Code sample of how to implement a CSS background gradient, provided a screenshot for demo purpose.
160 lines
5.7 KiB
Markdown
160 lines
5.7 KiB
Markdown
---
|
||
title: Background
|
||
---
|
||
## Background
|
||
The `background` property lets you use images and colors to create backgrounds for your web pages.
|
||
|
||
### Background Color
|
||
The `background-color` property allows you to choose the color of your element (a piece of HTML such as a header or paragraph). This can be the background for the entire page or the background of one section of your page.
|
||
|
||
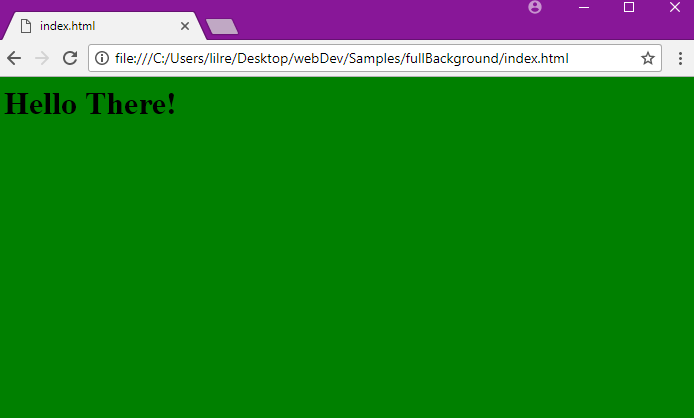
Here is an example of setting the background color for a web page to green.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-color: green;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
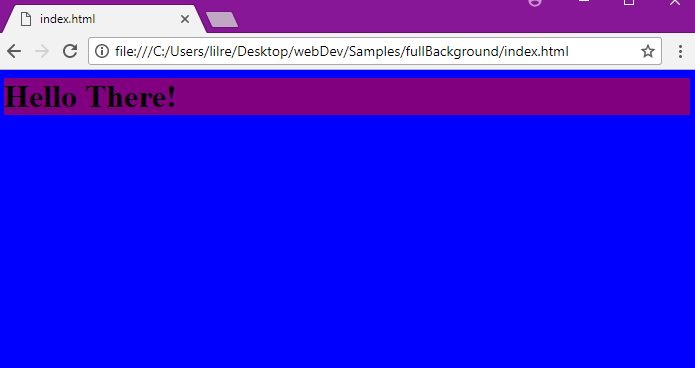
Here is an example of setting the background colors for two elements. This will set the background of the header to purple and the rest of the page to blue.
|
||
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-color: blue;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
h1 {
|
||
background–color: purple;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
In CSS color can be defined in the following ways:
|
||
* A valid "color" keyword name such as `blue`
|
||
* Numerical color values
|
||
+ A HEX value such as `#FFFFF` (This is the hex value for white.)
|
||
+ An abbreviated HEX value such as `#FFF`.
|
||
+ An RGB value such as `rgb(76,175,80)` (This is the RGB value for light green.)
