||
| Do NOT execute these commands unless you have verified that everything is working on the staging platform. You should not bypass or skip any testing on staging before proceeding further. |
|
||||
|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
|
||||
1. Make sure your `prod-staging` branch is pristine and in sync with the upstream.
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
git checkout prod-staging
|
||||
git fetch --all --prune
|
||||
git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Move changes from `prod-staging` to `prod-current` via a fast-forward merge
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git checkout prod-current
|
||||
git merge prod-staging
|
||||
git push upstream
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in anyway these commands will error out.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If they do, you may have done something incorrectly and you should just start over.
|
||||
|
||||
The above steps will automatically trigger a run on the build pipeline for the `prod-current` branch. Once a build artifact is ready, it will trigger a run on the release pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
**Additional Steps for Staff Action**
|
||||
|
||||
One a release run is triggered, members of the developer staff team will receive an automated manual intervention email. They can either _approve_ or _reject_ the release run.
|
||||
|
||||
If the changes are working nicely and have been tested on the staging platform, then it can be approved. The approval must be given within 4 hours of the release being triggered before getting rejected automatically. A staff can re-trigger the release run manually for rejected runs, or wait for the next cycle of release.
|
||||
|
||||
For staff use:
|
||||
|
||||
| Check your email for a direct link or [go to the release dashboard](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) after the build run is complete. |
|
||||
|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
|
||||
Once one of the staff members approves a release, the pipeline will push the changes live to freeCodeCamp.org's production CDN and API servers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Build, Test and Deployment Status
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the current test, build and deployment status of the codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
| Branch | Unit Tests | Integration Tests | Builds & Deployments |
|
||||
|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
|
||||
| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
|
||||
| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
|
||||
| `prod-next` (experimental, upcoming) | - | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
## Early access and beta testing
|
||||
|
||||
We welcome you to test these releases in a **"public beta testing"** mode and get early access to upcoming features to the platforms. Sometimes these features/changes are referred to as **next, beta, staging,** etc. interchangeably.
|
||||
|
||||
Your contributions via feedback and issue reports will help us in making the production platforms at `freeCodeCamp.org` more **resilient**, **consistent** and **stable** for everyone.
|
||||
|
||||
We thank you for reporting bugs that you encounter and help in making freeCodeCamp.org better. You rock!
|
||||
|
||||
### Identifying the upcoming version of the platforms
|
||||
|
||||
Currently a public beta testing version is available at:
|
||||
|
||||
| Application | Language | URL |
|
||||
|:----------- |:-------- |:---------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Learn | English | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
|
||||
| | Espanol | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
|
||||
| | Chinese | <https://chinese.freecodecamp.dev> |
|
||||
| News | English | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
|
||||
| Forum | English | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
|
||||
| | Chinese | <https://chinese.freecodecamp.dev/forum> |
|
||||
| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] The domain name is different than **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. This is intentional to prevent search engine indexing and avoid confusion for regular users of the platform.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> The above list not exhaustive of all the applications that we provision. Also not all language variants are deployed in staging to conserve resources.
|
||||
|
||||
### Identifying the current version of the platforms
|
||||
|
||||
**The current version of the platform is always available at [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
|
||||
|
||||
The dev-team merges changes from the `prod-staging` branch to `prod-current` when they release changes. The top commit should be what you see live on the site.
|
||||
|
||||
You can identify the exact version deployed by visiting the build and deployment logs available in the status section. Alternatively you can also ping us in the [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors) for a confirmation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Known Limitations
|
||||
|
||||
There are some known limitations and tradeoffs when using the beta version of the platform.
|
||||
|
||||
- #### All data / personal progress on these beta platforms will NOT be saved or carried over to production.
|
||||
|
||||
**Users on the beta version will have a separate account from the production.** The beta version uses a physically separate database from production. This gives us the ability to prevent any accidental loss of data or modifications. The dev team may purge the database on this beta version as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
- #### There are no guarantees on the uptime and reliability of the beta platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
Deployment is expected to be frequent and in rapid iterations, sometimes multiple times a day. As a result there will be unexpected downtime at times or broken functionality on the beta version.
|
||||
|
||||
- #### Do not send regular users to this site as a measure of confirming a fix
|
||||
|
||||
The beta site is and always has been to augment local development and testing, nothing else. It's not a promise of what’s coming, but a glimpse of what is being worked upon.
|
||||
|
||||
- #### Sign in page may look different than production
|
||||
|
||||
We use a test tenant for freeCodeCamp.dev on Auth0, and hence do not have the ability to set a custom domain. This makes it so that all the redirect callbacks and the login page appear at a default domain like: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. This does not affect the functionality and is as close to production as we can get.
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting issues and leaving feedback
|
||||
|
||||
Please open fresh issues for discussions and reporting bugs.
|
||||
|
||||
You may send an email to `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` if you have any queries. As always all security vulnerabilities should be reported to `security[at]freecodecamp.org` instead of the public tracker and forum.
|
||||
|
||||
# Flight Manual - Server Maintenance
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 1. The guide applies to the **freeCodeCamp Staff members only**.
|
||||
> 2. These instructions should not be considered exhaustive, please use caution.
|
||||
|
||||
As a member of the staff, you may have been given access to our cloud service providers like Azure, Digital Ocean, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some handy commands that you can use to work on the Virtual Machines (VM), for instance performing maintenance updates or doing general housekeeping.
|
||||
|
||||
## Get a list of the VMs
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] While you may already have SSH access to the VMs, that alone will not let you list VMs unless you been granted access to the cloud portals as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Azure
|
||||
|
||||
Install Azure CLI `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
|
||||
|
||||
> **(One-time) Install on macOS with [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
brew install azure-cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> **(One-time) Login:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
az login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> **Get the list of VM names and P addresses:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Digital Ocean
|
||||
|
||||
Install Digital Ocean CLI `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
|
||||
|
||||
> **(One-time) Install on macOS with [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
brew install doctl
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> **(One-time) Login:**
|
||||
|
||||
Authentication and context switching: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
doctl auth init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> **Get the list of VM names and IP addresses:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Spin new Resources
|
||||
|
||||
We are working on creating our IaC setup, and while that is in works you can use the Azure portal or the Azure CLI to spin new virtual machines and other resources.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] No matter your choice of spinning resources, we have a few [handy cloud-init config files](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init) to help you do some of the basic provisioning like installing docker or adding SSH keys, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Keep VMs updated
|
||||
|
||||
You should keep the VMs up to date by performing updates and upgrades. This will ensure that the virtual machine is patched with latest security fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING] Before you run these commands:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> - Make sure that the VM has been provisioned completely and there is no post-install steps running.
|
||||
> - If you are updating packages on a VM that is already serving an application, make sure the app has been stopped / saved. Package updates will cause network bandwidth, memory and/or CPU usage spikes leading to outages on running applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Update package information
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Upgrade installed packages
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo apt upgrade -y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Cleanup unused packages
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo apt autoremove -y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Work on Web Servers (Proxy)
|
||||
|
||||
We are running load balanced (Azure Load Balancer) instances for our web servers. These servers are running NGINX which reverse proxy all of the traffic to freeCodeCamp.org from various applications running on their own infrastructures.
|
||||
|
||||
The NGINX config is available on [this repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
|
||||
|
||||
### First Install
|
||||
|
||||
Provisioning VMs with the Code
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo su
|
||||
|
||||
cd /var/www/html
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/
|
||||
rm -rf nginx
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
|
||||
|
||||
Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
|
||||
|
||||
**OR**
|
||||
|
||||
Move over existing certificates:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
# Local
|
||||
scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
|
||||
scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
|
||||
|
||||
# Remote
|
||||
rm -rf ./ssl
|
||||
mv /tmp/ssl ./
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Update Upstream Configurations:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
vi configs/upstreams.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Setup networking and firewalls.
|
||||
|
||||
Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
|
||||
|
||||
Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Logging and Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo systemctl status nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Logging and monitoring for the servers are available at:
|
||||
|
||||
NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com'), our current basic monitoring dashboard. We are working on more granular metrics for better observability
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
|
||||
|
||||
Config changes to our NGINX instances are maintained on GitHub, these should be deployed on each instance like so:
|
||||
|
||||
1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo su
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Get the latest config code.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd /etc/nginx
|
||||
git fetch --all --prune
|
||||
git reset --hard origin/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
nginx -t
|
||||
nginx -s reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Work on API Instances
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo apt install build-essential
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### First Install
|
||||
|
||||
Provisioning VMs with the Code
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Node LTS.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm i -g npm@8
|
||||
npm i -g pm2
|
||||
pm2 install pm2-logrotate
|
||||
pm2 startup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Clone freeCodeCamp, setup env and keys.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
|
||||
cd freeCodeCamp
|
||||
git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create the `.env` from the secure credentials storage.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Create the `google-credentials.json` from the secure credentials storage.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Install dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Build the server
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run ensure-env && npm run build:curriculum && npm run build:server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Start Instances
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd api-server
|
||||
pm2 start ./lib/production-start.js -i max --max-memory-restart 600M --name org
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Logging and Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 monit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
|
||||
|
||||
Code changes need to be deployed to the API instances from time to time. It can be a rolling update or a manual update. The later is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!ATTENTION] The automated pipelines are not handling dependencies updates at the minute. We need to do a manual update before any deployment pipeline runs.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Stop all instances
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 stop all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Build the server
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run ensure-env && npm run build:curriculum && npm run build:server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Start Instances
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code, logic, via pipelines. You should not need to run these commands. These are here for documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Work on Client Instances
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo apt install build-essential
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### First Install
|
||||
|
||||
Provisioning VMs with the Code
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Node LTS.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm i -g npm@6
|
||||
npm i -g pm2
|
||||
npm install -g serve
|
||||
pm2 install pm2-logrotate
|
||||
pm2 startup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Clone client config, setup env and keys.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
|
||||
cd client
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start placeholder instances for the web client, these will be updated with artifacts from the Azure pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
> Todo: This setup needs to move to S3 or Azure Blob storage
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ```console
|
||||
> echo "serve -c ../../serve.json www -p 50505" >> client-start-primary.sh
|
||||
> chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
|
||||
> pm2 delete client-primary
|
||||
> pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
|
||||
> echo "serve -c ../../serve.json www -p 52525" >> client-start-secondary.sh
|
||||
> chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
|
||||
> pm2 delete client-secondary
|
||||
> pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
|
||||
### Logging and Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 monit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
|
||||
|
||||
Code changes need to be deployed to the API instances from time to time. It can be a rolling update or a manual update. The later is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!ATTENTION] The automated pipelines are not handling dependencies updates at the minute. We need to do a manual update before any deployment pipeline runs.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Stop all instances
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 stop all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install or update dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
3. Start Instances
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code, logic, via pipelines. You should not need to run these commands. These are here for documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Work on Chat Servers
|
||||
|
||||
Our chat servers are available with a HA configuration [recommended in Rocket.Chat docs](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). The `docker-compose` file for this is [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config).
|
||||
|
||||
We provision redundant NGINX instances which are themselves load balanced (Azure Load Balancer) in front of the Rocket.Chat cluster. The NGINX configuration file are [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config).
|
||||
|
||||
### First Install
|
||||
|
||||
Provisioning VMs with the Code
|
||||
|
||||
**NGINX Cluster:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo su
|
||||
|
||||
cd /var/www/html
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/
|
||||
rm -rf nginx
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
|
||||
|
||||
Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
|
||||
|
||||
**OR**
|
||||
|
||||
Move over existing certificates:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
# Local
|
||||
scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
|
||||
scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
|
||||
|
||||
# Remote
|
||||
rm -rf ./ssl
|
||||
mv /tmp/ssl ./
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Update Upstream Configurations:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
vi configs/upstreams.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Setup networking and firewalls.
|
||||
|
||||
Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
|
||||
|
||||
Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
**Docker Cluster:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Docker and configure from the repository
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
|
||||
cd chat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Configure the required environment variables and instance IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run rocket-chat server
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker-compose config
|
||||
docker-compose up -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Logging and Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo systemctl status nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Check status for running docker instances with:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker ps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
|
||||
|
||||
**NGINX Cluster:**
|
||||
|
||||
Config changes to our NGINX instances are maintained on GitHub, these should be deployed on each instance like so:
|
||||
|
||||
1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo su
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Get the latest config code.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd /etc/nginx
|
||||
git fetch --all --prune
|
||||
git reset --hard origin/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
nginx -t
|
||||
nginx -s reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Docker Cluster:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. SSH into the instance and navigate to the chat config path
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd ~/chat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Get the latest config code.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git fetch --all --prune
|
||||
git reset --hard origin/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Pull down the latest docker image for Rocket.Chat
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker-compose pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Update the running instances
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker-compose up -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Validate the instances are up
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker ps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Cleanup extraneous resources
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker system prune --volumes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
WARNING! This will remove:
|
||||
- all stopped containers
|
||||
- all networks not used by at least one container
|
||||
- all volumes not used by at least one container
|
||||
- all dangling images
|
||||
- all dangling build cache
|
||||
|
||||
Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Select yes (y) to remove everything that is not in use. This will remove all stopped containers, all networks and volumes not used by at least one container, and all dangling images and build caches.
|
||||
|
||||
## Work on Contributor Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### Deploy updates
|
||||
|
||||
ssh into the VM (hosted on Digital Ocean).
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd tools
|
||||
git pull origin master
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
npm run build
|
||||
pm2 restart contribute-app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Updating Node.js versions on VMs
|
||||
|
||||
List currently installed node & npm versions
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
nvm -v
|
||||
node -v
|
||||
npm -v
|
||||
|
||||
nvm ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install the latest Node.js LTS, and reinstall any global packages
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Verify installed packages
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm ls -g --depth=0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alias the `default` Node.js version to the current LTS (pinned to latest major version)
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
nvm alias default 16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(Optional) Uninstall old versions
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
nvm uninstall <version>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!ATTENTION] For client applications, the shell script can't be resurrected between Node.js versions with `pm2 resurrect`. Deploy processes from scratch instead. This should become nicer when we move to a docker based setup.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If using PM2 for processes you would also need to bring up the applications and save the process list for automatic recovery on restarts.
|
||||
|
||||
Get the uninstall instructions/commands with the `unstartup` command and use the output to remove the systemctl services
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 unstartup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Get the install instructions/commands with the `startup` command and use the output to add the systemctl services
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 startup
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Quick commands for PM2 to list, resurrect saved processes, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 resurrect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 save
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
pm2 logs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing and Updating Azure Pipeline Agents
|
||||
|
||||
See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops and follow the instructions to stop, remove and reinstall agents. Broadly you can follow the steps listed here.
|
||||
|
||||
You would need a PAT, that you can grab from here: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing agents on Deployment targets
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) and register the agent from scratch in the requisite [deployment groups](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] You should run the scripts in the home directory, and make sure no other `azagent` directory exists.
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating agents
|
||||
|
||||
Currently updating agents requires them to be removed and reconfigured. This is required for them to correctly pick up `PATH` values and other system environment variables. We need to do this for instance updating Node.js on our deployment target VMs.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate and check status of the service
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd ~/azagent
|
||||
sudo ./svc.sh status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Stop the service
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo ./svc.sh stop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Uninstall the service
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Remove the agent from the pipeline pool
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
./config.sh remove
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Remove the config files
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd ~
|
||||
rm -rf ~/azagent
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once You have completed the steps above, you can repeat the same steps as installing the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
# Flight Manual - Email Blast
|
||||
|
||||
We use [a CLI tool](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) to send out the weekly newsletter. To spin this up and begin the process:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Sign in to DigitalOcean, and spin up new droplets under the `Sendgrid` project. Use the Ubuntu Sendgrid snapshot with the most recent date. This comes pre-loaded with the CLI tool and the script to fetch emails from the database. With the current volume, three droplets are sufficient to send the emails in a timely manner.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Set up the script to fetch the email list.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
|
||||
cp sample.env .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to replace the placeholder values in the `.env` file with your credentials.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run the script.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
node get-emails.js emails.csv
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will save the email list in an `emails.csv` file.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Break the emails down into multiple files, depending on the number of droplets you need. This is easiest to do by using `scp` to pull the email list locally and using your preferred text editor to split them into multiple files. Each file will need the `email,unsubscribeId` header.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Switch to the CLI directory with `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` and configure the tool [per the documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README.md).
|
||||
|
||||
6. Run the tool to send the emails, following the [usage documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps.md).
|
||||
|
||||
7. When the email blast is complete, verify that no emails have failed before destroying the droplets.
|
||||
|
||||
# Flight Manual - Adding news instances for new languages
|
||||
|
||||
### Theme Changes
|
||||
|
||||
We use a custom [theme](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) for our news publication. Adding the following changes to the theme enables the addition of new languages.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Include an `else if` statement for the new [ISO language code](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) in [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
|
||||
2. Create an initial config folder by duplicating the [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) folder and changing its name to the new language code. (`en` —> `es` for Spanish)
|
||||
3. Inside the new language folder, change the variable names in `main.js` and `footer.js` to the relevant language short code (`enMain` —> `esMain` for Spanish)
|
||||
4. Duplicate the [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) and rename it to the new language code.
|
||||
5. In [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), add scripts for the newly created config files.
|
||||
6. Add the related language `day.js` script from [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) to the [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
|
||||
|
||||
### Ghost Dashboard Changes
|
||||
|
||||
Update the publication assets by going to the Ghost dashboard > settings > general and uploading the publications's [icon](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), [logo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png), and [cover](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png).
|
||||
81
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
Normal file
81
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
# Як додати тести Cypress
|
||||
|
||||
При внесенні змін до JavaScript, CSS або HTML, які можуть змінити функціональність або макет сторінки, важливо додати відповідні інтеграційні тести [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io).
|
||||
|
||||
Щоб дізнатися, як писати тести Cypress, або "специфікації", будь ласка, зверніться до офіційної [документації Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html).
|
||||
|
||||
## Where to add a test
|
||||
|
||||
- Тести Cypress знаходяться в каталозі `./cypress`.
|
||||
|
||||
- Тести Cypress для модуля навчальної програми знаходяться у відповідному каталозі навчальної програми, тобто `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Як проводити тести
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] За користування GitPod, будь ласка, перегляньте [Cypress-GitPod Setup](/how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Переконайтеся, що MongoDB і клієнтські програми запущені
|
||||
|
||||
- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
|
||||
|
||||
- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Запустіть тести cypress
|
||||
|
||||
To run tests against production builds, replace `dev` with `prd` below.
|
||||
|
||||
- Щоб запустити всі тести в каталозі `./cypress`:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run cypress:dev:run
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Для запуску одного тесту:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run cypress:dev:run -- --spec=cypress/pathToYourSpec/youSpecFileName.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Щоб створити збірку розробки, запустіть сервер розробки і виконайте всі існуючі тести cypress:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run e2e:dev:run
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Налаштування Cypress-GitPod
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Ensure you are on the _Feature Preview_ of GitPod _as of 01/02/2021_
|
||||
|
||||
- Перейдіть на [GitPod Docs - Feature Preview](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/feature-preview/), щоб подивитись як увімкнути _Feature Preview_
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Переконайтеся, що середовище розробки запущене
|
||||
|
||||
If starting the GitPod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
|
||||
|
||||
- Запустіть базу даних
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
mongod
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Заповніть базу даних
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run seed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Develop the server and client
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run develop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Встановіть інструменти збірки Cypress
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run cypress:install-build-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Коли запитається у терміналі, виберіть вашу розкладку клавіатури за мовою/регіоном
|
||||
|
||||
Тепер, [Cypress може бути запущений](/how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-run-the-cypress-tests)
|
||||
123
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
Normal file
123
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
> **Note:** This is an **optional** step and is required only when working with email workflows
|
||||
|
||||
- [Introduction](#introduction)
|
||||
- [Installing MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
|
||||
- [Using MailHog](#using-mailhog)
|
||||
- [Useful Links](#useful-links)
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Some email workflows, like updating a user's email, requires the back-end api-server to send outgoing emails. MailHog is an alternative to using an email service provider to send actual email messages. It is a developer tool for email testing that will catch the email messages sent by your freeCodeCamp instance.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing MailHog
|
||||
|
||||
MailHog can be installed on macOS, Windows and Linux or used via Docker
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Installing MailHog with Docker</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
If you have Docker installed then you can use
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
to start MailHog in the background and
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker stop mailhog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
to stop it.
|
||||
|
||||
When the installation completes, you can start [using MailHog](#using-mailhog).
