* Create index.md This file introduces flex-grow: with screen shots and code samples. As with all of my commits, this is a proper contribution effort, neither copy & paste nor a links list. * Update index.md Added title: 'Flex Grow' to avoid Travis CL no frontmatter error. * Update index.md Added labels to the code blocks. * fix: updated individual code items & sentences Added <code></code> tags to individual code items. Sorry for so many commits. I just saw the styling guide. * Create flexbox-display-flex.md (#2) * Create flexbox-display-flex.md This file introduces the concept of display:flex and flex-direction:[row | column]. * Rename guide/english/css/flexbox-display-flex.md to guide/english/css/flexbox-display-flex/index.md Changed the folder structure to comply with index.md. * Update index.md Added title: Display Flex to avoid Travice CL no frontmatter error. * Update index.md Added labels to the code blocks. * fix: update individual code items. Added <code></code> tags to individual code items. Sorry for so many commits. I just saw the styling guide. * Create index.md (#4) * Create index.md This file contains details about flex-basis, with screenshots and code samples. As with all of my commits, this is my own work not copy & paste or a lazy linkathon. * Update index.md Added the title; Flex Basis, to avoid Travis CI no frontmatter error. * Update index.md Added labels to the code blocks. * fix: added labels for code items Added <code></code> labels to individual code items. Sorry for all of the commits. I just saw the styling guide. Doing my own QC.
3.5 KiB
title
| title |
|---|
| Flex Grow |
Flex-grow
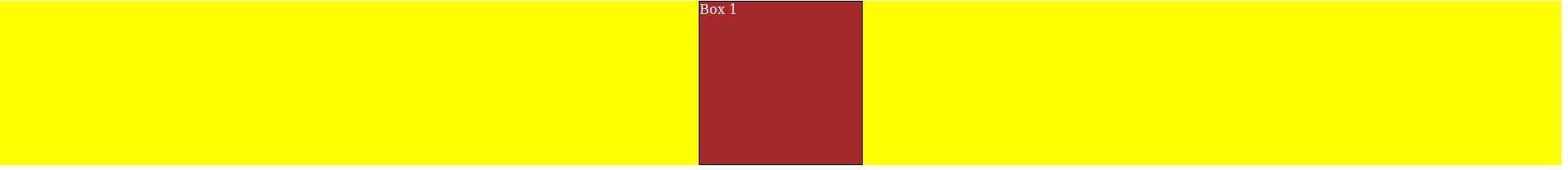
A flex item can be set to ‘grow’ along the main axis. What this means is that the item will occupy any total available space inside the flex container, making it wider or taller depending on the flex-direction of the flex container. When there are multiple flex items in a container, the available space is shared among them to provided proportions. flex-grow: has no effect with static dimensions; use min-width:, min-height: or flex-basis:.
Here’s an example with just one div in a flex container. Notice than min- is used with width and height to allow it to be affected. However, flex-grow: has not been applied in this instance.
.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
justify-content: center;
background-color: yellow;
}
.box {
background-color: brown;
min-width:200px;
min-height: 200px;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: solid 1px black;
color: white;
}
<div class="container">
<div class="box">Box 1</div>
</div>
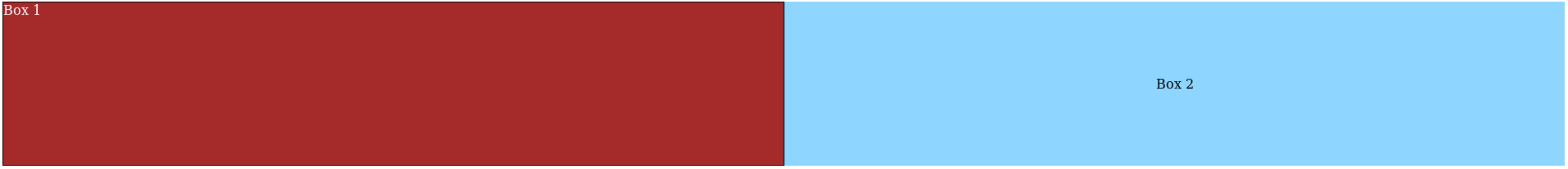
The next example shows the div with flex-grow: 1; applied to the .box class. With flex-grow: the div grows into the available space both sides of it.
.box {
background-color: brown;
min-width:200px;
min-height: 200px;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: solid 1px black;
color: white;
flex-grow: 1;
}
The value of 1 could have been any number because it only becomes significant when multiple flex items are allocated different proportions of free space. It is similar to cutting a cake into pieces, one piece is the whole cake, but if there are two people, they get (as close to) one equal piece each. Let’s take a look at that now.
In this example, the classes box and box2 both receive 1 piece of the free space each (50%), an equal allocation. If the number were 15, they’d both receive 15 smaller pieces of the space.
.box {
background-color: brown;
min-width:200px;
min-height: 200px;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: solid 1px black;
color: white;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.box2 {
display: flex;
min-width:200px;
min-height: 200px;
justify-content: center;
background: rgb(142, 213, 255);
align-items: center;
flex-grow: 1;
}
<div class="container">
<div class="box">Box 1</div>
<div class="box2">Box 2</div>
</div>
See what happens when Box 2 is allocated flex-grow: 2;.
.box2 {
display: flex;
min-width:200px;
min-height: 200px;
justify-content: center;
background: rgb(142, 213, 255);
align-items: center;
flex-grow: 2;
}
This time, Box 2 receives twice as much free space as Box 1. Remember, it does not make Box 2 twice as wide. It is simply allocated twice as much free space. To use the cake analogy, Box 1 receives one piece of cake, while Box 2 receives two pieces.