* fix: replace imgur with s3 for files with potential conflict (cherry picked from commit 4ec62c0e29a64b0288eade45fb510f25c622945a) * fix/remote extra link Co-Authored-By: Randell Dawson <5313213+RandellDawson@users.noreply.github.com> * fix: revert change
45 lines
1.8 KiB
Markdown
45 lines
1.8 KiB
Markdown
---
|
||
title: C++ Lists
|
||
---
|
||
|
||
# What is a STL List?
|
||
|
||
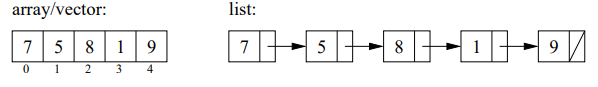
Lists in C++ are a powerful tool similar to its more well known cousin, C++ Vectors. While Vectors are a sequential container
|
||
where elements are indexed in a continuous chain, Lists are also a sequential container but they are organized differently.
|
||
List elements point to its next element so all elements are ordered in sequence but they don't use indexing.
|
||
How? You may ask. They do this not by indexing but using a special tool called iterators. Iterators are like special pointers
|
||
whose job is to maintain the order of the list elements kind of like the link between two train cars. Here is a nice visual
|
||
of how Lists are organized compared to Vectors and Arrays.
|
||
|
||
|
||
Traversal in a list is slow as compared to Vectors and Arrays, but once a position has been found, insertion and deletion are quick.
|
||
|
||
## How to declare a List
|
||
|
||
Possible declarations of a list:
|
||
```cpp
|
||
#include <list>
|
||
|
||
int main()
|
||
{
|
||
std::list<int> list1 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
|
||
std::list<int> list2 (list1);
|
||
std::list<int> list3 = list2;
|
||
std::list<int> list4 {list3};
|
||
std::list<int>* list5 = new std::list<int>(list4);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## Functions used with List
|
||
* size() : Returns the number of elements in the list
|
||
* begin() : Returns an iterator pointing to the first element of the list
|
||
* end() : Returns an iterator pointing to the theoretical last element which follows the last element
|
||
* push_front(data) – Adds a new element with value 'data' at the beginning of the list
|
||
* push_back(data) – Adds a new element with value 'data' at the end of the list
|
||
* pop_front() – Removes the first element of the list
|
||
* pop_back() – Removes the last element of the list
|
||
|
||
## How to use these Functions
|
||
|
||
Numbers.size();
|