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Installing MailHog on macOS</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
Install MailHog on macOS with [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
brew install mailhog
|
||||
brew services start mailhog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above commands will start a mailhog service in the background.
|
||||
|
||||
When the installation completes, you can start [using MailHog](#using-mailhog).
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Installing MailHog on Windows</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
Download the latest version of MailHog from [MailHog's official repository](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases). Locate and click on the link for your Windows version (32 or 64 bit) and a .exe file will be downloaded to your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
When the download completes, click to open the file. A Windows firewall notification may appear, requesting access permission for MailHog. A standard Windows command line prompt will open where MailHog will be running once firewall access is granted.
|
||||
|
||||
Close MailHog by closing the command prompt window. To start MailHog again, click on the MailHog executable (.exe) file that was downloaded initially - it is not necessary to download a new MailHog installation file.
|
||||
|
||||
Start [using MailHog](#using-mailhog).
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Installing MailHog on Linux</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
First, install [Go](https://golang.org).
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following commands to install GO on Debian-based systems like Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo apt-get install golang
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following commands to install GO on RPM-based systems like CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat Linux, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo dnf install golang
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, run the following commands to install GO.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo yum install golang
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now set the path for Go with the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
|
||||
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
|
||||
source ~/.profile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, enter the commands below to install and run MailHog.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
|
||||
sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
|
||||
mailhog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start [using MailHog](#using-mailhog).
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## Using MailHog
|
||||
|
||||
Open a new browser tab or window and navigate to [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) to open your MailHog inbox when the MailHog installation has completed and MailHog is running. The inbox will appear similar to the screenshot below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Emails sent by your freeCodeCamp installation will appear as below
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Two tabs that allow you to view either plain text or source content will be available when you open a given email. Ensure that the plain text tab is selected as below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
All links in the email should be clickable and resolve to their URL.
|
||||
|
||||
## Useful Links
|
||||
|
||||
- Check out the [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) repository for further information related to MailHog. Additional information is also available regarding custom MailHog configurations.
|
||||
203
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
Normal file
203
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,203 @@
|
||||
# Допомога з відеозавданнями
|
||||
|
||||
Відеозавдання - це новий тип завдання в навчальній програмі freeCodeCamp.
|
||||
|
||||
Відеозавдання - це маленька частина повноформатного відео-курсу на певну тему. Сторінка з відеозавданням містить Youtube відео. Кожна сторінка завдання має одне запитання з декількома варіантами відповідей, що стосуються відео. Користувач повинен відповісти правильно на питання перед тим, як перейти до наступного відеозавдання в курсі.
|
||||
|
||||
Сторінки з відеозавданнями створюються членами команди freeCodeCamp. YouTube відео також завантажуються членами команди freeCodeCamp. Багато відеозавдань ще не мають запитань, пов'язаних з ними.
|
||||
|
||||
Ви можете допомогти, створиши запитання з декількома варіантами відповіді, повʼязаних з розділом відео, та додавши ці питання до файлів markdown для відеозавдань.
|
||||
|
||||
## Challenge Template
|
||||
|
||||
Нижче наведено зразок того, як виглядають файли завдання markdown.
|
||||
|
||||
````md
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
|
||||
title: Challenge Title
|
||||
challengeType: 11
|
||||
videoId: 'YouTube videoId for video challenge'
|
||||
forumTopicId: 12345
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# --description--
|
||||
|
||||
Challenge description text, in markdown
|
||||
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<div>example code</div>
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
# --question--
|
||||
|
||||
На даний момент ці поля використовуються для Python завдань з декількома варіантами відповіді.
|
||||
|
||||
## --text--
|
||||
|
||||
The question text goes here.
|
||||
|
||||
## --answers--
|
||||
|
||||
Answer 1
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Answer 2
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
More answers
|
||||
|
||||
## --video-solution--
|
||||
|
||||
Номер правильної відповіді знаходиться тут.
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating questions for video challenges
|
||||
|
||||
### Access the video challenge markdown files
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the markdown files for video challenges at the following locations in the curriculum:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
|
||||
- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
|
||||
- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
|
||||
- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
|
||||
|
||||
Pick a challenge markdown file from the options above.
|
||||
|
||||
### Skim through the video associated with the challenge and create a multiple-choice question
|
||||
|
||||
First, find the videoId.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in the following code from the header of a video challenge markdown file, the videoId is "nVAaxZ34khk". On GitHub, the information should be laid out in a table format.
|
||||
|
||||
````
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
|
||||
videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
|
||||
---
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, access the YouTube video with that `videoId`. The URL for the video will be:
|
||||
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (replace `videoId` in the URL with the video's ID - without square brackets)
|
||||
|
||||
In the example above, the URL is https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
|
||||
|
||||
Skim the YouTube video with that videoId and think of a multiple-choice question based on the content of the video.
|
||||
|
||||
### Add the question to the markdown file
|
||||
|
||||
You can add the question locally or using the GitHub interface. To add the question locally, you need to [set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md). You can also find the file on GitHub and click the edit button to add the question right in your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
If a question has not yet been added to a particular video challenge, it will have the following default question:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
# --question--
|
||||
|
||||
## --text--
|
||||
|
||||
Question text
|
||||
|
||||
## --answers--
|
||||
|
||||
Answer 1
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Answer 2
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
More answers
|
||||
|
||||
## --video-solution--
|
||||
|
||||
1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Add/Update the question text under the part that shows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# --question--
|
||||
|
||||
## --text--
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Add/Update answers (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2`, and so on) under `## --answers--`. Make sure to update the number under `## --video-solution--` with the correct answer number. You can add more possible answers using the same format. The question and answers can be surrounded with quotation marks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Question examples
|
||||
|
||||
````md
|
||||
# --question--
|
||||
|
||||
## --text--
|
||||
|
||||
What does this JavaScript code log to the console?
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
console.log('hello world');
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
## --answers--
|
||||
|
||||
hello _world_
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**hello** world
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
hello world
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## --video-solution--
|
||||
|
||||
3
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
````md
|
||||
# --question--
|
||||
|
||||
## --text--
|
||||
|
||||
What will print out after running this code:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
width = 15
|
||||
height = 12.0
|
||||
print(height/3)
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
## --answers--
|
||||
|
||||
39
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
4
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
4.0
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
5.0
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
5
|
||||
|
||||
## --video-solution--
|
||||
|
||||
3 ````
|
||||
|
||||
For more examples, you can look at the markdown files for the following video course. All the challenges already have questions: [Python for Everybody Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
|
||||
|
||||
## Open a pull request
|
||||
|
||||
After creating one or more questions, you can commit the changes to a new branch and [open a pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request.md).
|
||||
183
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
Normal file
183
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
|
||||
# How to open a Pull Request (PR)
|
||||
|
||||
A pull request (PR) enables you to send changes from your fork on GitHub to freeCodeCamp.org's main repository. Once you are done making changes to the code, you can follow these guidelines to open a PR.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Your PR should be in English. See [here](index.md#translations) for how to contribute translations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prepare a good PR title
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend using [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull request. The convention has the following format:
|
||||
|
||||
> `<type>([optional scope(s)]): <description>`
|
||||
>
|
||||
> For example:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> `fix(learn): tests for the do...while loop challenge`
|
||||
|
||||
When opening a Pull Request(PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
|
||||
|
||||
**Type:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Type | When to select |
|
||||
|:----- |:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| fix | Changed or updated/improved functionality, tests, the verbiage of a lesson, etc. |
|
||||
| feat | Only if you are adding new functionality, tests, etc. |
|
||||
| chore | Changes that are not related to code, tests, or verbiage of a lesson. |
|
||||
| docs | Changes to `/docs` directory or the contributing guidelines, etc. |
|
||||
|
||||
**Scope:**
|
||||
|
||||
You can select a scope from [this list of labels](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
|
||||
|
||||
**Description:**
|
||||
|
||||
Keep it short (less than 30 characters) and simple, you can add more information in the PR description box and comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Some examples of good PRs titles would be:
|
||||
|
||||
- `fix(a11y): improved search bar contrast`
|
||||
- `feat: add more tests to HTML and CSS challenges`
|
||||
- `fix(api,client): prevent CORS errors on form submission`
|
||||
- `docs(i18n): Chinese translation of local setup`
|
||||
|
||||
## Proposing a Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
1. Once the edits have been committed, you will be prompted to create a pull request on your fork's GitHub Page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. By default, all pull requests should be against the freeCodeCamp main repo, `main` branch.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure that your Base Fork is set to freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp when raising a Pull Request.
|
||||
|
||||
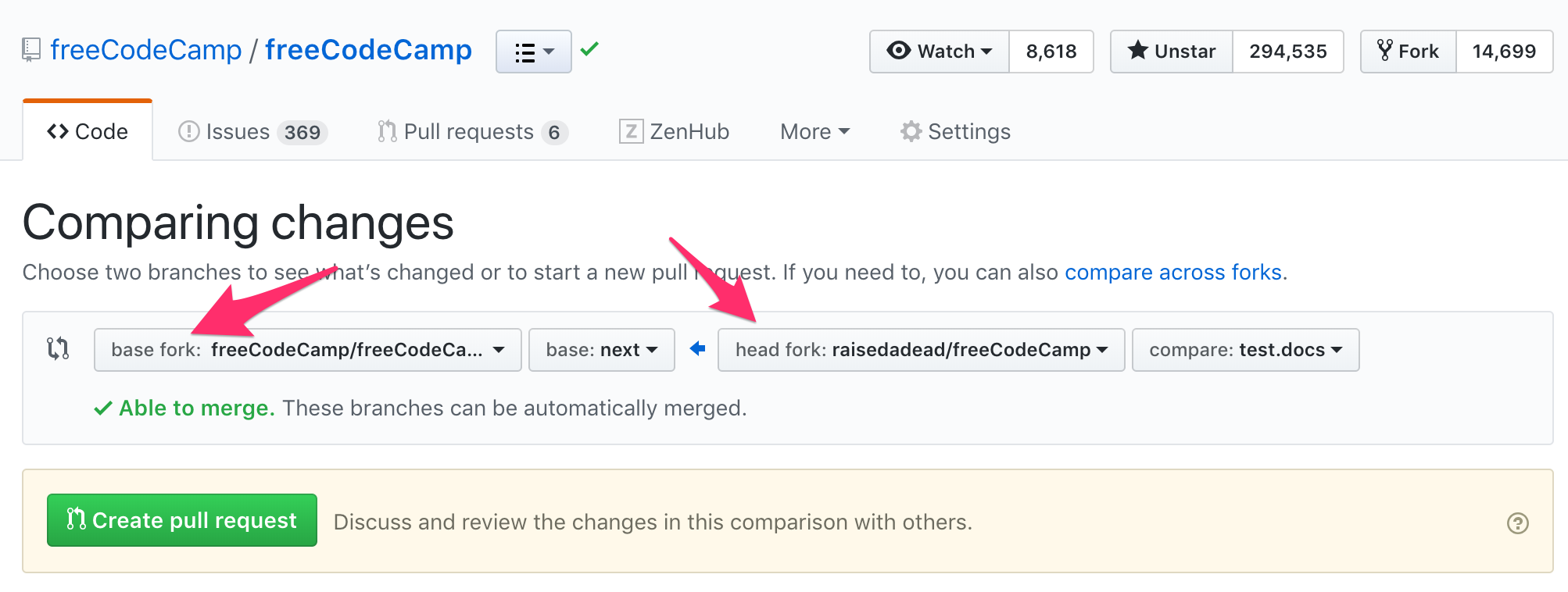
|
||||
|
||||
3. Submit the pull request from your branch to freeCodeCamp's `main` branch.
|
||||
|
||||
4. In the body of your PR include a more detailed summary of the changes you made and why.
|
||||
|
||||
- You will be presented with a pull request template. This is a checklist that you should have followed before opening the pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
- Fill in the details as you see fit. This information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
|
||||
|
||||
- If the PR is meant to address an existing GitHub Issue then, at the end of your PR's description body, use the keyword _Closes_ with the issue number to [automatically close that issue if the PR is accepted and merged](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
|
||||
|
||||
> Example: `Closes #123` will close issue 123
|
||||
|
||||
5. Indicate if you have tested on a local copy of the site or not.
|
||||
|
||||
- This is very important when making changes that are not just edits to text content like documentation or a challenge description. Examples of changes that need local testing include JavaScript, CSS, or HTML which could change the functionality or layout of a page.
|
||||
|
||||
- If your PR affects the behaviour of a page it should be accompanied by corresponding [Cypress integration tests](how-to-add-cypress-tests.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Feedback on pull requests
|
||||
|
||||
> Congratulations! :tada: on making a PR and thanks a lot for taking the time to contribute.
|
||||
|
||||
Our moderators will now take a look and leave you feedback. Please be patient with the fellow moderators and respect their time. All pull requests are reviewed in due course.
|
||||
|
||||
And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] If you are to be contributing more pull requests, we recommend you read the [making changes and syncing](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md#making-changes-locally) guidelines to avoid having to delete your fork.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conflicts on a pull request
|
||||
|
||||
Conflicts can arise because many contributors work on the repository, and changes can break your PR which is pending a review and merge.
|
||||
|
||||
More often than not you may not require a rebase, because we squash all commits, however, if a rebase is requested, here is what you should do.
|
||||
|
||||
### For usual bug fixes and features
|
||||
|
||||
When you are working on regular bugs and features on our development branch `main`, you are able to do a simple rebase:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Rebase your local copy:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git checkout <pr-branch>
|
||||
git pull --rebase upstream main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Resolve any conflicts and add / edit commits
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
# Either
|
||||
git add .
|
||||
git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
|
||||
|
||||
# Or
|
||||
git add .
|
||||
git commit --amend --no-edit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Push back your changes to the PR
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git push --force origin <pr-branch>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### For upcoming curriculum and features
|
||||
|
||||
When you are working on features for our upcoming curriculum `next-*` branches, you have to do a cherry pick:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Make sure your upstream comes in sync with your local:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git checkout main
|
||||
git fetch --all --prune
|
||||
git checkout next-python-projects
|
||||
git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Take backup
|
||||
|
||||
a. Either delete your local branch after taking a backup (if you still have it locally):
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git checkout <pr-branch-name>
|
||||
|
||||
# example:
|
||||
# git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
|
||||
|
||||
git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
|
||||
|
||||
# example:
|
||||
# git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
|
||||
|
||||
git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
b. Or just a backup of your pr branch (if you do not have it locally):
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
|
||||
|
||||
# example:
|
||||
# git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Start off with a clean slate:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
|
||||
git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Resolve any conflicts, and cleanup, install run tests
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run clean
|
||||
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
npm run test:curriculum --superblock=<superblock-name>
|
||||
|
||||
# example:
|
||||
|
||||
# npm run test:curriculum --superblock=python-for-everybody
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. If everything looks good push back to the PR
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
|
||||
```
|
||||
54
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-proofread-files.md
Normal file
54
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-proofread-files.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
# Як редагувати переклади
|
||||
|
||||
Наша команда з редагування відповідає за забезпечення точних перекладів оригінального тексту. Редактори гарантують високу якість перекладів наших матеріалів.
|
||||
|
||||
Всі наші переклади зроблені від руки, живими людьми. Редагування гарантує, що всі матеріали, як от наша навчальна програма, перекладені систематично та коректно.
|
||||
|
||||
Для того, щоб почати редагування, перейдіть на [нашу перекладацьку платформу](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) та зареєструйтеся. Select "Go to console" in the top navigation bar to switch from the public view to the workspace view.