|
||
+ RGBA value (RGB + alpha channel for contolling opacity)
|
||
- Note: The alpha parameter is a number between `0.0` (fully transparent) and `1.0` (fully opaque)
|
||
+ HSL (Hue, Saturation, Lightness) (e.g., `hsl(115, 75%, 73%)` is HSL for light green)
|
||
+ HSLA (HSL + alpha channel for controlling opacity)
|
||
|
||
### Background Images
|
||
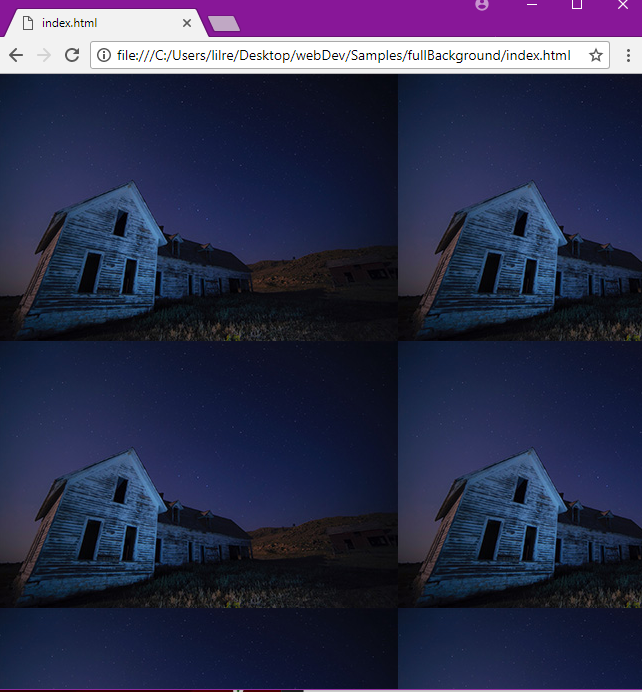
You can use the `background-image` property to set an image as a background for an element.
|
||
The image is repeated by default so that it covers the entire element.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-image: url("barn.jpg");
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
You can also use pictures or gifs that you find online by using their link (e.g., from a Google Images search).
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-image: url("https://mdn.mozillademos.org/files/11983/starsolid.gif");
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Background Image - The Repeat Property
|
||
The background image is repeated both vertically (up and down) and horizontally (across the web page) by default.
|
||
You can use the `background-repeat` property to repeat the image vertically or horizontally.
|
||
|
||
Here is an example that repeats the image vertically.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-image: url("barn.jpg");
|
||
background-repeat: repeat-y;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||

|
||
|
||
You can repeat the image horizontally by setting the `background-repeat` property to `repeat-x`.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-image: url("barn.jpg");
|
||
background-repeat: repeat-x;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
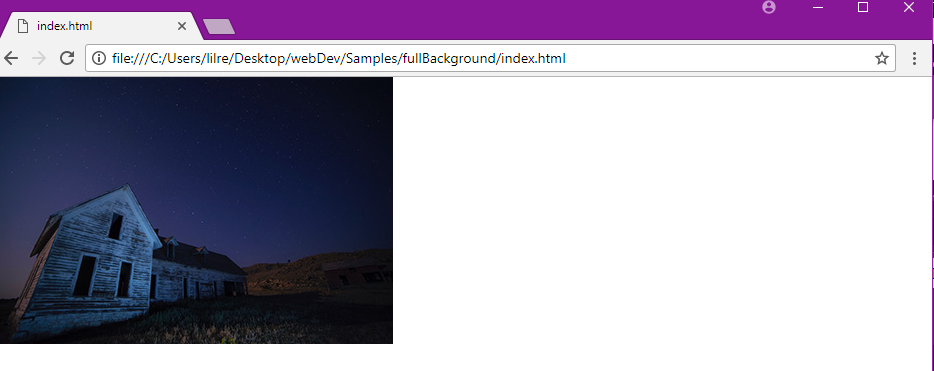
You can also use the `background-repeat` property to set an image to not repeat.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-image: url("barn.jpg");
|
||
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Background Image – The Position Property
|
||
You can use the `background-position` property to specify where your image will be located on a web page.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-image: url("barn.jpg");
|
||
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
||
background-position: right top;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
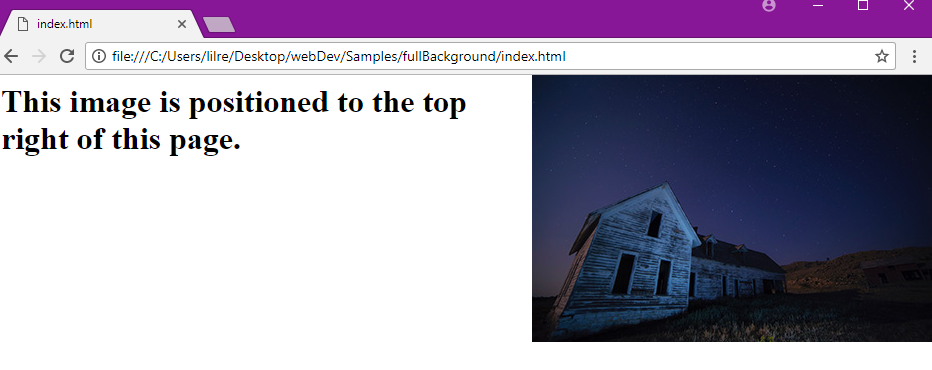
|
||
|
||
### Background Image – The Fixed Position
|
||
You can use the `background-attachment` property to set an image to a fixed position.