|
||||
|
||||
## Оберіть файл
|
||||
|
||||
Там ви побачите список проєктів, до яких вам надається доступ. Оберіть проєкт, який би ви хотіли редагувати, та мову.
|
||||
|
||||
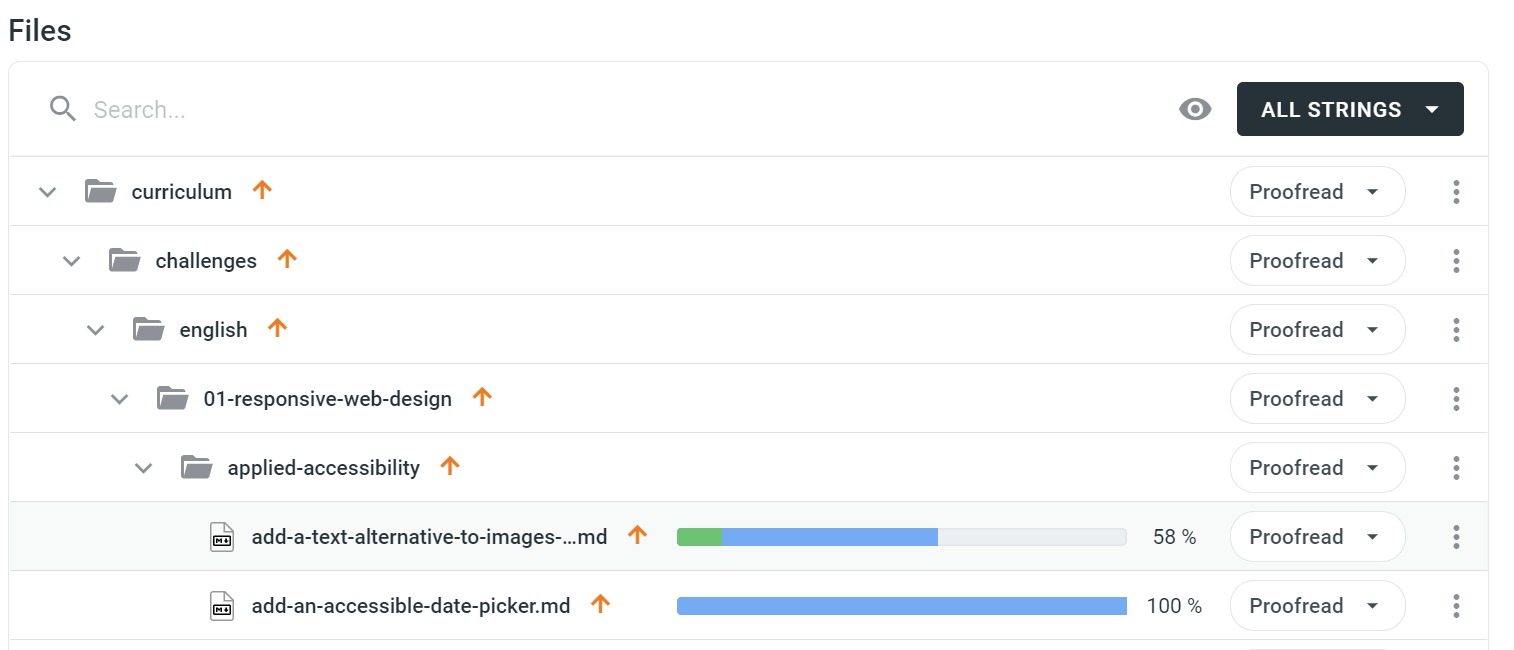
|
||||
|
||||
Тепер ви повинні побачити список доступних файлів. Виберіть ваш файл, натиснувши клавішу `Proofread` справа від файлу, тоді оберіть `Proofreading` з меню, що з'явилось.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Якщо ви у цьому робочому вікні, але хочете [перекладати файл](how-to-translate-files.md), а не редагувати, ви можете натомість обрати `Crowdsourcing` у запропонованому меню.
|
||||
|
||||
## Редагуйте переклади
|
||||
|
||||
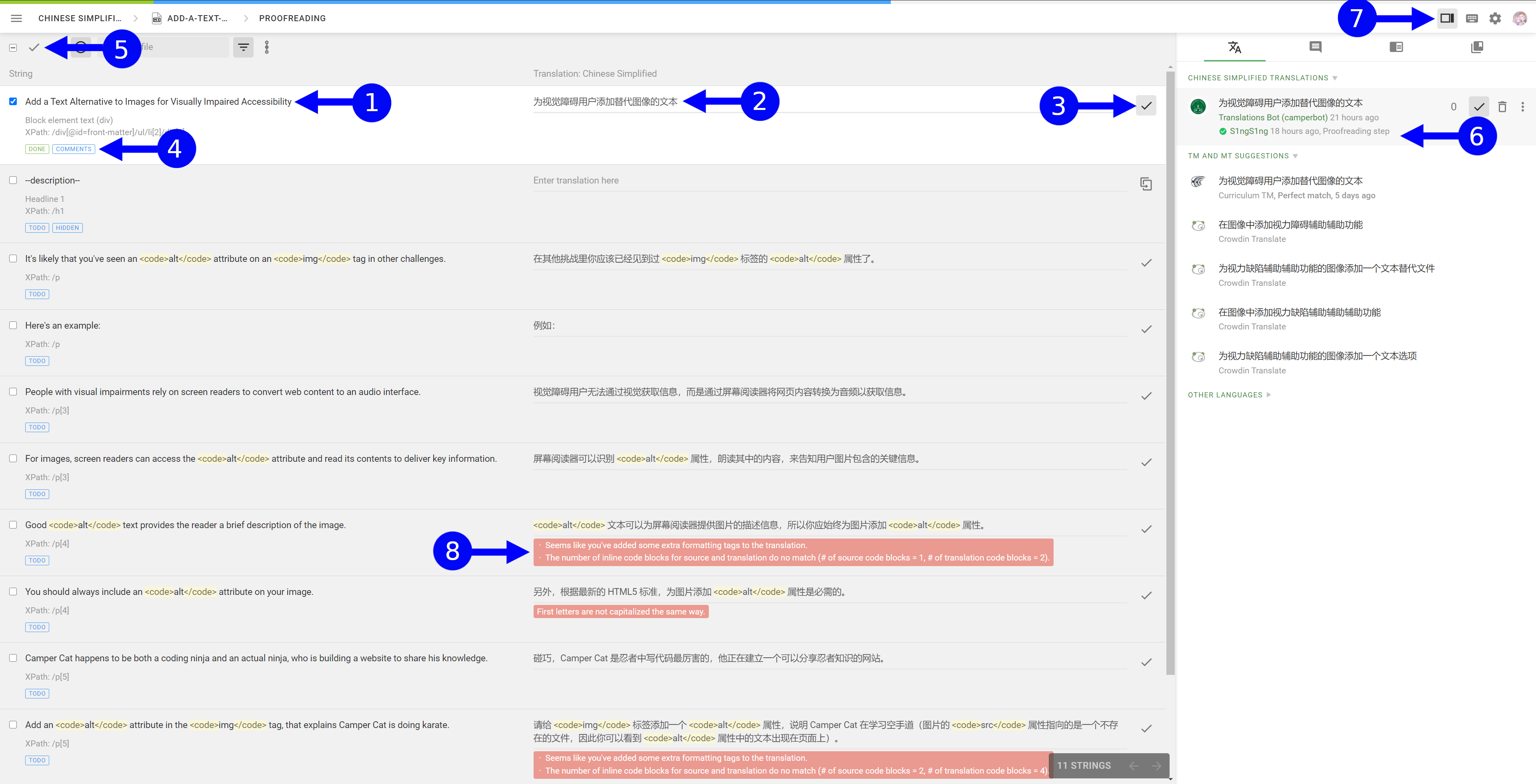
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
|
||||
|
||||
Тут ви побачите список рядків у вибраному файлі разом з їхніми перекладами. Тут показано переклад, який отримав найвищий бал (між голосами за та проти) від спільноти перекладачів.
|
||||
|
||||
Поки ви можете переглядати _ all_ запропоновані переклади для цього речення, оцінки спільноти (між голосами за та проти) повинні бути взяті до уваги під час вибору перекладу для затвердження. Спільнота може розглядати запропоновані переклади та рекомендувати, який саме найбільш точний і зрозумілий.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Це оригінальний рядок (англійською мовою).
|
||||
2. Це відповідний перекладений рядок. The most popular translation proposal, based on upvotes and downvotes, will be displayed here.
|
||||
3. Clicking this checkmark button will approve that translation.
|
||||
4. Crowdin will display the status of each string. `Done` means a translation has been approved and will be downloaded on our next Crowdin pull. `Todo` means the string has not been proofread. `Hidden` means the string is locked and _should not be translated_. `Comment` means the string has a related comment.
|
||||
5. Translations can be selected with the checkboxes and approved here in one bulk action.
|
||||
6. You can view the community proposed translations, their popularity scores, and Crowdin suggested translations here.
|
||||
7. This button shows/hides the right-hand side display pane, where you can view translations, comments, translation memory, and glossary terms.
|
||||
8. Crowdin displays error messages here from the quality assurance checks. In other words, if something does not seem correct in the translation, Crowdin will notify you. These translations should be approved with care.
|
||||
|
||||
No additional actions are required once a file has been proofread.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Approving a string in the proofreading view will mark it as complete and it will be downloaded in our next pull from Crowdin to GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
## Becoming a proofreader
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any questions, or are interested in becoming a proofreader, feel free to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors). We will typically grant you proofreading access if you have been contributing to freeCodeCamp for a while.
|
||||
|
||||
Our staff team and community moderators teams are always looking for kind volunteers like you who help us make high quality translations available to the world.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Crowdin will allow you to approve your translations. In general, it is best to allow another proofreader to review your proposed translations as extra safety to ensure there are no errors.
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating a channel on Chat for a world language
|
||||
|
||||
For the most part we encourage you to use the [contributors chat](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors) room for all correspondence. However if the team of volunteer translators grows for a certain language, we can consider creating additional break-out channel for the language.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are already a proofreader and are interested in having a dedicated channel on our chat servers for a specific language, [fill out this form](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
|
||||
575
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
Normal file
575
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,575 @@
|
||||
Follow these guidelines for setting up freeCodeCamp locally on your system. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of these contribution workflows – like fixing bugs in the codebase or curriculum – need you to run freeCodeCamp locally on your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] If you are not interested in setting up freeCodeCamp locally, consider using Gitpod, a free online dev environment.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
|
||||
>
|
||||
> (Starts a ready-to-code dev environment for freeCodeCamp in your browser.)
|
||||
|
||||
### How to prepare your local machine
|
||||
|
||||
Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
We primarily support development on Linux and Unix-based systems. Our staff and community contributors regularly work with the codebase using tools installed on Ubuntu and macOS.
|
||||
|
||||
We also support Windows 10 via WSL2, which you can prepare by [reading this guide](how-to-setup-wsl.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Some community members also develop on Windows 10 natively with Git for Windows (Git Bash), and other tools installed on Windows. We do not have official support for such a setup at this time, we recommend using WSL2 instead.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Prerequisites:
|
||||
|
||||
| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
|
||||
| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `16.x` | We use the "Active LTS" version, See [LTS Schedule](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
|
||||
| npm (comes bundled with Node) | `8.x` | We use the version bundled with Node.js Active LTS. |
|
||||
| [MongoDB Community Server](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `4.0.x` | - |
|
||||
|
||||
> [!ATTENTION] If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions. See [troubleshooting](#troubleshooting) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
If Node.js is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
node -v
|
||||
npm -v
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above, also known as Long Term Support (LTS) releases.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
|
||||
|
||||
2. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Install a code editor of your choice.
|
||||
|
||||
We highly recommend using [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) or [Atom](https://atom.io/). These are great, free and open source code editors.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Set up linting for your code editor.
|
||||
|
||||
You should have [ESLint running in your editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), and it will highlight anything that doesn't conform to [freeCodeCamp's JavaScript Style Guide](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] Please do not ignore any linting errors. They are meant to **help** you and to ensure a clean and simple codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
## Fork the repository on GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of freeCodeCamp's main repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of freeCodeCamp on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
|
||||
|
||||
**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repository:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the freeCodeCamp repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
|
||||
|
||||
2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
|
||||
|
||||
3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the freeCodeCamp repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub (screenshot)
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub" />
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## Clone your fork from GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository that should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING] If you are working on a WSL2 Linux Distro, you might get performance and stability issues by running this project in a folder which is shared between Windows and WSL2 (e.g. `/mnt/c/Users/`). Therefore we recommend to clone this repo into a folder which is mainly used by your WSL2 Linux Distro and not directly shared with Windows (e.g. `~/PROJECTS/`).
|
||||
>
|
||||
> See [this GitHub Issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) for further Information about this problem.
|
||||
|
||||
Run these commands on your local machine:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
|
||||
|
||||
_i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will download the entire freeCodeCamp repository to your projects directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
|
||||
|
||||
## Set up syncing from parent
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
|
||||
|
||||
[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred `upstream` repository. Your fork referred to as the `origin` repository.
|
||||
|
||||
You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change directory to the new freeCodeCamp directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cd freeCodeCamp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git remote -v
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
|
||||
origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
|
||||
upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
|
||||
upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Running freeCodeCamp locally
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have a local copy of freeCodeCamp, you can follow these instructions to run it locally. This will allow you to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Preview edits to pages as they would appear on the learning platform.
|
||||
- Work on UI related issues and enhancements.
|
||||
- Debug and fix issues with the application servers and client apps.
|
||||
|
||||
If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
|
||||
|
||||
And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/home).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] You may skip running freeCodeCamp locally if you are simply editing files. For instance, performing a `rebase`, or resolving `merge` conflicts.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> You can always return to this part of the instructions later. You should **only** skip this step if you do not need to run the apps on your machine.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [Skip to making changes](#making-changes-locally).
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Set up the environment variable file
|
||||
|
||||
The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` that is accessed dynamically during the installation step.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
# Create a copy of the "sample.env" and name it ".env".
|
||||
# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- tabs:start -->
|
||||
|
||||
#### **macOS/Linux**
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
cp sample.env .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### **Windows**
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
copy sample.env .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- tabs:end -->
|
||||
|
||||
The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] Keep in mind if you want to use services like Auth0 or Algolia, you'll have to acquire your own API keys for those services and edit the entries accordingly in the `.env` file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Install dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: Start MongoDB and seed the database
|
||||
|
||||
Before you can run the application locally, you will need to start the MongoDB service.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Unless you have MongoDB running in a setup different than the default, the URL stored as the `MONGOHQ_URL` value in the `.env` file should work fine. If you are using a custom configuration, modify this value as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
Start the MongoDB server in a separate terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- tabs:start -->
|
||||
|
||||
#### **macOS/Linux**
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
mongod
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### **Windows**
|
||||
|
||||
- On Windows, you must specify the full path to the `mongod` binary
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
"C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.6\bin\mongod"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- tabs:end -->
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to replace `3.6` with the version you have installed
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] You can avoid having to start MongoDB every time by installing it as a background service. You can [learn more about it in their documentation for your OS](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's seed the database. In this step, we run the below command that fills the MongoDB server with some initial data sets that are required by services. These include a few schemas, among other things.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run seed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4: Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server
|
||||
|
||||
You can now start up the API server and the client applications.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run develop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This single command will fire up all the services, including the API server and the client applications available for you to work on.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Once ready, open a web browser and **visit <http://localhost:8000>**. If the app loads, congratulations – you're all set! You now have a copy of freeCodeCamp's entire learning platform running on your local machine.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] The API Server serves APIs at `http://localhost:3000`. The Gatsby app serves the client application at `http://localhost:8000`
|
||||
|
||||
> If you visit <http://localhost:3000/explorer> you should see the available APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sign in with a local user
|
||||
|
||||
Your local setup automatically populates a local user in the database. Clicking the `Sign In` button will automatically authenticate you into the local application.
|
||||
|
||||
However, accessing the user portfolio page is a little tricky. In development, Gatsby takes over serving the client-side pages and hence you will get a `404` page for the user portfolio when working locally.
|
||||
|
||||
Simply clicking the **"Preview Custom 404 Page"** button will forward you to the correct page.
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
How to sign in when working locally (screenshot)
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/29990697/71541249-f63cdf00-2923-11ea-8a85-cefb6f9c9977.gif" alt="How to sign in when working locally" />
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## Making changes locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to your local clone of your fork.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You should get an output like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
On branch main
|
||||
Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
|
||||
|
||||
nothing to commit, working directory clean
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not on main or your working directory is not clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git checkout main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Sync the latest changes from the freeCodeCamp upstream `main` branch to your local main branch:
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING] If you have any outstanding pull request that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
|
||||
|
||||
This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp. It is important that you rebase your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
|
||||
|
||||
Update your local copy of the freeCodeCamp upstream repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp main:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git reset --hard upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git push origin main --force
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can validate your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git diff upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The resulting output should be empty.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create a fresh new branch:
|
||||
|
||||
Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your local work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
|
||||
|
||||
Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful and unique.
|
||||
|
||||
Some examples of good branch names are:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
fix/update-challenges-for-react
|
||||
fix/update-guide-for-html-css
|
||||
fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
|
||||
feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
|
||||
translate/add-spanish-basic-html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run freeCodeCamp locally to preview the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
On branch feat/documentation
|
||||
Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes were not staged for commit:
|
||||
(use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
|
||||
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
|
||||
|
||||
modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
|
||||
modified: docs/README.md
|
||||
modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
|
||||
modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git add .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
On branch feat/documentation
|
||||
Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes to be committed:
|
||||
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
|
||||
|
||||
modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
|
||||
modified: docs/README.md
|
||||
modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
|
||||
modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
|
||||
feat: add guide article for alexa skills
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Optional:
|
||||
|
||||
We highly recommend making a conventional commit message. This is a good practice that you will see on some of the popular Open Source repositories. As a developer, this encourages you to follow standard practices.
|
||||
|
||||
Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
fix: update HTML guide article
|
||||
fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
|
||||
feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
|
||||
docs: update contributing guidelines
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
|
||||
|
||||
This does not take any additional time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
|
||||
|
||||
9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git commit --amend
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
|
||||
|
||||
10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git push origin branch/name-here
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
|
||||
|
||||
After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick commands reference
|
||||
|
||||
A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
|
||||
|
||||
| command | description |
|
||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
|
||||
| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. |
|
||||
| `npm run develop` | Starts the freeCodeCamp API Server and Client Applications. |
|
||||
| `npm run storybook` | Starts Storybook for component library development. |
|
||||
| `npm test` | Run all JS tests in the system, including client, server, lint and challenge tests. |
|
||||
| `npm run test-client` | Run the client test suite. |
|
||||
| `npm run test:curriculum` | Run the curriculum test suite. |
|
||||
| `npm run test:curriculum --block='Basic HTML and HTML5'` | Test a specific Block. |
|
||||
| `npm run test:curriculum --superblock='responsive-web-design'` | Test a specific SuperBlock. |
|
||||
| `npm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Run the curriculum test suite, without bailing after the first error |
|
||||
| `npm run test-server` | Run the server test suite. |
|
||||
| `npm run e2e` | Run the Cypress end to end tests. |
|
||||
| `npm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
### Issues with installing the recommended prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on a different OS and/or are still running into issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Please avoid creating GitHub issues for prerequisite issues. They are out of the scope of this project.
|
||||
|
||||
### Issues with the UI, Fonts, build errors, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
If you face issues with the UI, Fonts or see builds errors a cleanup can be useful:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run clean
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
npm run seed
|
||||
npm run develop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
Use the shortcut
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
npm run clean-and-develop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you continue to face issues with the build, cleaning up the workspace is recommend.
|
||||
|
||||
Use `git clean` in interactive mode:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clean -ifdX
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
How to clean git untracked files (screenshot)
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="How to clean git untracked files" />
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Issues with API, login, Challenge Submissions, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
If you can't sign in, and instead you see a banner with an error message that it will be reported to freeCodeCamp, please double-check that your local port `3000` is not in use by a different program.
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- tabs:start -->
|
||||
|
||||
#### **macOS/Linux/WSL on Windows - From Terminal:**
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
netstat -a | grep "3000"
|
||||
|
||||
tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### **On Windows - From Elevated PowerShell:**
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
netstat -ab | Select-String "3000"
|
||||
|
||||
TCP 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTENING
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- tabs:end -->
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Issues installing dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
|
||||
|
||||
The first time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth. Be patient, and if you are still stuck we recommend using GitPod instead of an offline setup.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] If you are using Apple Devices with M1 Chip to run the application locally, it is suggested to use Node v14.7 or above. You might run into issues with dependencies like Sharp otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting Help
|
||||
|
||||
If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors).
|
||||
|
||||
There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
|
||||
133
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-setup-wsl.md
Normal file
133
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-setup-wsl.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
# Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Before you follow these instructions make sure your system meets the requirements
|
||||
>
|
||||
> **WSL 2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Version 2004, Build 19041 or higher) - available for all distributions including Windows 10 Home.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> **Docker Desktop for Windows**: See respective requirements for [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) and [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
|
||||
|
||||
This guide covers some common steps with the setup of WSL2. Once some of the common issues with WSL2 are addressed, you should be able to follow [this local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md) to work with freeCodeCamp on Windows running a WSL distro like Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enable WSL
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) to install WSL1 and followed by upgrading to WSL2.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
1. We recommended using Ubuntu-18.04 or above with WSL2.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> While you may use other non-debian based distros, they all come with their own gotchas and are beyond the scope of this guide.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Update the dependencies for the OS
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt upgrade -y
|
||||
|
||||
# cleanup
|
||||
sudo apt autoremove -y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Set up Git
|
||||
|
||||
Git comes pre-installed with Ubuntu 18.04, verify your Git version with `git --version`.
|
||||
|
||||
```output
|
||||
~
|
||||
❯ git --version
|
||||
git version 2.25.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(Optional but recommended) You can now proceed to [setting up your ssh keys](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) with GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing a Code Editor
|
||||
|
||||
We highly recommend installing [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) on Windows 10. It has great support for WSL and automatically installs all the necessary extensions on your WSL distro.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, you will edit and store your code on Ubuntu-18.04 with VS Code installed on Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
If you use [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), you may need to update your Node interpreter and Npm package manager to what is installed on your WSL distro.
|
||||
|
||||
You can check these settings by going to Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and NPM.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing Docker Desktop
|
||||
|
||||
**Docker Desktop for Windows** allows you to install and run databases like MongoDB and other services like NGINX and more. This is useful to avoid common pitfalls with installing MongoDB or other services directly on Windows or WSL2.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructuction on the [official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) and install Docker Desktop for your Windows distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
There are some minimum hardware requirements for the best experience.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configure Docker Desktop for WSL
|
||||
|
||||
Once Docker Desktop is installed, [follow these instructions](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) and configure it to use the Ubuntu-18.04 installation as a backend.
|
||||
|
||||
This makes it so that the containers run on the WSL side instead of running on Windows. You will be able to access the services over `http://localhost` on both Windows and Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install MongoDB from Docker Hub
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have configured Docker Desktop to work with WSL2, follow these steps to start a MongoDB service:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Launch a new Ubuntu-18.04 terminal
|
||||
|
||||
2. Pull `MongoDB 4.0.x` from dockerhub
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker pull mongo:4.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Start the MongoDB service at port `27017`, and configure it to run automatically on system restarts
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docker run -it \
|
||||
-v mongodata:/data/db \
|
||||
-p 27017:27017 \
|
||||
--name mongodb \
|
||||
--restart unless-stopped \
|
||||
-d mongo:4.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. You can now access the service from both Windows or Ubuntu at `mongodb://localhost:27017`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing Node.js and npm
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend you install the LTS release for Node.js with a node version manager - [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating).
|
||||
|
||||
Once installed use these commands to install and use the Node.js version as needed
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
nvm install --lts
|
||||
|
||||
# OR
|
||||
# nvm install <version>
|
||||
|
||||
nvm install 14
|
||||
|
||||
# Usage
|
||||
# nvm use <version>
|
||||
|
||||
nvm use 12
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Node.js comes bundled with `npm`, you can update to the latest versions of `npm` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm install -g npm@latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Set up freeCodeCamp locally
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have installed the pre-requisites, follow [our local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md) to clone, install and setup freeCodeCamp locally on your machine.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Please note, at this time the set up for Cypress tests (and related GUI needs) are a work in progress. You should still be able to work on most of the codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
## Useful Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code and Docker](https://devlog.sh/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - an article by Mrugesh Mohapatra (Staff Developer at freeCodeCamp.org)
|
||||
- Frequently asked questions on:
|
||||
- [Windows Subsystem for Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
|
||||
- [Docker Desktop for Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
|
||||
191
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
Normal file
191
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
|
||||
# How to Test Translations Locally
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] This process is not required, but documented in case you would like to preview what your translations will look like.
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to test your translations on a local instance of the freeCodeCamp `/learn` site, first ensure you have [set up the codebase](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Enabling a Language
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few steps to take in order to allow the codebase to build in your desired language.
|
||||
|
||||
First, visit the `config/i18n/all-langs.js` file to add the language to the available languages list and configure the values. There are four objects here.
|
||||
|
||||
- `availableLangs`: For both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays, add the text name of the language. This is the value that will be used in the `.env` file later.
|
||||
- `i18nextCodes`: These are the ISO language codes for each language. You will need to add the appropriate ISO code for the language you are enabling. These do need to be unique for each language.
|
||||
- `langDisplayNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
|
||||
- `langCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. These should be Unicode CLDR codes instead of ISO codes.
|
||||
|
||||
As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `all-langs.js` objects should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const availableLangs = {
|
||||
client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
|
||||
curriculum: [
|
||||
'english',
|
||||
'espanol',
|
||||
'chinese',
|
||||
'chinese-traditional',
|
||||
'dothraki'
|
||||
]
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const i18nextCodes = {
|
||||
english: 'en',
|
||||
espanol: 'es',
|
||||
chinese: 'zh',
|
||||
'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
|
||||
dothraki: 'mis'
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const langDisplayNames = {
|
||||
english: 'English',
|
||||
espanol: 'Español',
|
||||
chinese: '中文(简体字)',
|
||||
'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
|
||||
dothraki: 'Dothraki'
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const langCodes = {
|
||||
english: 'en-US',
|
||||
espanol: 'es-419',
|
||||
chinese: 'zh',
|
||||
'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
|
||||
dothraki: 'mis'
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, open the `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.js` file. This data is used for the search bar that loads `/news` articles. While it is unlikely that you are going to test this functionality, missing the data for your language can lead to errors when attempting to build the codebase locally.
|
||||
|
||||
Add an object for your language to the `algoliaIndices` object. You should use the values for the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
|
||||
|
||||
If you were to add Dothraki:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const algoliaIndices = {
|
||||
english: {
|
||||
name: 'news',
|
||||
searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
|
||||
},
|
||||
espanol: {
|
||||
name: 'news-es',
|
||||
searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
|
||||
},
|
||||
chinese: {
|
||||
name: 'news-zh',
|
||||
searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
|
||||
},
|
||||
'chinese-traditional': {
|
||||
name: 'news-zh',
|
||||
searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
|
||||
},
|
||||
dothraki: {
|
||||
name: 'news',
|
||||
searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you will need to tell the client which certifications are translated, and which are still in English. Open the `utils/is-audited.js` file. Within the `auditedCerts`, add a new key with your language's `availableLangs` value. Assign the value of that key to an array containing the _dashed names_ for the certifications that have been translated. Refer to the existing data for those dashed names.
|
||||
|
||||
Continuing the work to enable Dothraki - we have translated the first three certifications:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const auditedCerts = {
|
||||
espanol: [
|
||||
'responsive-web-design',
|
||||
'javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures'
|
||||
],
|
||||
chinese: [
|
||||
'responsive-web-design',
|
||||
'javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures',
|
||||
'front-end-development-libraries',
|
||||
'data-visualization',
|
||||
'back-end-development-and-apis',
|
||||
'quality-assurance'
|
||||
],
|
||||
'chinese-traditional': [
|
||||
'responsive-web-design',
|
||||
'javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures',
|
||||
'front-end-development-libraries',
|
||||
'data-visualization',
|
||||
'back-end-development-and-apis',
|
||||
'quality-assurance'
|
||||
],
|
||||
dothraki: [
|
||||
'responsive-web-design',
|
||||
'javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures',
|
||||
'front-end-development-libraries'
|
||||
]
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, in your `.env` file, set `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` to your new language (use the `availableLangs` value.)
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
CLIENT_LOCALE="dothraki"
|
||||
CURRICULUM_LOCALE="dothraki"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Enabling Localized Videos
|
||||
|
||||
For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx` file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
|
||||
|
||||
```tsx
|
||||
query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
|
||||
challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
|
||||
videoId
|
||||
videoLocaleIds {
|
||||
espanol
|
||||
italian
|
||||
portuguese
|
||||
dothraki
|
||||
}
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.js` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
videoLocaleIds:
|
||||
espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
|
||||
italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
|
||||
portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
|
||||
dothraki: new-id-here
|
||||
dashedName: introduction-why-program
|
||||
---
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
export interface VideoLocaleIds {
|
||||
espanol?: string;
|
||||
italian?: string;
|
||||
portuguese?: string;
|
||||
dothraki?: string;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And finally update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
|
||||
is: challengeTypes.video,
|
||||
then: Joi.object().keys({
|
||||
espanol: Joi.string(),
|
||||
italian: Joi.string(),
|
||||
portuguese: Joi.string(),
|
||||
dothraki: Joi.string()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}),
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading Translations
|
||||
|
||||
Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have the access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Once these are in place, you should be able to run `npm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!ATTENTION] While you may perform translations locally for the purpose of testing, we remind everyone that translations should _not_ be submitted through GitHub and should only be done through Crowdin. Be sure to reset your local codebase after you are done testing.
|
||||
148
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-translate-files.md
Normal file
148
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-translate-files.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
|
||||
# How to Translate freeCodeCamp's resources
|
||||
|
||||
It's our dream to provide you with the resources to learn, no matter the world language you speak. To help us with this massive effort, we have integrated our open-source code-base & curriculum with [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/) - A tool to help us localize our code-base.
|
||||
|
||||
The translation workflow is split into two main activities:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Translating** curriculum files, documentation and UI elements like buttons, labels, etc.:
|
||||
|
||||
As a translator you can sign up on [our translation platform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) and contribute translations in any of the 30+ languages enabled in there.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Proofreading** the translations for all of the above.
|
||||
|
||||
Proofreaders verify that the community contributed translations are uniform in tone and free of common issues like typos, etc. In short, they ensure that the quality of translations is high. Note that we do not use machine translations for a reason.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING] We are no longer using GitHub to translate files directly, if you are a returning contributor head to our [translation platform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) instead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prepare yourself for contributions
|
||||
|
||||
> The freeCodeCamp Localization Roadmap – There Are No Speed Limits
|
||||
|
||||
You can translate as much as you want, when you want. It's only a matter of how much time and energy you are willing to invest as a volunteer translator.
|
||||
|
||||
We just ask that you understand the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Translations are a team effort.**
|
||||
|
||||
Translating freeCodeCamp's resources is one of the most fun and rewarding experiences as a contributor, and it works best if you involve your friends and colleagues who speak the same world language as you.
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend joining [our community forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) and [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors) with your friends and showing your interest before starting off with translations. Crowdin makes it easy to contribute translations, but it's still a lot of work.
|
||||
|
||||
We want you to enjoy contributing and not burn out or lose interest.
|
||||
|
||||
A small group of 4-5 individuals is a good size to start your niche for your world language. You can then recruit even more friends to join the team.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **It costs quite a lot to spin servers for each language.**
|
||||
|
||||
On the surface it might not seem how complicated the technical stack is, but it costs quite a lot to keep the engines running. This includes provisioning additional servers and dedicating staff to look after them.
|
||||
|
||||
freeCodeCamp.org is committed to providing these for free as always, however we need to prioritize resources for those who need them the most. The last thing we want is to shutdown servers for a language if the translation activity dies off & things become outdated.
|
||||
|
||||
Once a language reaches at least a few certifications on the curriculum we can begin deploying the language live on [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn), while you continue to translate the remaining certifications.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, we would want to deploy at least the entire front-end certifications suite when we ship a new world language for the first time.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **But what about the languages not listed on the translation platform?**
|
||||
|
||||
We have looked at our user base and added 30+ most widely spoken languages to the list of enabled languages on the translations platform. Some languages like Chinese and Spanish are already deployed live on **"/learn"** at this moment.
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, the list does not include hundreds of languages out there. We get dozens of requests from contributors like you every day who want to help translate the site into a language they speak.
|
||||
|
||||
We are definitely looking forward to adding more languages to the list, but as you may already guess, it would only be feasible if we get enough momentum around a world language.
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like us to include a new world language, we recommend getting your friends excited about this.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have a small group of people (at least 4-5) interested and committed, we can hop on a call. We will explain all the details and walk you through some of the tools and processes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure you come say "Hi" in our [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors). We post regular updates about translating resources and answer a lot of your queries in there.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, head to our [translation platform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) and login (if you have not contributed to translations before, you will need to create an account).