|
||
A fixed position makes it so an image does not scroll with the rest of the page.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background-image: url("barn.jpg");
|
||
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
||
background-position: right top;
|
||
background-attachment: fixed;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
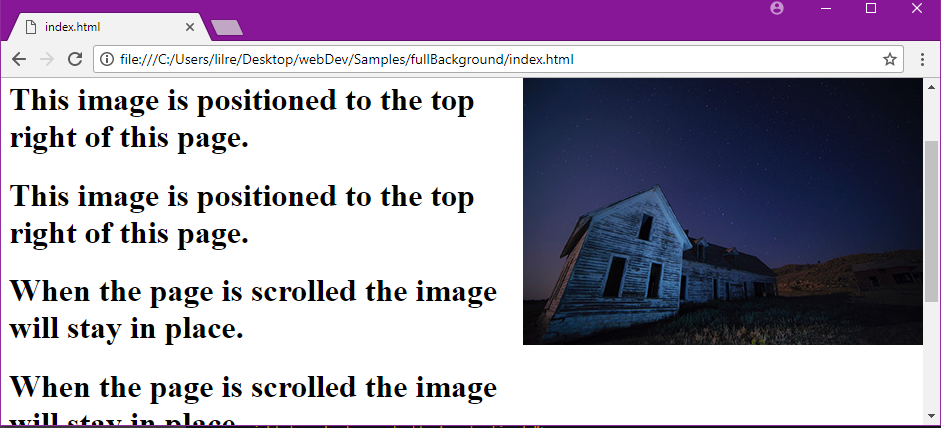
|
||
|
||
### Background Gradients
|
||
A gradient is a transition between two or more colors and can be used via CSS similar to a background image.
|
||
|
||
The syntax of a gradient background can be quite complex and is often still used with vendor prefixes due to inconsistencies between supported browsers.
|
||
|
||
Below is an example of a background gradient:
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
```css
|
||
header {
|
||
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, #069, #099);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
The [Colorzilla Gradient Editor](http://www.colorzilla.com/gradient-editor/) is a great online tool for generating custom gradients and the associated css markup.
|
||
|
||
### Background – The Shorthand Property
|
||
You can write the background properties on a single line. This is called the shorthand property.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background: url("barn.jpg") no-repeat right top;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
You can leave out properties you don’t need when using the shorthand property, but the properties
|
||
must be used in a certain order. The order is:
|
||
* color
|
||
* image
|
||
* repeat
|
||
* attachment
|
||
* position
|
||
|
||
### Multiple Background Images
|
||
You can specify multiple background images in a single `background` property.
|
||
```css
|
||
body {
|
||
background: url("barn.jpg"), url("stars.jpg"), linear-gradient(rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.5), rgba(255, 255, 0, 0.5));
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
The first image (or gradient) specified is the most on top, the second comes after, and so on.
|
||
If one of the elements is not correct due to its URL or its syntax, the whole line will be ignored by the browser.
|
||
|
||
### Other Resources
|
||
* [Background CSS Property Reference: MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/background)
|
||
* [List of Named Colors](https://htmlcolorcodes.com/color-names/)
|
||
* [Color Picker Tool](https://www.color-hex.com/)
|