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, go through the detailed walk-thru below to understand the translation tools and workflows at your disposal.
|
||||
|
||||
Happy translating.
|
||||
|
||||
## Select a Project and File
|
||||
|
||||
Once you visit the translation platform, you should see multiple "projects" available for translation:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Contributing documentation](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs) project, which contains the files for this documentation site.
|
||||
2. [Coding Curriculum](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum) project, which contains our challenge files for our curriculum.
|
||||
3. [Learn User Interface](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui) project which contains strings for UI elements like buttons, labels, etc. for our learning platform.
|
||||
|
||||
Select any project you want to contribute to, and you will see a list of available languages for translation.
|
||||
|
||||
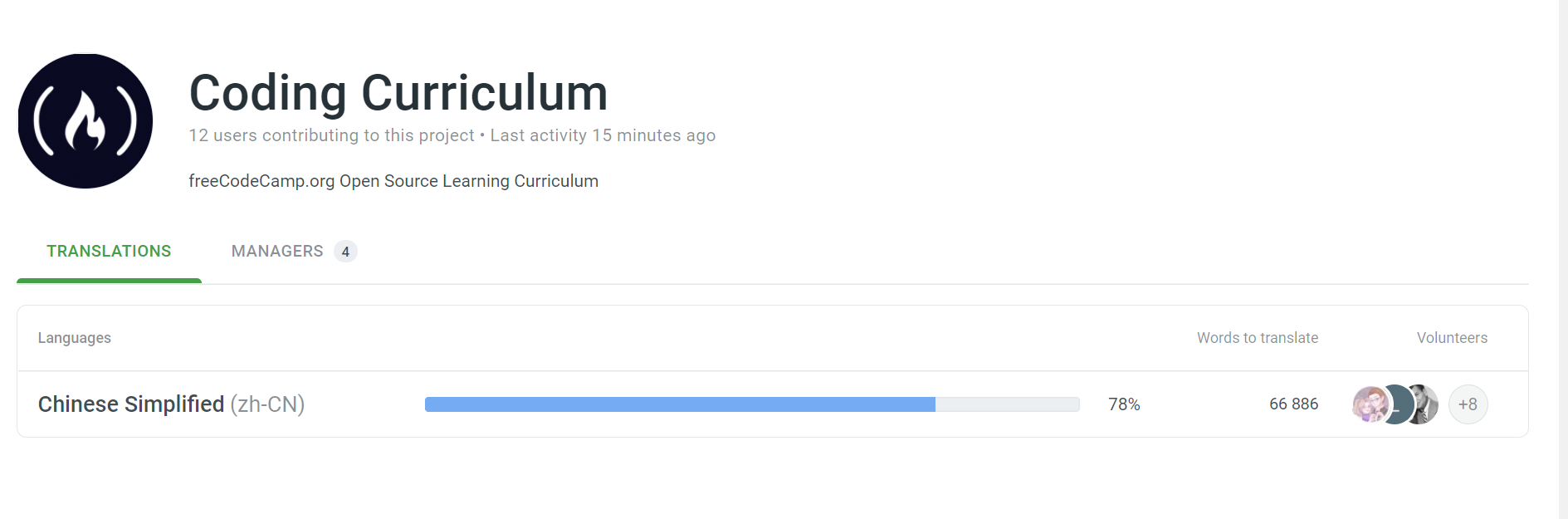
|
||||
|
||||
Select the language you want to work on, and you will see the complete file tree.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Each file and folder will show a progress bar. The **blue** portion of the progress bar indicates what percentage of the file has been translated, while the **green** portion of the progress bar indicates what percentage of the file has been approved by the proofreading team.
|
||||
|
||||
Select a file to work on and Crowdin will open the editor view.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] When the editor view opens, you will need to click the settings icon (shown as a gear) and switch the 'HTML tags displaying' setting to 'SHOW'. This will ensure you can see tags such as `<code></code>` instead of `<0></0>`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Translate Curriculum
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Crowdin separates a document into translatable "strings", usually sentences. Each string is translated individually. Referring to the image above:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A string highlighted in green already has a proposed translation.
|
||||
2. A string highlighted in red does _not_ have a proposed translation.
|
||||
3. A string with greyed out text is not translatable. This is the case for code blocks and other content that must not be translated. You will be unable to select these strings in the editor.
|
||||
4. If a contributor has proposed a translation to a string, Crowdin will display those proposals here. You will not be able to save an identical translation - instead, if a translation is accurate, you should click the `+` icon to "upvote" it. An inaccurate translation can be "downvoted" with the `-` icon.
|
||||
5. Crowdin will recommend translations based on Translation Memory (TM) or Machine Translation (MT). Translation Memory refers to similar or identical strings that we have translated/approved in other files. Machine Translation refers to translations recommended by their integrated library.
|
||||
6. This is the editor pane, where you may write your proposed translation for the selected string.
|
||||
7. The currently selected string in the editor will be highlighted in yellow.
|
||||
8. Here you will see tags indicating the state of the string. `Done` means the string has at least one proposed translation. `Todo` means the string does not have any proposed translations.
|
||||
9. Here you can see the comments window. If you have questions or concerns about a particular string, you can leave a comment on the string here for other translators to see.
|
||||
10. These two "pane" buttons will hide the left (document) and right (comments) views.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] If you see a hidden string that includes translations, please notify us in the [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors) so we can remove the translation from memory.
|
||||
|
||||
When you have completed a translation for a string, select the `Save` button to store your translation on Crowdin. Other contributors will then be able to vote on your translation and proofreaders will be able to approve it.
|
||||
|
||||
You are welcome to translate as many strings as you like - there are no additional steps required when you complete a full file or propose a new translation. Clicking the `Save` button is all that is needed to store a translation.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] If you see something in the English source file that is inaccurate or incorrect, please do not fix it through the translation flow. Instead, leave a comment on the string to notify us that there is a discrepancy, or create a GitHub issue.
|
||||
|
||||
## Translate Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
Translating our contributing documentation is a similar flow to translating our curriculum files.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Our contributing documentation is powered by `docsify`, and we have special parsing for message boxes like this one. If you see strings that start with `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]`, or `[!TIP]`, these words should NOT be translated.
|
||||
|
||||
## Rate Translations
|
||||
|
||||
Crowdin allows you to rate the existing proposed translations. If you attempt to save a translation, you may see a message indicating that you cannot save a duplicate translation - this means another contributor has proposed that identical translation. If you agree with that translation, click the `+` button to "upvote" the translation.
|
||||
|
||||
If you see a translation that is inaccurate or does not provide the same clarity as the original string, click the `-` button to "downvote" the translation.
|
||||
|
||||
Crowdin uses these votes to give a score to each proposed translation for a string, which helps the proofreading team determine which translation is the best fit for each string.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quality Assurance Checks
|
||||
|
||||
We have enabled some quality assurance steps that will verify a translation is as accurate as possible - this helps our proofreaders review proposed translations.
|
||||
|
||||
When you attempt to save a translation, you may see a warning message appear with a notification regarding your proposed translation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This message appears when Crowdin's QA system has identified a potential error in the proposed translation. In this example, we have modified the text of a `<code>` tag and Crowdin has caught that.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING] You have the option to save a translation in spite of errors. If you do, by clicking "Save Anyway", you should also tag a proofreader or project manager and explain why the QA message needs to be ignored in this case.
|
||||
|
||||
## Translation Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these guidelines to ensure our translations are as accurate as possible:
|
||||
|
||||
- Do not translate the content within `<code>` tags. These tags indicate text that is found in code and should be left in English.
|
||||
- Do not add additional content. If you feel a challenge requires changes in the text content or additional information, you should propose the changes through a GitHub issue or a pull request that modifies the English file.
|
||||
- Do not change the order of content.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors) and we will be happy to assist you.
|
||||
15
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
Normal file
15
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# Як використовувати Docker на Windows Home
|
||||
|
||||
Є декілька підводних каменів, яких треба уникнути, коли налаштовуєте Docker на Windows Home. По-перше, ви маєте використовувати [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) як адміністратор. На жаль, Windows Home не підтримує Docker для робочого столу Windows, тому замість нього необхідно використовувати панель інструментів. Він повинен бути запущений від імені Адміністратора, так як при установці використовуються символічні посилання, які інакше створити неможливо.
|
||||
|
||||
Після встановлення панелі інструментів запустіть термінал Docker Quickstart від імені адміністратора. Це створить `default` віртуальну машину, якщо вона ще не створена. Як тільки це сталося, закрийте термінал і відкрийте VirtualBox (знову від Адміністратора). Ви можете побачити `default` машину. Цей сайт є доволі ресурсомістким, тому зупиніть віртуальну машину і підвищить налаштування наскільки ви зможете - зокрема, пам'ять. Було підтверджено, що він працює з 4 ГБ оперативної пам'яті.
|
||||
|
||||
Після того, як ви будете переконані, що Docker працює, скопіюйте репозиторій freeCodeCamp в середину папки `C:\Users`. Ці каталоги є загальними, надаючи Docker доступ до локальних каталогів, які йому необхідні під час установки.
|
||||
|
||||
Якщо ви бачите такі повідомлення як
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
коли ви `npm запустіть docker:init` це, ймовірно, буде вирахувано.
|
||||
494
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
Normal file
494
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,494 @@
|
||||
# How to work on coding challenges
|
||||
|
||||
Our goal is to develop a fun and clear interactive learning experience.
|
||||
|
||||
Designing interactive coding challenges is difficult. It would be much easier to write a lengthy explanation or to create a video tutorial. But for our core curriculum, we're sticking with what works best for most people - a fully interactive, video game-like experience.
|
||||
|
||||
We want campers to achieve a flow state. We want them to build momentum and blast through our curriculum with as few snags as possible. We want them to go into the projects with confidence and gain a wide exposure to programming concepts.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that for Version 7.0 of the freeCodeCamp curriculum, we are moving toward [an entirely project-focused model with a lot more repetition](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/).
|
||||
|
||||
Creating these challenges requires immense creativity and attention to detail. There's plenty of help available. You'll have support from a whole team of contributors to whom you can bounce ideas off and demo your challenges.
|
||||
|
||||
And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors).
|
||||
|
||||
With your help, we can design an interactive coding curriculum that will help millions of people learn to code for years to come.
|
||||
|
||||
The content for each challenge is stored in its markdown file. This markdown file is later converted to HTML using our tools to create interactive web pages.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find all of freeCodeCamp.org's curricular content in the [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges) directory.
|
||||
|
||||
## Set up the tooling for the curriculum
|
||||
|
||||
Before you work on the curriculum, you would need to set up some tooling to help you test your changes. You can use any option from the below:
|
||||
|
||||
- You can [set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md). This is **highly recommended** for regular/repeat contributions. This setup allows you to work and test your changes.
|
||||
- Use Gitpod, a free online dev environment. Clicking the button below will start a ready-to-code dev environment for freeCodeCamp in your browser. It only takes a few minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
|
||||
|
||||
- Edit the files on GitHub's interface by clicking the pencil icon for the corresponding file. While this is the quickest way, It is **not recommended**, because you are unable to test your changes on GitHub. If our maintainers conclude that the changes you made need to be tested locally, you would need to follow the methods above instead.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to work on practice projects
|
||||
|
||||
The practice projects have some additional tooling to help create new projects and steps. To read more, see [these docs](how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Challenge Template
|
||||
|
||||
````md
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
|
||||
title: 'Challenge Title'
|
||||
challengeType: Integer, defined in `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
|
||||
videoUrl: 'url of video explanation'
|
||||
forumTopicId: 12345
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# --description--
|
||||
|
||||
Challenge description text, in markdown
|
||||
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<div>example code</div>
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
# --instructions--
|
||||
|
||||
Challenge instruction text, in markdown
|
||||
|
||||
# --hints--
|
||||
|
||||
Tests to run against user code, in pairs of markdown text and code block test code.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
Code for test one
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want dynamic output based on the user's code, --fcc-expected-- and --fcc-actual-- will be replaced with the expected and actual values of the test's assertion. Take care if you have multiple assertions since the first failing assertion will determine the values of --fcc-expected-- and --fcc-actual--.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
assert.equal(
|
||||
'this will replace --fcc-actual--',
|
||||
'this will replace --fcc-expected--'
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# --seed--
|
||||
|
||||
## --before-user-code--
|
||||
|
||||
```lang
|
||||
Code evaluated before the user’s code.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## --after-user-code--
|
||||
|
||||
```lang
|
||||
Code evaluated after the user’s code, and just before the tests
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## --seed-contents--
|
||||
|
||||
Boilerplate code to render to the editor. This section should only contain code inside backticks, like the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
<p class="main-text">Hello world!</p>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```css
|
||||
body {
|
||||
margin: 0;
|
||||
background-color: #3a3240;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.main-text {
|
||||
color: #aea8d3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# --solutions--
|
||||
|
||||
Solutions are used for the CI tests to ensure that changes to the hints will still pass as intended
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// first solution - the language(s) should match the seed.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// second solution - so if the seed is written in HTML...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// third solution etc. - Your solutions should be in HTML.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# --question--
|
||||
|
||||
These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
|
||||
|
||||
## --text--
|
||||
|
||||
The question text goes here.
|
||||
|
||||
## --answers--
|
||||
|
||||
Answer 1
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Answer 2
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
More answers
|
||||
|
||||
## --video-solution--
|
||||
|
||||
The number for the correct answer goes here.
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 1. In the above sections, examples of `lang` are:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> - `html` - HTML/CSS
|
||||
> - `js` - JavaScript
|
||||
> - `jsx` - JSX
|
||||
|
||||
## Numbering Challenges
|
||||
|
||||
Every challenge needs an `id`. If you don't specify one, then MongoDB will create a new random one when it saves the data; however, we don't want it to do that, since we want the challenge ids to be consistent across different environments (staging, production, lots of different developers, etc.).
|
||||
|
||||
To generate a new one in a shell (assuming MongoDB is running separately):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Run `mongo` command.
|
||||
2. Run `ObjectId()` command.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ mongo
|
||||
MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
|
||||
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
|
||||
MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
|
||||
...
|
||||
$ ObjectId()
|
||||
ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
The result is a new id, for example `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` above.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have your id, put it into the markdown file as the `id` field at the top, e.g.
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
---
|
||||
id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
|
||||
title: Challenge Title
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Naming challenges
|
||||
|
||||
Naming things is hard. We've made it easier by imposing some constraints.
|
||||
|
||||
All challenge titles should be explicit and should follow this pattern:
|
||||
|
||||
\[verb\]\[object clause\]
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some example challenge names:
|
||||
|
||||
- Use Clockwise Notation to Specify the Padding of an Element
|
||||
- Condense arrays with .reduce
|
||||
- Use Bracket Notation to Find the First Character in a String
|
||||
|
||||
## Challenge descriptions/instructions
|
||||
|
||||
Sentences should be clear and concise with minimal jargon. If used, jargon should be immediately defined in plain English.
|
||||
|
||||
Keep paragraphs short (around 1-4 sentences). People are more likely to read several short paragraphs than a wall of text.
|
||||
|
||||
Challenge text should use the second person ("you") to help to give it a conversational tone. This way the text and instructions seem to speak directly to the camper working through the challenge. Try to avoid using the first person ("I", "we", "let's", and "us").
|
||||
|
||||
Don't use outbound links. These interrupt the flow. Campers should never have to google anything during these challenges. If there are resources you think campers would benefit from, add them to the challenge's Guide-related article.
|
||||
|
||||
You can add diagrams if necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
Don't use emojis or emoticons in challenges. freeCodeCamp has a global community, and the cultural meaning of an emoji or emoticon may be different around the world. Also, emojis can render differently on different systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Proper nouns should use correct capitalization when possible. Below is a list of words as they should appear in the challenges.
|
||||
|
||||
- JavaScript (capital letters in "J" and "S" and no abbreviations)
|
||||
- Node.js
|
||||
- Although sometimes inaccurate, non-hyphenated forms of 'back end' and 'front end' should be used, as they are more widely used.
|
||||
|
||||
### The 2-minute rule
|
||||
|
||||
Each challenge should be solvable within 120 seconds by a native English speaker who has completed the challenges leading up to it. This includes the amount of time it takes to read the directions/instructions understand the seeded code, write their code and get all the tests to pass.
|
||||
|
||||
If it takes longer than two minutes to complete the challenge, you have two options:
|
||||
|
||||
- Simplify the challenge, or
|
||||
- Split the challenge into two challenges.
|
||||
|
||||
The 2-minute rule forces you, the challenge designer, to make your directions concise, your seed code clear, and your tests straight-forward.
|
||||
|
||||
We track how long it takes for campers to solve changes and use this information to identify challenges that need to be simplified or split.
|
||||
|
||||
### Modularity
|
||||
|
||||
Each challenge should teach exactly one concept, and that concept should be apparent from the challenge's name.
|
||||
|
||||
We can reinforce previously covered concepts through repetition and variations - for example, introducing h1 elements in one challenge, then h3 elements a few challenges later.
|
||||
|
||||
Our goal is to have thousands of 2-minute challenges. These can flow together and reiterate previously-covered concepts.
|
||||
|
||||
### Formatting challenge text
|
||||
|
||||
Here are specific formatting guidelines for challenge text and examples:
|
||||
|
||||
- Language keywords go in `` \` `` backticks. For example, HTML tag names or CSS property names.
|
||||
- References to code parts (i.e. function, method, or variable names) should be wrapped in `` \` `` backticks. See example below:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
Use `parseInt` to convert the variable `realNumber` into an integer.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- References to file names and path directories (e.g. `package.json`, `src/components`) should be wrapped in `` \` `` backticks.
|
||||
- Multi-line code blocks **must be preceded by an empty line**. The next line must start with three backticks followed immediately by one of the [supported languages](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). To complete the code block, you must start a new line which only has three backticks and **another empty line**. See example below:
|
||||
- Whitespace matters in Markdown, so we recommend that you make it visible in your editor.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** If you are going to use an example code in YAML, use `yaml` instead of `yml` for the language to the right of the backticks.
|
||||
|
||||
The following is an example of code:
|
||||
|
||||
````md
|
||||
```{language}
|
||||
|
||||
[YOUR CODE HERE]
|
||||
|
||||
````
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
- Additional information in the form of a note should be surrounded by blank lines, and formatted: `**Note:** Rest of note text...`
|
||||
- If multiple notes are needed, then list all of the notes in separate sentences using the format: `**Notes:** First note text. Second note text.`
|
||||
- Use single-quotes where applicable
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** The equivalent _Markdown_ should be used in place of _HTML_ tags.
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing tests
|
||||
|
||||
Challenges should have the minimum number of tests necessary to verify that a camper understands a concept.
|
||||
|
||||
Our goal is to communicate the single point that the challenge is trying to teach, and test that they have understood that point.
|
||||
|
||||
Challenge tests can make use of the Node.js and Chai.js assertion libraries. Also, if needed, user-generated code can be accessed in the `code` variable. In addition, the `__helpers` object exposes several functions that simplify the process of writing tests. The available functions are defined in _client/src/utils/curriculum-helpers.ts_.
|
||||
|
||||
## Formatting seed code
|
||||
|
||||
Here are specific formatting guidelines for the challenge seed code:
|
||||
|
||||
- Use two spaces to indent
|
||||
- JavaScript statements end with a semicolon
|
||||
- Use double quotes where applicable
|
||||
|
||||
### Seed code comments
|
||||
|
||||
We have a [comment dictionary](/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.js) that contains the only comments that can be used within the seed code. The exact case and spacing of the dictionary comment must be used. The comment dictionary should not be expanded without prior discussion with the dev-team.
|
||||
|
||||
Comments used should have a space between the comment characters and the comment themselves. In general, comments should be used sparingly. Always consider rewriting a challenge's description or instructions if it could avoid using a seed code comment.
|
||||
|
||||
Example of valid single line JavaScript comment:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Only change code below this line
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
Example of a valid CSS comment:
|
||||
|
||||
```css
|
||||
/* Only change code above this line */
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If a challenge only has a single place where code changes are needed, please use the comments in the following example to instruct the user where changes should be made.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var a = 3;
|
||||
var b = 17;
|
||||
var c = 12;
|
||||
|
||||
// Only change code below this line
|
||||
a = a + 12;
|
||||
b = 9 + b;
|
||||
c = c + 7;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If a challenge has multiple places where the user is expected to change code (i.e. the React challenges)
|
||||
|
||||
```jsx
|
||||
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
|
||||
constructor(props) {
|
||||
super(props);
|
||||
this.state = {
|
||||
text: 'Hello'
|
||||
};
|
||||
// Change code below this line
|
||||
|
||||
// Change code above this line
|
||||
}
|
||||
handleClick() {
|
||||
this.setState({
|
||||
text: 'You clicked!'
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{/* Change code below this line */}
|
||||
<button>Click Me</button>
|
||||
{/* Change code above this line */}
|
||||
<h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Translation of seed code comments
|
||||
|
||||
There are separate comment dictionaries for each language. The [English version of the comment dictionary](/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.js) is the basis for the translations found in the corresponding non-English versions of the files. The non-English version of the Chinese comment dictionary would be located at `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.js`. Each dictionary consists of an array of objects with a unique `id` property and a `text` property. Only the `text` should be modified to encompass the translation of the corresponding English comment.
|
||||
|
||||
Some comments may contain a word/phrase that should not be translated. For example, variable names or proper library names like "React" should not be translated. See the comment below as an example. The word `myGlobal` should not be translated.
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Declare the myGlobal variable below this line
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> We are working on an integration to make it possible to work on i18n for the comment dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hints and Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
Each challenge has a `Get a Hint` button, so a user can access any hints/solutions which have been created for the challenge. Curriculum hints/solutions topics are located on [our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) under the `Guide` category.
|
||||
|
||||
If you find a problem with an existing challenge's hints/solutions topic, you can make suggestions in the [contributors category](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) on the forum. Moderators and users with trust level 3 will review the comments and decide whether or not to include the changes in the corresponding hint/solutions topic.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding new Challenge hints/solutions Topics
|
||||
|
||||
Take the following steps when adding a new challenge hints/solutions related topic.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start by following the same steps for creating a new topic but review the next for creating the title.
|
||||
2. The title of the topic should start with `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide:` concatenated with the actual title of the curriculum challenge. For example, if the challenge is named "`Chunky Monkey`", the topic title would be "`freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`".
|
||||
3. `camperbot` should be the owner of these topics/posts, so you will need to request an admin to change the ownership of the main post to `camperbot`.
|
||||
4. Once the new topic is created, a forum topic id is created. It is located at the end of the forum topic URL. This id must be added to the frontmatter of the curriculum challenge file via the normal pull request process for the `Get a Hint` button to link to the topic.
|
||||
|
||||
### Guidelines for content of hints and solutions topics
|
||||
|
||||
When proposing a solution for a curriculum challenge related Guide topic, the full code must be added. This includes all the original seed code plus any changes needed to pass all the challenge tests. The following template should be used when creating new hints/solutions topics:
|
||||
|
||||
````md
|
||||
# Challenge Name Goes Here
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Problem Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
This summarizes what needs to be done without just restating the challenge description and/or instructions. This is an optional section
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
|
||||
- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Hints
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 1
|
||||
|
||||
Hint goes here
|
||||
|
||||
### Hint 2
|
||||
|
||||
Hint goes here
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function myFunc() {
|
||||
console.log('Hello World!');
|
||||
}
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code Explanation
|
||||
|
||||
- Code explanation goes here
|
||||
- Code explanation goes here
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant Links
|
||||
|
||||
- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
|
||||
- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing Challenges
|
||||
|
||||
Before you [create a pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request.md) for your changes, you need to validate that the changes you have made do not inadvertently cause problems with the challenge.
|
||||
|
||||
1. To test all challenges run the below command from the root directory
|
||||
|
||||
````
|
||||
npm run test:curriculum
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. You can also test a block or a superblock of challenges with these commands
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
npm run test:curriculum --block='Basic HTML and HTML5'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
npm run test:curriculum --superblock=responsive-web-design
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You are also able to test one challenge individually by performing the following steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Switch to the `curriculum` directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd curriculum
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Run the following for each challenge file for which you have changed (replacing `challenge-title-goes-here` with the full title of the challenge):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
npm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here ```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have verified that each challenge you've worked on passes the tests, [please create a pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request.md).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] You can set the environment variable `LOCALE` in the `.env` to the language of the challenge(s) you need to test.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> The currently accepted values are `english` and `chinese`, with `english` being set by default.
|
||||
|
||||
### Useful Links
|
||||
|
||||
Creating and Editing Challenges:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Challenge types](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - what the numeric challenge type values mean (enum).
|
||||
|
||||
2. [Contributing to FreeCodeCamp - Writing ES6 Challenge Tests](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - a video following [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) as he contributes to the old version of the curriculum.
|
||||
267
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
Normal file
267
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,267 @@
|
||||
# How to work on localized client webapp
|
||||
|
||||
The react based client web app that powers our learning platform is built using Gatsby. It is translated into various world languages using [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) and [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/).
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about setting up the client application locally for development by following [our local setup guide here](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md). By default the application is available only in English.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have setup the project locally you should be able to follow this documentation to run the client in the language of your choice from the list of available languages.
|
||||
|
||||
This could be helpful when you are working on a feature that specifically targets something that involves localization, and requires you to validate for instance a button's label in a different language.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] You do not need to follow this document for translating freeCodeCamp's curriculum or contributing documentation. Read [this guide here](how-to-translate-files.md) instead.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's understand how the i18n frameworks and tooling work.
|
||||
|
||||
## File Structure
|
||||
|
||||
Most of files for translating the platform are located in the [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n) folder. Each language has a directory within that containing JSON files with the translations.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
config/i18n
|
||||
└── all-langs.js
|
||||
...
|
||||
client/i18n
|
||||
├── configForTests.js
|
||||
├── config.js
|
||||
├── locales
|
||||
│ ├── chinese
|
||||
│ │ ├── intro.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── links.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── meta-tags.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── motivation.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── translations.json
|
||||
│ │ └── trending.json
|
||||
... ...
|
||||
│ ├── dothraki
|
||||
│ │ ├── intro.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── links.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── meta-tags.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── motivation.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── translations.json
|
||||
│ │ └── trending.json
|
||||
... ...
|
||||
│ ├── english
|
||||
│ │ ├── intro.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── links.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── meta-tags.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── motivation.json
|
||||
│ │ ├── translations.json
|
||||
│ │ └── trending.json
|
||||
│ └── espanol
|
||||
│ ├── intro.json
|
||||
│ ├── links.json
|
||||
│ ├── meta-tags.json
|
||||
│ ├── motivation.json
|
||||
│ ├── translations.json
|
||||
│ └── trending.json
|
||||
├── locales.test.js
|
||||
├── schema-validation.js
|
||||
└── validate-keys.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Some of these files are translated on our translation platform (Crowdin), some are not.
|
||||
|
||||
**Files translated on our translation platform:**
|
||||
|
||||
- The `translations.json` file contains the majority of the text that appears on the user interface elements. The keys are used in the codebase to get the correct text for whatever language is set. This file needs to have the exact same keys in all languages.
|
||||
|
||||
- The `intro.json` file contains the key-value pairs for the introduction text on the certification pages.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to add/update translations for the keys please [read this guide here](how-to-translate-files.md).
|
||||
|
||||
**Files NOT translated on our translations platform:**
|
||||
|
||||
- The `motivation.json` files are not required to have the same quotes, compliments, or array length. Just the same JSON structure.
|
||||
|
||||
- The `trending.json` file contains the titles and links for the trending news articles in the website's footer.
|
||||
|
||||
- The `meta-tags.json` file contains the information for our website's meta tag information.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes to these files are typically done by the staff team. If you see something out of the ordinary we recommend you reach us in the [contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors).
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing the client app in a world language
|
||||
|
||||
You can test the client app in any language available in the [list of languages here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/6b4a6a02568b809fc216ea8566ff5df446d1da4e/config/i18n/all-langs.js#L5).
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
const availableLangs = {
|
||||
client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese'],
|
||||
...
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are testing a new language, create a folder with the language name as the title next to the other languages and copy the JSON files from another language into your new folder.
|
||||
|
||||
Add the language to the `client` array as seen above in the [`config/i18n/all-langs.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/config/i18n/all-langs.js) file.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, follow the instructions in the comments in the same file to add/update the rest of the variables as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, set the `CLIENT_LOCALE` variable in your `.env` file to the locale you want to build and you're ready.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to Structure Components
|
||||
|
||||
If you are working on a feature or a bug for the client web app, say for example adding new UI items on the settings page, you should follow the guidelines below. They will help you prepare the components for localization into all the supported world languages.
|
||||
|
||||
### Functional Component
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
|
||||
|
||||
// in the render method:
|
||||
const { t } = useTranslation();
|
||||
|
||||
// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
|
||||
<p>{t('key')}</p>; // more details below
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Class Component
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
|
||||
|
||||
// withTranslation adds the "t" function to props:
|
||||
const { t } = this.props;
|
||||
|
||||
// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
|
||||
<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // more details below
|
||||
|
||||
// export without redux:
|
||||
export default withTranslation()(Component);
|
||||
|
||||
// or with redux:
|
||||
export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Translate Using the "t" Function
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Translation
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// in the component:
|
||||
<p>{t('p1')}</p>
|
||||
|
||||
// in the JSON file:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"p1": "My paragraph"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// output:
|
||||
<p>My paragraph</p>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### With Dynamic Data
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// in the component:
|
||||
const username = 'moT';
|
||||
|
||||
<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
|
||||
|
||||
// in the JSON file:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// output:
|
||||
<p>Welcome moT</p>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above example passes an object to the `t` function with a `username` variable. The variable will be used in the JSON value where `{{username}}` is.
|
||||
|
||||
## Translate with the `Trans` Component
|
||||
|
||||
The general rule is to use the "t" function when you can. But there's a `Trans` component for when that isn't enough, usually when you have elements embedded in the text. You can use the `Trans` component with any type of react component.
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Elements Nested
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// in the component:
|
||||
import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
// in the JSON file:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"fcc": {
|
||||
"greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// output:
|
||||
<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can place the key inside the component tags like the above example if the text contains "simple" tags with no attributes. `br`, `strong`, `i`, and `p` are the default, but that list can be expanded in the i18n config.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complex Elements Nested
|
||||
|
||||
Other times, you will want to have certain text inside another element, an anchor tag is a good example:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// in the component:
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
|
||||
<a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
|
||||
</Trans>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
// in the JSON file:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// output:
|
||||
<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, the key is set in the attributes of the `Trans` component. The `<0>` and `</0>` in the JSON represent the first child of the component, in this case, the anchor element. If there were more children, they would just count up from there using the same syntax. You can find the children of a component in the react dev tools by inspecting it. `placeholder` is simply there because the linter complains about empty `<a>` elements.
|
||||
|
||||
### With a Variable
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// in the component:
|
||||
const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
|
||||
<a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
|
||||
{{ email }}
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</Trans>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
// in the JSON file:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"fcc": {
|
||||
"email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// output:
|
||||
<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, the key and a variable are set in the attributes of the `Trans` component. `{{ email }}` needs to be somewhere in the `Trans` component as well, it doesn't matter where.
|
||||
|
||||
## Changing Text
|
||||
|
||||
To change text on the client side of things, go to the relevant `.json` file, find the key that is being used in the React component, and change the value to the new text you want. You should search the codebase for that key to make sure it isn't being used elsewhere. Or, if it is, that the changes make sense in all places.
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding Text
|
||||
|
||||
If the text you want to add to the client exists in the relevant `.json` file, use the existing key. Otherwise, create a new key.
|
||||
|
||||
The English file is the "source of truth" for all of the `.json` files sharing the same name. If you need to add a new key, add it there. Then, add the key to **all** of the `translations.json` files.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Use English text for all languages if the file is translated through Crowdin. The tests will fail if you don't.
|
||||
|
||||
It would be nice to keep the keys in the same order across all the files as well. Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] The underscore (`_`) is a reserved character for keys in the client side files. See [the documentation](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) for how they are used.
|
||||
|
||||
## Helpful Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
- [react-i18next docs](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
|
||||
- [i18next docs](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
|
||||
123
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
Normal file
123
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
# How to Work on Practice Projects
|
||||
|
||||
The `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` folder contains tools to help facilitate the creation and maintenance of the freeCodeCamp project-based curriculum.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a new project
|
||||
|
||||
Run `npm run create-project`. This opens up a command line ui that guides you through the process. Once that has finished, there should be a new challenge in the English curriculum that you can use for the first step of the project. For example, if you created a project called `test-project` in the Responsive Web Design certification, it would be in `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to create new steps, the following tools simplify that process.
|
||||
|
||||
## create-next-step
|
||||
|
||||
A one-off script that will automatically add the next step based on the last step numbered as `step-xxx.md` where `xxx` represents the 3-digit step number of the last step. The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code with the editable region markers (ERMs) removed.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** This script also runs [reorder-steps](#reorder-steps).
|
||||
|
||||
### How to run script:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change to the directory of the project.
|
||||
2. Run the following npm command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm run create-next-step
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## create-empty-steps
|
||||
|
||||
A one-off script that automatically adds a specified number of steps at a specific starting step number. The challenge seed code for all steps created will be empty.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** This script also runs [reorder-steps](#reorder-steps).
|
||||
|
||||
### How to run script:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change to the directory of the project.
|
||||
2. Run the following npm command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm run create-empty-steps start=X num=Y # where X is the starting step number and Y is the number of steps to create.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## create-step-between
|
||||
|
||||
A one-off script that automatically adds a new step between two existing consecutive steps. The challenge seed code will use the existing starting step's challenge seed code with the editable region markers (ERMs) removed.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** This script also runs [reorder-steps](#reorder-steps).
|
||||
|
||||
### How to run script:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change to the directory of the project.
|
||||
2. Run the following npm command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm run create-step-between start=X # where X is the starting step number
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## delete-step
|
||||
|
||||
A one-off script that deletes an existing step and then reorders the remaining step files in the project's folder as well as updates the `challengeOrder` property array in the project's `meta.json` with the new order of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to run script
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change to the directory of the project.
|
||||
2. Run the following npm command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm run delete-step num=x # where x is the step number to be deleted.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## reorder-steps
|
||||
|
||||
A one-off script that automatically reorders the step files in a project's markdown files based on the filename. It also updates the `challengeOrder` property array in the project's `meta.json` with the new order of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
### Working Example
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you start with the following project structure:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
step-001.md
|
||||
step-002.md
|
||||
step-003.md
|
||||
step-004.md
|
||||
step-005.md
|
||||
step-006.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At some point you decide you need to delete `step-002.md`, because that step is no longer needed. Also, you decide to break down `step-004.md` into three steps instead of just one.
|
||||
|
||||
To accomplish this restructure, you would need to delete `step-002.md` and then add a `step-004a.md` and a `step-004b.md`. The new folder structure would look like the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
step-001.md
|
||||
step-003.md
|
||||
step-004.md
|
||||
step-004a.md
|
||||
step-004b.md
|
||||
step-005.md
|
||||
step-006.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You now need the file names to be `step-001.md` through `step-007.md`, because you removed one but gained two more for a net difference of one file. Also, the frontmatter of each file below a deleted step or added step will need to be modified by making the `title` key value match the new step number. For example, after renaming `step-3.md` to `step-2.md`, you would need to change `step-2.md`'s title from `Step 03` to `Step 02`.
|
||||
|
||||
See below for the actual project folder changes needed:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
step-001.md
|
||||
step-003.md renamed to step-002.md and title changes to "Step 2"
|
||||
step-004.md renames to step-003.md and title changes to "Step 3"
|
||||
step-004a.md renames to step-004.md and title changes to "Step 4"
|
||||
step-004b.md renames to step-005.md and title changes to "Step 5"
|
||||
step-005.md renames to step-006.md and title changes to "Step 6"
|
||||
step-006.md renames to step-007.md and title changes to "Step 7"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Along with the above changes, the `challengeOrder` key in the project's `meta.json` file needs to reflect the new step order. This is needed because each step below a step deletion and/or step addition changes the `title` associated with each of the affected step's challenge `id`.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to run script
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change to the directory of the project.
|
||||
2. Run the following npm command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm run reorder-steps
|
||||
```
|
||||
54
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
Normal file
54
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
# Як працювати з темою документації
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] A quick reminder that you do not need to setup anything for working on the content for the documentation site.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> To work on the contributing guidelines, you can edit or add files in the `docs` directory [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). When your changes are merged, it will be made available automatically at the documentation site.
|
||||
|
||||
## Структура веб-сайту для документації
|
||||
|
||||
The site is generated using [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org), and served using GitHub pages.
|
||||
|
||||
Typically you would not need to change any configuration or build the site locally. Хочете дізнатись більше? Ось як це працює:
|
||||
|
||||
- The homepage's source for this site is available in [`docs/index.html`](index.html).
|
||||
- We serve this file as a SPA using `docsify` and GitHub Pages.
|
||||
- The `docsify` script generates the content of `markdown` files in `docs` directory on demand.
|
||||
- The homepage is generated from the [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage.md).
|
||||
- the sidebar navigation is generated from [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Serving the documentation site locally
|
||||
|
||||
Clone freeCodeCamp:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
|
||||
docsify serve docs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install `docsify`:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm install -g docsify
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and serve the `/docs` directory
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
docsify serve docs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, if you have installed freeCodeCamp locally (see the local setup guide), we bundle the CLI with the development tools so you can run any of the below commands as needed from the root of the repo:
|
||||
|
||||
### Serve and launch the documentation site only
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run docs:serve
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Serve the documentation site alongside freeCodeCamp locally:
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
npm run develop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> The documentation site should be available at <http://localhost:3200>
|
||||
100
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
Normal file
100
docs/i18n/ukrainian/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
# How to work on freeCodeCamp.org's developer news theme
|
||||
|
||||
The developer news also known as [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) site is powered by [Ghost](https://ghost.org/). We use a custom theme for the look and feel of the site. The source code of the theme is available here: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
|
||||
|
||||
## The Theme
|
||||
|
||||
Ghost uses a simple templating language called [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) for its themes. The theme used on `/news` is based off of the default [casper theme](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper).
|
||||
|
||||
The default theme is commented pretty heavily so that it should be fairly easy to work out what's going on just by reading the code and the comments. Once you feel comfortable with how everything works, Ghost also has a full [theme API documentation](https://themes.ghost.org) which explains every possible Handlebars helper and template.
|
||||
|
||||
**The main files are:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `default.hbs` - The main template file
|
||||
- `index.hbs` - Used for the home page
|
||||
- `post.hbs` - Used for individual posts
|
||||
- `page.hbs` - Used for individual pages
|
||||
- `tag.hbs` - Used for tag archives
|
||||
- `author.hbs` - Used for author archives
|
||||
|
||||
One really neat trick is that you can also create custom one-off templates just by adding the slug of a page to a template file. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
- `page-about.hbs` - Custom template for the `/about/` page
|
||||
- `tag-news.hbs` - Custom template for `/tag/news/` archive
|
||||
- `author-ali.hbs` - Custom template for `/author/ali/` archive
|
||||
|
||||
## Development
|
||||
|
||||
1. Get Ghost installed locally.
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
|
||||
mkdir ghost-local-site
|
||||
cd ghost-local-site
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
ghost install local
|
||||
ghost start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> Note: Currently freeCodeCamp uses Ghost version `2.9.0`, so make sure you are using a version higher than that.
|
||||
|
||||
Be sure to run `ghost` commands from the `ghost-local-site` directory. Follow additional instructions on [Ghost's official documentation](https://docs.ghost.org) if are not familiar with its interface.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Fork and clone the repository in your theme directory (replacing `YOUR_USERNAME` with your GitHub username):
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
cd content/themes/
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Make sure you have all the pre-requisites.
|
||||
|
||||
The theme styles are compiled using Gulp/PostCSS to polyfill future CSS spec. You'll need [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Make sure that your Node.js version is compatible with `ghost`.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Install dependencies and develop the theme
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
npm run develop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Now you can edit `/assets/css/` files, which will be compiled to `/assets/built/` automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Access the development site.
|
||||
|
||||
a. Enter `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` into your address bar. Continue with the setup prompted on the page (if running ghost for the first time).
|
||||
|
||||
b. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Restart Ghost, on a separate terminal once to ensure the theme is available.
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
cd ghost-local-site
|
||||
ghost restart
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
c. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Once you've done this, go to `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` and scroll to the bottom. Make sure you click activate on the `freecodecamp-news-theme`.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Zip the final code and make a pull-request
|
||||
|
||||
The `zip` Gulp task packages the theme files into `dist/<theme-name>.zip`, which we can then upload to the production site.
|
||||
|
||||
When you make a PR, please make sure you have run the below script prior to commiting the code and sending a PR.
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
npm run zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Other Reference and resources
|
||||
|
||||
### PostCSS Features Used
|
||||
|
||||
- Autoprefixer - Don't worry about writing browser prefixes of any kind, it's all done automatically with support for the latest 2 major versions of every browser.
|
||||
- Variables - Simple pure CSS variables
|
||||
- [Color Function](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
|
||||
|
||||
### SVG Icons
|
||||
|
||||
The theme uses inline SVG icons, included via Handlebars partials. You can find all icons inside `/partials/icons`. To use an icon just include the name of the relevant file, eg. To include the SVG icon in `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` - use `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can add your own SVG icons in the same manner.
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
This page describes how to contribute to the freeCodeCamp tutorials and projects that are completed using the CodeRoad VS Code extension.
|
||||
|
||||
## How the tutorials work
|
||||
|
||||
The freeCodeCamp tutorials that use CodeRoad each have their own repo under the freeCodeCamp GitHub organization. They all start with `learn-`. For example, `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
|
||||
|
||||
Each tutorial repo has a `main` branch and a "version" branch, e.g. `v1.0.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
The two main files on the `main` branch are `TUTORIAL.md` and `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` contains all the instructions, hints, titles, and so on, for the tutorial. `coderoad.yaml` contains instructions for CodeRoad, such as what commands to run and when, what files to watch for changes, and what version branch to use for the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
The "version" branch contains the commits that will be loaded on each step of a tutorial. The commit messages on this branch have to be specific. The first commit needs `INIT` for its message and contains all the files to load before the first lesson.
|
||||
|
||||
Subsequent commit messages have to match the step number in `TUTORIAL.md` from the `main` branch. For example, the commit with the message `10.1` will be loaded when a user goes to step `10.1`.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to make changes to commits on a version branch, you would need to rebase and edit the commits you want to change. This will rewrite the Git history, so we cannot accept PRs to these types of branches. Once a version branch is on the freeCodeCamp repo, it should never change.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
|
||||
|
||||
## How to contribute
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Install the [CodeRoad CLI tools](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) with `npm install -g @coderoad/cli`.
|
||||
|
||||
There have been some issues with the latest version. If `coderoad --version` doesn't work after installing, downgrade to `0.7.0` with `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Working on `main`
|
||||
|
||||
This set of instructions is for PRs that only make minor changes on `main` to **existing lessons**. That mainly consists of typo, grammar, hint, and instructional changes or fixes in the `TUTORIAL.md` file.
|
||||
|
||||
For everything else, including adding or deleting lessons, follow the [working on a version branch instructions](#working-on-version-branch). You will not need to create a new version branch for this - you can create a PR following the instructions below.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> These changes will use the existing version branch. If they are substantial, feel free to add them to `CHANGELOG.md`. Most of the time, a good commit message should work
|
||||
|
||||
You never need to modify the `tutorial.json` file directly. That will be created with the CLI tools.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are only making minor changes like fixing a typo or grammatical error, you don't have to test your changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these instructions to make a PR, keeping in mind that instructions usually use the lessons around them for context:
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a copy of the latest version branch with `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` - you do not need to check this branch out, it just needs to exist.
|
||||
- Create and checkout a new branch off of `main`
|
||||
- Make **and commit** your changes. Reminder: You don't need to change anything in the `tutorial.json` file. You likely only need to make changes to `TUTORIAL.md`
|
||||
- Run `coderoad build` to recreate the `tutorial.json` file
|
||||
- Commit the changes with `update json` as the message
|
||||
- Make a PR
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing changes on `main`
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to test your changes to `main` after using the above instructions, follow these instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to run a container
|
||||
- Start the tutorial using the `tutorial.json` file on the new branch
|
||||
|
||||
### Reviewing PR's to `main`
|
||||
|
||||
If reviewing a PR that only changes `main` with instructional or grammar issues as described above, the changes in `TUTORIAL.md` should match the changes in `tutorial.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `tutorial.json` file should not have changes to commit hashes, or step/level ids. Startup or level commands or file watchers likely should not be changed either. There are exceptions if there's an issue with a step, but they should be treated with more caution.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, keep in mind that instructions usually use the lessons around them for context, so make sure they make sense.
|
||||
|
||||
### Working on version branch
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Reminder: Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
|
||||
|
||||
There's no easy way to see exactly what changed between version branches since the Git history will be rewritten. Accepting new version branches to use will need to be done with careful consideration and testing.
|
||||
|
||||
These instructions are for changing anything on a "version" branch, such as tests, test text, reset files, adding and deleting steps, among other things.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these instructions to create a new version:
|
||||
|
||||
- Checkout the **latest** version branch with `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`
|
||||
- Create a new branch off of that, incrementing the version, with `git checkout -b vX.X.Y`
|
||||
- Make your changes to the version branch. See more info in the [CodeRoad Documentation](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial) for how to work with tutorials
|
||||
- Push the new branch to your fork with `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
|
||||
- Checkout the `main` branch
|
||||
- Create a new branch off `main`. e.g. `feat/version-X.X.Y`
|
||||
- Change the `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` to your fork of the repo. This is so you and reviewers can test it before pushing it to the freeCodeCamp repo. Change the version to the new branch in the two spots of that file. Add your changes for the new version to `CHANGELOG.md`. Make any other changes you need.
|
||||
- Commit your changes with the message `feat: release version X.X.Y - <optional description>`
|
||||
- Run `coderoad build` to create a new `tutorial.json` file
|
||||
- Add and commit the file
|
||||
- Push the changes to your fork
|
||||
- Test your changes following the [testing instructions below](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Make any additional changes and commit them as you just did, or, if you are satisfied, follow the rest of the instructions
|
||||
- Make a PR to `main` using your new `feat/version-X.X.Y` branch. Give it a title of `version X.X.Y ready for review`. This will not be merged, it is just to let reviewers know that there is a new version ready
|
||||
- Leave it here for reviewers
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing changes to a version branch
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to run a container
|
||||
- Start the tutorial using the `tutorial.json` file on whatever fork the changes are on. Make sure to use the file on the `feat: version-X.X.Y` branch and not the `main` branch
|
||||
|
||||
### Pushing a new version
|
||||
|
||||
Before pushing a new version, view the new `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (will be merged to `main`) branch on the user's fork. Make sure there are additions to the `CHANGELOG.md` file that include the new changes, and the version in the two spots of `coderoad.yaml` matches the new version branch.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have write access to the freeCodeCamp repo, have verified the `CHANGELOG` and `coderoad.yaml` files, have tested the changes using the instructions above, and want to push a new version of a tutorial:
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Reminder: Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
|
||||
|
||||
- If you don't have a remote to where the new changes exist, create a remote to the user's fork with `git remote add <users_fork>`
|
||||
- Delete any **local** branches that share a name with the new branches. Likely named either `vX.X.Y` or `feat/version-X.X.Y`
|
||||
- Checkout the new version branch with `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y`
|
||||
- Push the new version branch to the freeCodeCamp repo with `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y`. You need to push the new branch before you update `main` with the new `tutorial.json` file
|
||||
- Checkout the users branch that will be merged into `main` with `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
|
||||
- Change the `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` back to the freeCodeCamp repo
|
||||
- Add and commit the changes
|
||||
- Run `coderoad build` to create the new `tutorial.json` file
|
||||
- Add and commit the file
|
||||
- Push the changes to your fork with `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y`
|
||||
- Make a PR to `main` on the freeCodeCamp repo
|
||||
- If you are satisfied, merge it or leave it and ask for a review from someone
|
||||
- After the PR is merged, open the tutorial by following the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to make sure it's loading properly, and that you can get through a few steps
|
||||
- Finally, if any PRs for this version exists, close them
|
||||
|
||||
### How to revert to a previous version
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a new branch off the latest `main` with `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
|
||||
- Revert all commits on this branch up to and including the commit of the version after the one you want to revert to. For example, you may have commits that look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
fix: typo
|
||||
release: version 1.0.1
|
||||
fix: typo
|
||||
release: version 1.0.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to revert to v1.0.0, revert all the commits from `release: version 1.0.1` and after
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a PR. Give it a title of `revert: to version X.X.X`
|
||||
43
docs/i18n/ukrainian/index.md
Normal file
43
docs/i18n/ukrainian/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Спільнота [freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) існує завдяки тисячам подібних до вас волонтерам. Якщо ви хочете долучитися до проєкту аби поділитися своїм часом та досвідом, ми з радістю приймемо вас до себе.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] Перш ніж продовжити, прочитайте, будь ласка, наш короткий [Кодекс поведінки](https://www.freecodecamp.org/code-of-conduct). У нашій спільноті ми чітко керуємося цими правилами, щоб кожен міг вільно та безпечно долучитися до freeCodeCamp.org.
|
||||
|
||||
You are welcome to create, update and fix bugs in our [curriculum](#curriculum), help us fix bugs in freeCodeCamp.org's [learning platform](#learning-platform), or [help us translate](#translations) freeCodeCamp.org to world languages.
|
||||
|
||||
We answer the most common questions about contributing [in our contributor FAQ](FAQ.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Happy contributing.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Навчальна програма
|
||||
|
||||
Нашу навчальну програму курує міжнародна спільнота freeCodeCamp. Завдяки цьому ми можемо постійно враховувати та додавати думки експертів-волонтерів.
|
||||
|
||||
Ви можете допомогти нам збагатити та покращити навчальну програму. Ви також можете оновлювати історії користувачів з проєктів, щоб доповнити поняття тих чи інших концепцій. Ви також можете покращити наші автоматизовані тести, щоб ми могли максимально точно перевіряти код людей.
|
||||
|
||||
**Якщо ви хочете поліпшити нашу навчальну програму, то почитайте [як зробити внесок до навчальної програми](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md).**
|
||||
|
||||
## Переклади
|
||||
|
||||
We are localizing freeCodeCamp.org to major world languages.
|
||||
|
||||
Certifications are already live in some major world languages like [Chinese (中文)](https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/learn), [Spanish (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn/), [Italian (Italiano)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn/), [Portuguese (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn/). We encourage you to read the [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/world-language-translation-effort) and share it with your friends to get them excited about this.
|
||||
|
||||
**If you're interested in translating, here's [how to translate freeCodeCamp's resources](how-to-translate-files.md).**
|
||||
|
||||
## Навчальна платформа
|
||||
|
||||
Our learning platform runs on a modern JavaScript stack. It has various components, tools, and libraries. These include Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
Broadly, we have a Node.js based API server, a set of React-based client applications, testing scripts to evaluate camper-submitted curriculum projects, and more. If you want to productively contribute to the learning platform, we recommend some familiarity with these tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Якщо ви хочете допомогти нам покращити нашу кодову базу...
|
||||
|
||||
**Ви можете застосувати Gitpod — безплатне онлайн-середовище розробки, що запускає готове до кодування середовище для freeCodeCamp у вашому браузері.**
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
|
||||
|
||||
Або ви можете...
|
||||
|
||||
**[встановити freeCodeCamp локально](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md) на свій комп'ютер.**
|
||||
539
docs/i18n/ukrainian/moderator-handbook.md
Normal file
539
docs/i18n/ukrainian/moderator-handbook.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,539 @@
|
||||
# The Official freeCodeCamp Moderator Handbook
|
||||
|
||||
This handbook will help you moderate different places in our community. This covers conversations and interactions in issues & pull request threads on GitHub, the community forum, the chat rooms and other official communities that we foster.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] All freeCodeCamp moderators are community-wide moderators. That is we trust you to oversee any of these places.
|
||||
|
||||
You can serve as a moderator on any of the platforms that are of the most interest to you. Some moderators just help out on GitHub, while others just help out on the forum. Some moderators are active everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
The bottom line is that we want you to enjoy being a moderator, and invest your scarce time in places that are of interest to you.
|
||||
|
||||
> "With great power comes great responsibility." - Uncle Ben
|
||||
|
||||
As a moderator, temperament is more important than technical skill.
|
||||
|
||||
Listen. Be Helpful. Don't abuse your power.
|
||||
|
||||
freeCodeCamp is an inclusive community, and we need to keep it that way.
|
||||
|
||||
We have a single code of conduct that governs our entire community. The fewer the rules, the easier they are to remember. You can read those rules and commit them to memory [here](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] As a moderator we would add you to one or more teams on GitHub, our community forum(s) & chat servers. If you are missing access on a platform that you would like to moderate please [reach out to a staff member](FAQ.md#additional-assistance).
|
||||
|
||||
## Moderating GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
Moderators have two primary responsibilities on GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Triaging and responding to issues
|
||||
2. Reviewing and merging pull requests (a.k.a QA).
|
||||
|
||||
### Moderating GitHub Issues
|
||||
|
||||
We use our main [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) repo as a common issue tracker for all of our repositories. We get new issues every day, all of which need to be triaged, labeled and addressed. This is also a great place to start helping with open-source codebase contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Issue Triage
|
||||
|
||||
[Triaging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage) is a process of prioritizing attention to each new issue report. We have an extensive list of labels that we use to mark each issue's priority, category, status, and scope.
|
||||
|
||||
You can help us organize and triage the issue reports by applying labels from [this list](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels). Usually, a description is available alongside the label explaining its meaning.
|
||||
|
||||
Please pay special attention to the labels `"help wanted"` and `"first timers only"`. These are to be added to threads that you think can be opened up to potential contributors for making a pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
A `"first timer only"` label should be applied to a trivial issue (ex. a typo fix) and should include additional information. You can use this [reply template](moderator-handbook.md#first-timer-only-issues) for triage.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Closing Stale, Outdated, Inactive Issues and Pull Requests
|
||||
|
||||
- Stale issues or PRs are those that have not seen any activity from the author for 21 days (3 weeks from the last activity), but only after a moderator has requested more information/changes.
|
||||
|
||||
- Activity is defined as: Comments requesting an update on the PR and triages like `status: update needed` label etc.
|
||||
|
||||
- If the contributor asks for additional assistance or even time, the above can be relaxed and revisited after a response is given. In any case, the mods should use their best judgment to resolve the outstanding PR's status.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] We recommend you use this list of standard [reply templates](moderator-handbook.md#reply-templates) while triaging issues.
|
||||
|
||||
### Moderating Pull Requests
|
||||
|
||||
Pull Requests (PRs) are how contributors submit changes to freeCodeCamp's repository. We must perform Quality Assurance (QA) on pull requests before we decide whether to merge them, request changes, or close them.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Types of Pull Requests
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Challenge Instruction Edits**
|
||||
|
||||
These are changes to the text of challenges - the Description, Instructions, or Test Text.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also review these right on GitHub and decide whether to merge them. We need to be a bit more careful about these because millions of people will encounter this text as they work through the freeCodeCamp curriculum. Does the pull request make the text more clear without making it much longer? Are the edits relevant and not overly pedantic? Remember that our goal is for challenges to be as clear and as short as possible. They aren't the place for obscure details. Contributors may try to add links to resources to the challenges.
|
||||
|
||||
You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](moderator-handbook.md#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
|
||||
|
||||
If the change looks good, please ensure to leave an approval with a "LGTM" comment. Once a pull request gets at least two approvals (including yours) from the moderators or the dev-team, you can go ahead and merge it.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Challenge Code Edits**
|
||||
|
||||
These are changes to the code in a challenge - the Challenge Seed, Challenge Solution, and Test Strings.
|
||||
|
||||
These pull requests need to be pulled down from GitHub and tested on your local computer or Gitpod to make sure the challenge tests can still be passed with the current solution, and the new code doesn't introduce any errors.
|
||||
|
||||
Some contributors may try to add additional tests to cover pedantic corner-cases. We need to be careful to not make the challenge too complicated. These challenges and their tests should be as simple and intuitive as possible. Aside from the algorithm challenges and interview prep section, learners should be able to solve each challenge within about 2 minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](moderator-handbook.md#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
|
||||
|
||||
If the change looks good, please ensure to leave an approval with a "LGTM" comment. Once a pull request gets at least two approvals (including yours) from the moderators or the dev-team, you can go ahead and merge it.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Platform Changes**
|
||||
|
||||
These code edits change the functionality of the freeCodeCamp platform itself.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes contributors try to make changes without much explanation, but for code changes, we need to make sure there's a genuine need for the change. These pull requests should reference an existing GitHub issue where the reasons for the change are discussed. Then you can open the pull request on your computer and test them out locally.
|
||||
|
||||
After you've done so, if the changes look good, don't merge them quite yet. You can comment on the pull request saying "LGTM", then mention **"@freeCodeCamp/dev-team"** so they can take a final look.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **Automated PRs (Dependabot)**
|
||||
|
||||
Some PRs are automated dependency updates made via an integration. You should not merge or approve these PRs. One of the dev-team members will take care of reviewing and merging such automated PRs.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to review, merge or close pull requests
|
||||
|
||||
##### Assign yourself to a pull request:
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, when you choose a pull request to review, you should assign yourself to it. You can do this by clicking the "assign yourself" link below the "assignees" part on the right-hand column of GitHub's interface.
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the type of pull request it is, follow the corresponding rules listed previously.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Ensure the CI checks are passing:
|
||||
|
||||
Before merging any pull request, make sure that GitHub is reporting all checks to be passing (green check marks) on the pull requests. If you see any of the checks failing, please investigate and clarify the root cause. Is the change being made breaking our tests? Will the site build correctly if the PR is merged? These checks are critical for the stability of the platform.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING] Merging a PR that fails CI/CD checks can cause difficulties for all stakeholders, including the dev-team and contributors.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Handling merge conflicts:
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes there will be a Merge Conflict.
|
||||
|
||||
This means that another pull request has made a change to that same part of that same file. GitHub has a tool for addressing these merge conflicts right on GitHub. You can try to address these conflicts. Just use your best judgment.
|
||||
|
||||
The pull request's changes will be on top, and the main branch's changes will be on the bottom. Sometimes there will be redundant information in there that can be deleted. Before you finish, be sure to delete the `<<<<<<`, `======`, and `>>>>>>` that Git adds to indicate areas of conflict.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are uncertain, please ask one of the fellow moderators or the dev-team for assistance.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Merging a valid pull request:
|
||||
|
||||
If the pull request looks ready to merge (and doesn't require additional approvals - remember we require at least two), you can go ahead and merge it. Be sure to use the default **"Squash and Merge"** option. This will squash all the pull requests commits down into a single commit, making the Git history much easier to read.
|
||||
|
||||
> You should then comment on the pull request, thanking the contributor in your own personal way.
|
||||
|
||||
If the pull request author is a "first-time contributor" you should also congratulate them on their first merged pull request to the repository. You can look at the upper right-hand corner of the PR's body to determine a first-time contributor. It will show `First-time contributor` as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
First time contributor badge on pull requests (screenshot)
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="First time contributor badge on pull requests" />
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
If the pull request doesn't look ready to merge, you can politely reply telling the author what they should do to get it ready. Hopefully, they will reply and get their pull request closer to ready.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need a second opinion on a pull request, go ahead and leave your comments on the pull request, then add the "discussing" label to the pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Closing an invalid pull request:
|
||||
|
||||
Often, a pull request will be low effort. You can usually tell this immediately when the contributor didn't bother checking the checkboxes in the Pull Request Template or used a generic pull request title like "made changes" or "Update index.md".
|
||||
|
||||
There are also situations where the contributor is trying to add a link to their website, include a library they created, or have a frivolous edit that doesn't help anyone but themselves.
|
||||
|
||||
You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](moderator-handbook.md#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Other guidelines for Moderators on GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
Though you will have write access to freeCodeCamp's repository, **you should never push code directly to freeCodeCamp repositories**. All code should enter freeCodeCamp's codebase in the form of a pull request from a fork of the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, you should never accept your own PRs. They must be reviewed by another moderator, just like any other PR.
|
||||
|
||||
If you notice anyone breaking the [code of conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) on GitHub issues, or opening pull requests with malicious content or code, email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to the offending pull request, and we can consider banning them from freeCodeCamp's GitHub organization entirely.
|
||||
|
||||
## Moderating the Forum
|
||||
|
||||
As a Moderator, you help keep our community an enjoyable place for anyone to learn and get help. You will deal with flagged posts and handle spam, off-topic, and other inappropriate conversations.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that once you are a moderator on the forum, you will start to see blue moderator hints about forum members, like "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!" or "[person] hasn't posted in a long time - let's welcome them back."
|
||||
|
||||
![A blue text message saying "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
|
||||
|
||||
These are opportunities for you to welcome them and make them feel extra special. You never know which person who's marginally involved may become our next super-helper, helping many other people in their coding journey. Even the slightest kindness may trigger a cascade of good deeds.
|
||||
|
||||
### Deleting forum posts
|
||||
|
||||
Forum moderators can delete user's posts. You should only do this for the following instances:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Someone has posted a pornographic or graphically violent image.
|
||||
2. Someone has posted a link or code that is malicious in nature and could harm other campers who click on it.
|
||||
3. Someone has flooded a thread with lots of spam messages.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dealing with spam
|
||||
|
||||
For the first spam post of a user, send them a message explaining the problem, and remove the link or post as appropriate. Leave a note on the user's profile explaining the action you have taken. If the problem persists, then quietly block the user from posting (using the silence option on the User Admin panel). Send the user a warning with the Code of Conduct. Check the box in the private message indicating that your message is a "formal warning."
|
||||
|
||||
You can ask questions and report incidents in the [staff forum section](https://forum.freecodecamp.com/c/staff).
|
||||
|
||||
### Dealing with off-topic conversations
|
||||
|
||||
Posts or topics that seem to be in the wrong place can be re-categorized or renamed to whatever would be appropriate.
|
||||
|
||||
In exceptional circumstances, it may be appropriate for a moderator to fork a discussion into multiple threads.
|
||||
|
||||
Again, if you have any problems or questions, make a post with your actions in the Staff category, and tag another moderator if you want them to review your moderating actions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Underage Users
|
||||
|
||||
Our [Terms of Service](https://www.freecodecamp.org/terms) require that freeCodeCamp users be at least 13 years of age. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the below message and delete their forum account (if deletion is not available, suspending the account is sufficient).
|
||||
|
||||
**Email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` to delete the user's freeCodeCamp account as well.**
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
SUBJECT: Users under 13 are not allowed to use the forum per Terms of Service
|
||||
|
||||
It has come to our attention that you are under 13 years of age. Per the [freeCodeCamp terms of service](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service), you must be at least 13 years old to use the site or the forum. We will be deleting both your freeCodeCamp account and your forum account. This restriction keeps us in compliance with United States laws.
|
||||
|
||||
Please rejoin once you have reached at least 13 years of age.
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you for understanding.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Moderating Facebook
|
||||
|
||||
If you see anything that seems to break our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), you should delete it immediately.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes people will post things that they think are funny. They don't realize that what they said or what they shared could be interpreted as offensive. You should delete such posts, but not necessarily ban the person. Hopefully, the user will come to understand that what they posted was inappropriate because the post was deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
But if it is an egregious offense that can't reasonably be attributed to a cultural difference or a misunderstanding of the English language. In that case, you should strongly consider blocking the member from the Facebook group.
|
||||
|
||||
## Moderating Chat
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how moderators deal with violations of our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) on our chat server:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Make sure the user intended to violate the Code of Conduct.**
|
||||
|
||||
Not all violations of the CoC were intended as such. A new camper might post a large amount of code for help, unaware that this can be considered spamming. In these cases, you can just ask them to paste their code with services like CodePen or Pastebin.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **If the camper clearly and intentionally violates the Code of Conduct, the moderator will proceed as follows:**
|
||||
|
||||
Kick or mute the offending person from the chat room. To kick or mute someone, left-click on their profile picture, select the three dots, and select "Remove from room" to kick or "Mute user" to prevent them from sending messages. Then report a short summary of the event in the #mod-log channel. Here's an example of what such a summary might look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Kicked: _@username_
|
||||
Reason(s): _Spamming, trolling_
|
||||
Evidence: _One or more links to the offending message(s)_
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Creating a Private Discussion**
|
||||
|
||||
There may be situations where you need to address a concern with a camper privately. This should not be done through DMs, which can lead to situations where you claim one thing and the camper claims another. Instead, use the bot's functionality to create a private discussion:
|
||||
|
||||
- Call the `!fCC private username` command, where `username` is the camper's chat username.
|
||||
- The bot will create a new channel, and add the mentioned camper and all moderators with the `Your Friendly Moderator` role. While all moderators are added to the channel for transparency, the moderator who calls this command should be the only one to interact with the camper unless they request assistance.
|
||||
- When the conversation is complete, call the `!fCC close` command _in the private channel_ to have the bot close and delete that channel.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **Deleting Messages**
|
||||
|
||||
Moderators can delete messages on our chat server. They should only exercise this ability in four very specific situations:
|
||||
|
||||
- Someone has posted a pornographic or graphically violent image.
|
||||
|
||||
- Someone has posted a link or code that is malicious in nature and could harm other campers who click on it.
|
||||
|
||||
- Someone has flooded the chat with lots of spam messages to such an extreme extent (usually involving bots) to render chat completely unusable.
|
||||
|
||||
- Someone has posted an advertisement and/or a self-promoting message/image (social media).
|
||||
|
||||
In all other situations - even situations where the code of conduct is violated - moderators should not delete the messages as they are important historic records. When you do delete a message, make sure you take a screenshot of it first! The screenshot can be logged in the #mod-log channel.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] If the message contains material that would be illegal to take a screenshot of, copy the message link instead - provide that message link to @raisedadead to forward to Discord's Trust and Safety team.
|
||||
|
||||
5. **Don’t use @all or @here**
|
||||
|
||||
Don’t use @all or @here under any circumstances! Every single person in that chat room will get a notification. In some cases, tens of thousands of people.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, if you want people to see an announcement, you can pin it to the channel to allow everyone to read it.
|
||||
|
||||
6. **Don’t threaten to take action**
|
||||
|
||||
If a camper breaks the code of conduct, don’t threaten to take moderator action, and never warn them in public. Instead, talk to them privately using the bot's `private` command. No one else in that channel needs to know that you banned/suspended the person. If a violation was clearly unintended and doesn't warrant a suspension or private conversation, make the offending camper aware of his / her actions without making it come across as a warning. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
- Camper posts a wall of code to request help:
|
||||
|
||||
Moderator: @username Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code.
|
||||
|
||||
- Or if you really have to explain why:
|
||||
|
||||
Moderator: @username Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code, because it disrupts the chat for everyone and could be considered spamming according to our Code of Conduct.
|
||||
|
||||
- For mild and unintentional violations of the code of conduct:
|
||||
|
||||
Moderator: This is a friendly reminder for everyone to follow the code of conduct: https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
|
||||
|
||||
7. **Don’t brag about being a moderator**
|
||||
|
||||
Do not see yourself as above the community. You are the community. And the community has trusted you to help protect something rare that we all share - a _welcoming_ place for new developers.
|
||||
|
||||
If you brag about being a moderator, people may feel uneasy around you, in the same way that people may feel uneasy around a police officer, even if they’re doing nothing wrong. This is just human nature.
|
||||
|
||||
8. **Don’t contradict other moderators**
|
||||
|
||||
If you disagree with a moderator's action, talk with them in private or bring it up in the #mod-chat channel. Never override a moderator's action, and never contradict the other moderator(s) publicly. Instead, have a cool-headed discussion in `#mod-chat` and convince the moderator that they themselves should reverse their ban or change their point of view.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember: we’re all on the same team. We want to dignify the role of moderators and present a unified front.
|
||||
|
||||
9. **Talk with other moderators**
|
||||
|
||||
We have a room for moderators only. Use it! If you feel uncomfortable with handling a certain situation, ask other moderators for help. If you think something should be discussed, do it. You're part of the team, and we value every team member's input! Even if you totally disagree with anything in these guidelines or the Code of Conduct!
|
||||
|
||||
10. **Temporarily inactive**
|
||||
|
||||
If you're not going to be active as a Moderator for a while due to vacation, illness, or any other reason, make sure to let the others know in the `#mod-chat` channel. This is so we know if we can count on you to be regularly active on the server or not.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to become a moderator
|
||||
|
||||
Suppose you are helping people in the community consistently over time. In that case, our Moderator Team will eventually take notice, and one of them will mention you as a possible moderator to [our staff](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). There are no shortcuts to becoming a moderator.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are approved, we will add you to our Moderator Teams on [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), and chat etc.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] For GitHub: After you've been accepted as a moderator, you will receive a Github repository invitation. You'll need to head over towards [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organisation Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) to be able to accept the invitation.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> This is required for us to be able to give you write access to some of our repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
## How we retire inactive moderators
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that we will frequently remove mods whom we think are inactive. When we do this, we will send the following message:
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
This is a standard message notifying you that, since you don't seem to have been an active moderator recently, we're removing you from our Moderator team. We deeply appreciate your help in the past.
|
||||
|
||||
If you think we did this in error, or once you're ready to come back and contribute more, just reply to this message letting me know.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## How our Contributors room works
|
||||
|
||||
Anyone is welcome in the [Contributors room on our chat server](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors). It is the designated chat room for moderators and other campers who contribute to our community in any number of ways, including through study groups.
|
||||
|
||||
We assume contributors will read anything in this room that directly mentions them with an `@username`. Everything else is optional, but feel free to read anything anyone posts in there and interact.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dealing with solicitors
|
||||
|
||||
You may be approached by organizations who want to partner or co-brand with freeCodeCamp somehow. Once you realize that this is what they're after, **please stop talking to them** and tell them to email `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
|
||||
|
||||
We get proposals like this all the time, and the staff are in the best position to judge whether such a relationship will be worth it for our community (and it rarely is).
|
||||
|
||||
## Dealing with (mental) health inquiries
|
||||
|
||||
You may come across situations where users seek medical advice or are dealing with mental health issues and are looking for support.
|
||||
|
||||
As a matter of policy, you should avoid talking privately about these matters. Should the situation reflect back to freeCodeCamp, we want to have the conversation(s) on record. Make it clear that we are not medical professionals and that you encourage the user to find professional help.
|
||||
|
||||
As difficult as it sometimes can be, avoid giving any tips or advice other than pointing the user in the direction of professional help!
|
||||
|
||||
If this happens on our chat server: Create a private channel for the user and the mod team. This can be done with the bot's `private` command.
|
||||
|
||||
- The user is guaranteed some privacy
|
||||
- Public chat is no longer disrupted
|
||||
- Other team members can pitch in, should you be uncomfortable dealing with the situation yourself
|
||||
|
||||
Helpful URLs:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
|
||||
|
||||
## A note on free speech
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes people will defend something offensive or incendiary that they said as "free speech."
|
||||
|
||||
This XKCD comic summarizes perfectly most communities' thoughts on free speech. So if someone defends something in the name of "free speech", feel free to send it to them.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center"><img src='https://aws1.discourse-cdn.com/freecodecamp/original/3X/4/3/43a8b2eafe4c8622e02838f66f1dc6227de32c70.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks for reading this, and thanks for helping the developer community!
|
||||
|
||||
## Reply Templates
|
||||
|
||||
These are some of the standard reply templates that you may use while reviewing pull requests and triaging issues and pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
> You can make your own with GitHub's built-in [**Saved replies**](https://github.com/settings/replies/) feature or use the ones below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Thank you
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
|
||||
We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Thank you and congrats
|
||||
|
||||
> For thanking and encouraging first-time contributors.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
|
||||
We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Build Error
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Hey @username
|
||||
|
||||
We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
|
||||
|
||||
Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md#testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Syncing Fork
|
||||
|
||||
> When PR is not up to date with the `main` branch.
|
||||
|
||||
````markdown
|
||||
Hey @username
|
||||
|
||||
We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
|
||||
|
||||
To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
|
||||
|
||||
Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
|
||||
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
|
||||
git pull upstream main
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to reference the [Syncing a Fork](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
### Merge Conflicts
|
||||
|
||||
> When PR has merge conflicts that need to be resolved.¹
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Hey @username
|
||||
|
||||
We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
|
||||
|
||||
Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
|
||||
|
||||
Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
¹ If a first-time-contributor has a merge conflict, maintainers will resolve the conflict for them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Duplicate
|
||||
|
||||
> When PR is repetitive or a duplicate.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Hey @username
|
||||
|
||||
This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as duplicate.
|
||||
|
||||
If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks again! 😊
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors).
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Closing invalid pull requests
|
||||
|
||||
> When PR is invalid.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Hey @username
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you for opening this pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you and happy coding.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> When PR adds links to external resources.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Thank you for your pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
|
||||
|
||||
If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you, and happy coding.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Closing Invalid Issues
|
||||
|
||||
> When an issue relates to the camper's code.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Thank you for reporting this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
|
||||
|
||||
If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you and happy coding.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> When an issue is duplicate of an earlier issue
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Thank you for reporting this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
|
||||
|
||||
If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> When an issue is fixed in staging.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Thank you for reporting this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### First Timer Only Issues
|
||||
|
||||
> When an issue is deemed to be eligible for first time code contributors.
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
Thanks for opening this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
This looks like something that can be fixed by "first time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
|
||||
|
||||
List of files:
|
||||
|
||||
1. ...
|
||||
2. ...
|
||||
3. ...
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in [our chat room](https://chat.freecodecamp.org/channel/contributors) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing, our moderators will guide you through this.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
|
||||
|
||||
Happy contributing.
|
||||
```
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user